Huaping Liu
Towards Next-Generation SLAM: A Survey on 3DGS-SLAM Focusing on Performance, Robustness, and Future Directions
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Traditional Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) systems often face limitations including coarse rendering quality, insufficient recovery of scene details, and poor robustness in dynamic environments. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), with its efficient explicit representation and high-quality rendering capabilities, offers a new reconstruction paradigm for SLAM. This survey comprehensively reviews key technical approaches for integrating 3DGS with SLAM. We analyze performance optimization of representative methods across four critical dimensions: rendering quality, tracking accuracy, reconstruction speed, and memory consumption, delving into their design principles and breakthroughs. Furthermore, we examine methods for enhancing the robustness of 3DGS-SLAM in complex environments such as motion blur and dynamic environments. Finally, we discuss future challenges and development trends in this area. This survey aims to provide a technical reference for researchers and foster the development of next-generation SLAM systems characterized by high fidelity, efficiency, and robustness.
UV-M3TL: A Unified and Versatile Multimodal Multi-Task Learning Framework for Assistive Driving Perception
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) need to understand human driver behavior while perceiving their navigation context, but jointly learning these heterogeneous tasks would cause inter-task negative transfer and impair system performance. Here, we propose a Unified and Versatile Multimodal Multi-Task Learning (UV-M3TL) framework to simultaneously recognize driver behavior, driver emotion, vehicle behavior, and traffic context, while mitigating inter-task negative transfer. Our framework incorporates two core components: dual-branch spatial channel multimodal embedding (DB-SCME) and adaptive feature-decoupled multi-task loss (AFD-Loss). DB-SCME enhances cross-task knowledge transfer while mitigating task conflicts by employing a dual-branch structure to explicitly model salient task-shared and task-specific features. AFD-Loss improves the stability of joint optimization while guiding the model to learn diverse multi-task representations by introducing an adaptive weighting mechanism based on learning dynamics and feature decoupling constraints. We evaluate our method on the AIDE dataset, and the experimental results demonstrate that UV-M3TL achieves state-of-the-art performance across all four tasks. To further prove the versatility, we evaluate UV-M3TL on additional public multi-task perception benchmarks (BDD100K, CityScapes, NYUD-v2, and PASCAL-Context), where it consistently delivers strong performance across diverse task combinations, attaining state-of-the-art results on most tasks.
Towards Efficient 3D Object Detection for Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaboration via Risk-Intent Selection
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaborative Perception (VICP) is pivotal for resolving occlusion in autonomous driving, yet the trade-off between communication bandwidth and feature redundancy remains a critical bottleneck. While intermediate fusion mitigates data volume compared to raw sharing, existing frameworks typically rely on spatial compression or static confidence maps, which inefficiently transmit spatially redundant features from non-critical background regions. To address this, we propose Risk-intent Selective detection (RiSe), an interaction-aware framework that shifts the paradigm from identifying visible regions to prioritizing risk-critical ones. Specifically, we introduce a Potential Field-Trajectory Correlation Model (PTCM) grounded in potential field theory to quantitatively assess kinematic risks. Complementing this, an Intention-Driven Area Prediction Module (IDAPM) leverages ego-motion priors to proactively predict and filter key Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) areas essential for decision-making. By integrating these components, RiSe implements a semantic-selective fusion scheme that transmits high-fidelity features only from high-interaction regions, effectively acting as a feature denoiser. Extensive experiments on the DeepAccident dataset demonstrate that our method reduces communication volume to 0.71\% of full feature sharing while maintaining state-of-the-art detection accuracy, establishing a competitive Pareto frontier between bandwidth efficiency and perception performance.
