Zhenzhen Hu
Disentangling Foreground and Background for vision-Language Navigation via Online Augmentation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Following language instructions, vision-language navigation (VLN) agents are tasked with navigating unseen environments. While augmenting multifaceted visual representations has propelled advancements in VLN, the significance of foreground and background in visual observations remains underexplored. Intuitively, foreground regions provide semantic cues, whereas the background encompasses spatial connectivity information. Inspired on this insight, we propose a Consensus-driven Online Feature Augmentation strategy (COFA) with alternative foreground and background features to facilitate the navigable generalization. Specifically, we first leverage semantically-enhanced landmark identification to disentangle foreground and background as candidate augmented features. Subsequently, a consensus-driven online augmentation strategy encourages the agent to consolidate two-stage voting results on feature preferences according to diverse instructions and navigational locations. Experiments on REVERIE and R2R demonstrate that our online foreground-background augmentation boosts the generalization of baseline and attains state-of-the-art performance.
Generalizable Engagement Estimation in Conversation via Domain Prompting and Parallel Attention
Aug 20, 2025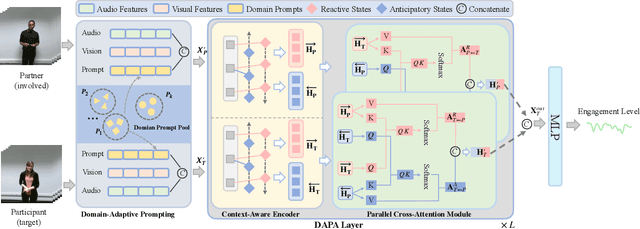
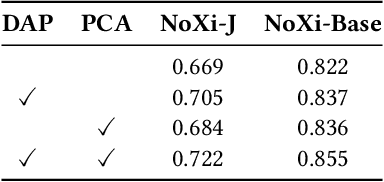
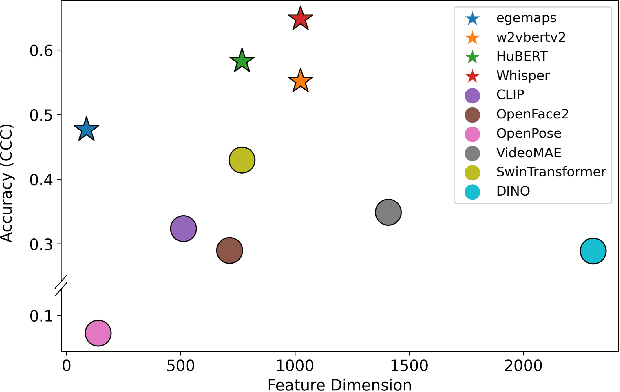
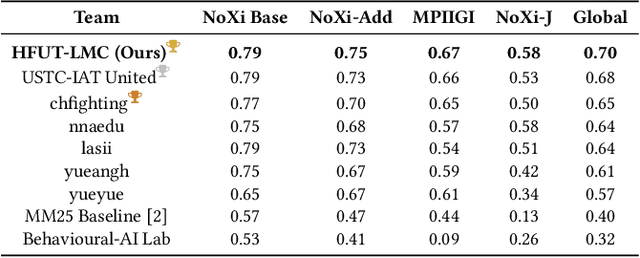
Abstract:Accurate engagement estimation is essential for adaptive human-computer interaction systems, yet robust deployment is hindered by poor generalizability across diverse domains and challenges in modeling complex interaction dynamics.To tackle these issues, we propose DAPA (Domain-Adaptive Parallel Attention), a novel framework for generalizable conversational engagement modeling. DAPA introduces a Domain Prompting mechanism by prepending learnable domain-specific vectors to the input, explicitly conditioning the model on the data's origin to facilitate domain-aware adaptation while preserving generalizable engagement representations. To capture interactional synchrony, the framework also incorporates a Parallel Cross-Attention module that explicitly aligns reactive (forward BiLSTM) and anticipatory (backward BiLSTM) states between participants.Extensive experiments demonstrate that DAPA establishes a new state-of-the-art performance on several cross-cultural and cross-linguistic benchmarks, notably achieving an absolute improvement of 0.45 in Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) over a strong baseline on the NoXi-J test set. The superiority of our method was also confirmed by winning the first place in the Multi-Domain Engagement Estimation Challenge at MultiMediate'25.
Listening to the Unspoken: Exploring 365 Aspects of Multimodal Interview Performance Assessment
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Interview performance assessment is essential for determining candidates' suitability for professional positions. To ensure holistic and fair evaluations, we propose a novel and comprehensive framework that explores ``365'' aspects of interview performance by integrating \textit{three} modalities (video, audio, and text), \textit{six} responses per candidate, and \textit{five} key evaluation dimensions. The framework employs modality-specific feature extractors to encode heterogeneous data streams and subsequently fused via a Shared Compression Multilayer Perceptron. This module compresses multimodal embeddings into a unified latent space, facilitating efficient feature interaction. To enhance prediction robustness, we incorporate a two-level ensemble learning strategy: (1) independent regression heads predict scores for each response, and (2) predictions are aggregated across responses using a mean-pooling mechanism to produce final scores for the five target dimensions. By listening to the unspoken, our approach captures both explicit and implicit cues from multimodal data, enabling comprehensive and unbiased assessments. Achieving a multi-dimensional average MSE of 0.1824, our framework secured first place in the AVI Challenge 2025, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness in advancing automated and multimodal interview performance assessment. The full implementation is available at https://github.com/MSA-LMC/365Aspects.