CollabVLA: Self-Reflective Vision-Language-Action Model Dreaming Together with Human
Sep 18, 2025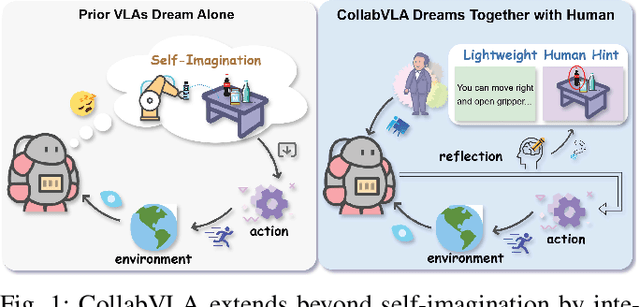
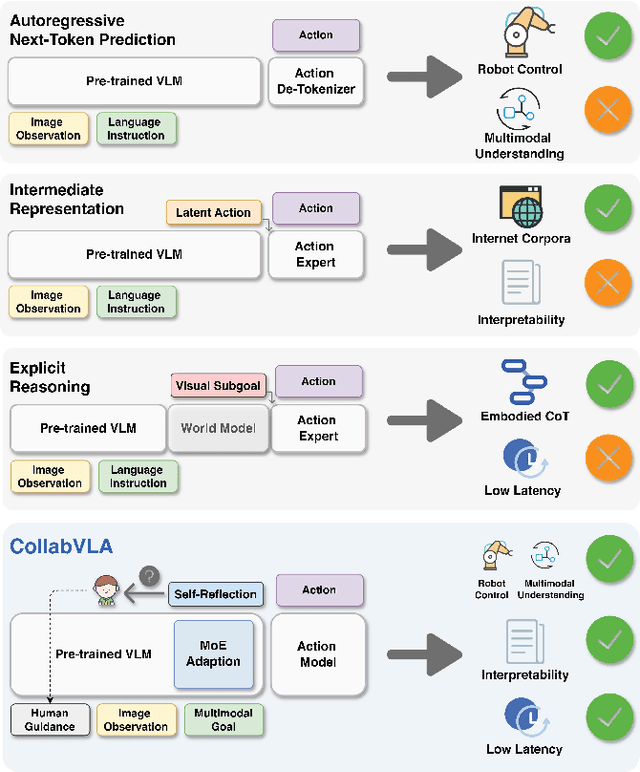
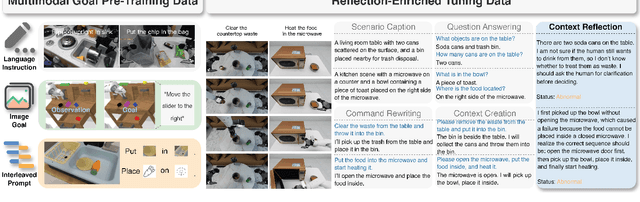
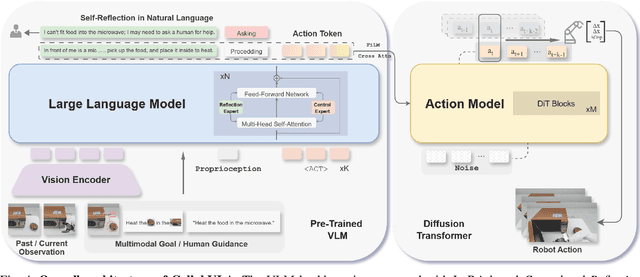
Abstract:In this work, we present CollabVLA, a self-reflective vision-language-action framework that transforms a standard visuomotor policy into a collaborative assistant. CollabVLA tackles key limitations of prior VLAs, including domain overfitting, non-interpretable reasoning, and the high latency of auxiliary generative models, by integrating VLM-based reflective reasoning with diffusion-based action generation under a mixture-of-experts design. Through a two-stage training recipe of action grounding and reflection tuning, it supports explicit self-reflection and proactively solicits human guidance when confronted with uncertainty or repeated failure. It cuts normalized Time by ~2x and Dream counts by ~4x vs. generative agents, achieving higher success rates, improved interpretability, and balanced low latency compared with existing methods. This work takes a pioneering step toward shifting VLAs from opaque controllers to genuinely assistive agents capable of reasoning, acting, and collaborating with humans.
Track Any Motions under Any Disturbances
Sep 17, 2025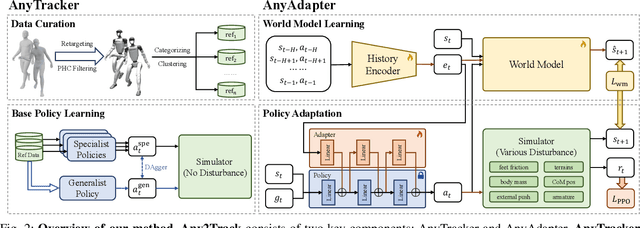
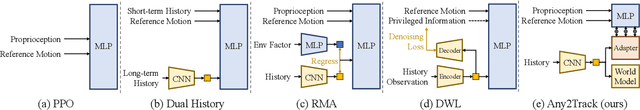
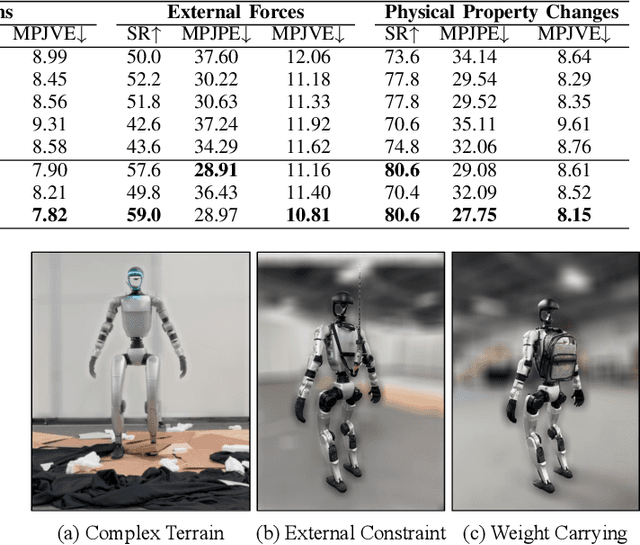

Abstract:A foundational humanoid motion tracker is expected to be able to track diverse, highly dynamic, and contact-rich motions. More importantly, it needs to operate stably in real-world scenarios against various dynamics disturbances, including terrains, external forces, and physical property changes for general practical use. To achieve this goal, we propose Any2Track (Track Any motions under Any disturbances), a two-stage RL framework to track various motions under multiple disturbances in the real world. Any2Track reformulates dynamics adaptability as an additional capability on top of basic action execution and consists of two key components: AnyTracker and AnyAdapter. AnyTracker is a general motion tracker with a series of careful designs to track various motions within a single policy. AnyAdapter is a history-informed adaptation module that endows the tracker with online dynamics adaptability to overcome the sim2real gap and multiple real-world disturbances. We deploy Any2Track on Unitree G1 hardware and achieve a successful sim2real transfer in a zero-shot manner. Any2Track performs exceptionally well in tracking various motions under multiple real-world disturbances.
S2R-Bench: A Sim-to-Real Evaluation Benchmark for Autonomous Driving
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Safety is a long-standing and the final pursuit in the development of autonomous driving systems, with a significant portion of safety challenge arising from perception. How to effectively evaluate the safety as well as the reliability of perception algorithms is becoming an emerging issue. Despite its critical importance, existing perception methods exhibit a limitation in their robustness, primarily due to the use of benchmarks are entierly simulated, which fail to align predicted results with actual outcomes, particularly under extreme weather conditions and sensor anomalies that are prevalent in real-world scenarios. To fill this gap, in this study, we propose a Sim-to-Real Evaluation Benchmark for Autonomous Driving (S2R-Bench). We collect diverse sensor anomaly data under various road conditions to evaluate the robustness of autonomous driving perception methods in a comprehensive and realistic manner. This is the first corruption robustness benchmark based on real-world scenarios, encompassing various road conditions, weather conditions, lighting intensities, and time periods. By comparing real-world data with simulated data, we demonstrate the reliability and practical significance of the collected data for real-world applications. We hope that this dataset will advance future research and contribute to the development of more robust perception models for autonomous driving. This dataset is released on https://github.com/adept-thu/S2R-Bench.
Maximum Total Correlation Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Simplicity is a powerful inductive bias. In reinforcement learning, regularization is used for simpler policies, data augmentation for simpler representations, and sparse reward functions for simpler objectives, all that, with the underlying motivation to increase generalizability and robustness by focusing on the essentials. Supplementary to these techniques, we investigate how to promote simple behavior throughout the episode. To that end, we introduce a modification of the reinforcement learning problem that additionally maximizes the total correlation within the induced trajectories. We propose a practical algorithm that optimizes all models, including policy and state representation, based on a lower-bound approximation. In simulated robot environments, our method naturally generates policies that induce periodic and compressible trajectories, and that exhibit superior robustness to noise and changes in dynamics compared to baseline methods, while also improving performance in the original tasks.