Traits Run Deep: Enhancing Personality Assessment via Psychology-Guided LLM Representations and Multimodal Apparent Behaviors
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Accurate and reliable personality assessment plays a vital role in many fields, such as emotional intelligence, mental health diagnostics, and personalized education. Unlike fleeting emotions, personality traits are stable, often subconsciously leaked through language, facial expressions, and body behaviors, with asynchronous patterns across modalities. It was hard to model personality semantics with traditional superficial features and seemed impossible to achieve effective cross-modal understanding. To address these challenges, we propose a novel personality assessment framework called \textit{\textbf{Traits Run Deep}}. It employs \textit{\textbf{psychology-informed prompts}} to elicit high-level personality-relevant semantic representations. Besides, it devises a \textit{\textbf{Text-Centric Trait Fusion Network}} that anchors rich text semantics to align and integrate asynchronous signals from other modalities. To be specific, such fusion module includes a Chunk-Wise Projector to decrease dimensionality, a Cross-Modal Connector and a Text Feature Enhancer for effective modality fusion and an ensemble regression head to improve generalization in data-scarce situations. To our knowledge, we are the first to apply personality-specific prompts to guide large language models (LLMs) in extracting personality-aware semantics for improved representation quality. Furthermore, extracting and fusing audio-visual apparent behavior features further improves the accuracy. Experimental results on the AVI validation set have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed components, i.e., approximately a 45\% reduction in mean squared error (MSE). Final evaluations on the test set of the AVI Challenge 2025 confirm our method's superiority, ranking first in the Personality Assessment track. The source code will be made available at https://github.com/MSA-LMC/TraitsRunDeep.
Rebalancing Contrastive Alignment with Learnable Semantic Gaps in Text-Video Retrieval
May 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-video retrieval have been largely driven by contrastive learning frameworks. However, existing methods overlook a key source of optimization tension: the separation between text and video distributions in the representation space (referred to as the modality gap), and the prevalence of false negatives in batch sampling. These factors lead to conflicting gradients under the InfoNCE loss, impeding stable alignment. To mitigate this, we propose GARE, a Gap-Aware Retrieval framework that introduces a learnable, pair-specific increment Delta_ij between text t_i and video v_j to offload the tension from the global anchor representation. We first derive the ideal form of Delta_ij via a coupled multivariate first-order Taylor approximation of the InfoNCE loss under a trust-region constraint, revealing it as a mechanism for resolving gradient conflicts by guiding updates along a locally optimal descent direction. Due to the high cost of directly computing Delta_ij, we introduce a lightweight neural module conditioned on the semantic gap between each video-text pair, enabling structure-aware correction guided by gradient supervision. To further stabilize learning and promote interpretability, we regularize Delta using three components: a trust-region constraint to prevent oscillation, a directional diversity term to promote semantic coverage, and an information bottleneck to limit redundancy. Experiments across four retrieval benchmarks show that GARE consistently improves alignment accuracy and robustness to noisy supervision, confirming the effectiveness of gap-aware tension mitigation.
Concept Drift Guided LayerNorm Tuning for Efficient Multimodal Metaphor Identification
May 16, 2025Abstract:Metaphorical imagination, the ability to connect seemingly unrelated concepts, is fundamental to human cognition and communication. While understanding linguistic metaphors has advanced significantly, grasping multimodal metaphors, such as those found in internet memes, presents unique challenges due to their unconventional expressions and implied meanings. Existing methods for multimodal metaphor identification often struggle to bridge the gap between literal and figurative interpretations. Additionally, generative approaches that utilize large language models or text-to-image models, while promising, suffer from high computational costs. This paper introduces \textbf{C}oncept \textbf{D}rift \textbf{G}uided \textbf{L}ayerNorm \textbf{T}uning (\textbf{CDGLT}), a novel and training-efficient framework for multimodal metaphor identification. CDGLT incorporates two key innovations: (1) Concept Drift, a mechanism that leverages Spherical Linear Interpolation (SLERP) of cross-modal embeddings from a CLIP encoder to generate a new, divergent concept embedding. This drifted concept helps to alleviate the gap between literal features and the figurative task. (2) A prompt construction strategy, that adapts the method of feature extraction and fusion using pre-trained language models for the multimodal metaphor identification task. CDGLT achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MET-Meme benchmark while significantly reducing training costs compared to existing generative methods. Ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of both Concept Drift and our adapted LN Tuning approach. Our method represents a significant step towards efficient and accurate multimodal metaphor understanding. The code is available: \href{https://github.com/Qianvenh/CDGLT}{https://github.com/Qianvenh/CDGLT}.
VAEmo: Efficient Representation Learning for Visual-Audio Emotion with Knowledge Injection
May 05, 2025Abstract:Audiovisual emotion recognition (AVER) aims to infer human emotions from nonverbal visual-audio (VA) cues, offering modality-complementary and language-agnostic advantages. However, AVER remains challenging due to the inherent ambiguity of emotional expressions, cross-modal expressive disparities, and the scarcity of reliably annotated data. Recent self-supervised AVER approaches have introduced strong multimodal representations, yet they predominantly rely on modality-specific encoders and coarse content-level alignment, limiting fine-grained emotional semantic modeling. To address these issues, we propose VAEmo, an efficient two-stage framework for emotion-centric joint VA representation learning with external knowledge injection. In Stage 1, a unified and lightweight representation network is pre-trained on large-scale speaker-centric VA corpora via masked reconstruction and contrastive objectives, mitigating the modality gap and learning expressive, complementary representations without emotion labels. In Stage 2, multimodal large language models automatically generate detailed affective descriptions according to our well-designed chain