Learn to Think: Bootstrapping LLM Reasoning Capability Through Graph Representation Learning
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across various domains. However, they still face significant challenges, including high computational costs for training and limitations in solving complex reasoning problems. Although existing methods have extended the reasoning capabilities of LLMs through structured paradigms, these approaches often rely on task-specific prompts and predefined reasoning processes, which constrain their flexibility and generalizability. To address these limitations, we propose a novel framework that leverages graph learning to enable more flexible and adaptive reasoning capabilities for LLMs. Specifically, this approach models the reasoning process of a problem as a graph and employs LLM-based graph learning to guide the adaptive generation of each reasoning step. To further enhance the adaptability of the model, we introduce a Graph Neural Network (GNN) module to perform representation learning on the generated reasoning process, enabling real-time adjustments to both the model and the prompt. Experimental results demonstrate that this method significantly improves reasoning performance across multiple tasks without requiring additional training or task-specific prompt design. Code can be found in https://github.com/zch65458525/L2T.
FlowDreamer: A RGB-D World Model with Flow-based Motion Representations for Robot Manipulation
May 15, 2025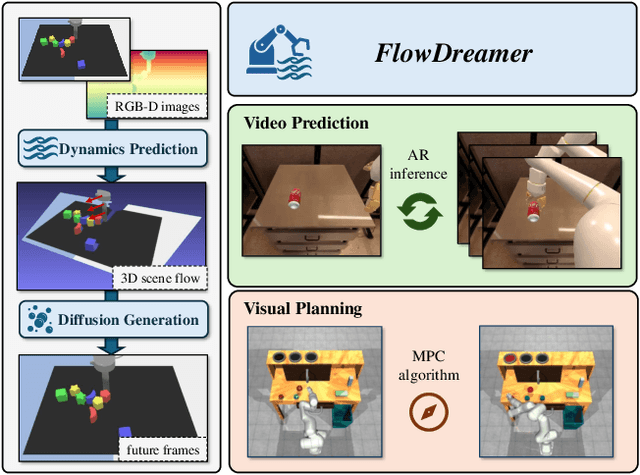
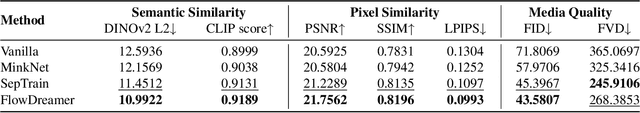
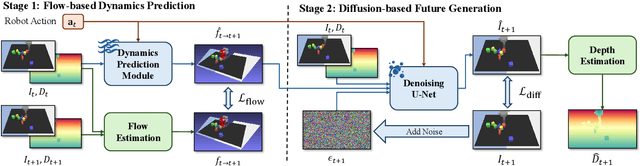
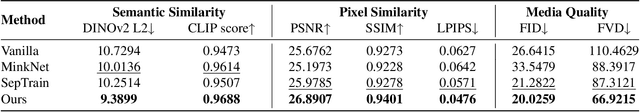
Abstract:This paper investigates training better visual world models for robot manipulation, i.e., models that can predict future visual observations by conditioning on past frames and robot actions. Specifically, we consider world models that operate on RGB-D frames (RGB-D world models). As opposed to canonical approaches that handle dynamics prediction mostly implicitly and reconcile it with visual rendering in a single model, we introduce FlowDreamer, which adopts 3D scene flow as explicit motion representations. FlowDreamer first predicts 3D scene flow from past frame and action conditions with a U-Net, and then a diffusion model will predict the future frame utilizing the scene flow. FlowDreamer is trained end-to-end despite its modularized nature. We conduct experiments on 4 different benchmarks, covering both video prediction and visual planning tasks. The results demonstrate that FlowDreamer achieves better performance compared to other baseline RGB-D world models by 7% on semantic similarity, 11% on pixel quality, and 6% on success rate in various robot manipulation domains.
Large Language Model Enhancers for Graph Neural Networks: An Analysis from the Perspective of Causal Mechanism Identification
May 15, 2025Abstract:The use of large language models (LLMs) as feature enhancers to optimize node representations, which are then used as inputs for graph neural networks (GNNs), has shown significant potential in graph representation learning. However, the fundamental properties of this approach remain underexplored. To address this issue, we propose conducting a more in-depth analysis of this issue based on the interchange intervention method. First, we construct a synthetic graph dataset with controllable causal relationships, enabling precise manipulation of semantic relationships and causal modeling to provide data for analysis. Using this dataset, we conduct interchange interventions to examine the deeper properties of LLM enhancers and GNNs, uncovering their underlying logic and internal mechanisms. Building on the analytical results, we design a plug-and-play optimization module to improve the information transfer between LLM enhancers and GNNs. Experiments across multiple datasets and models validate the proposed module.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge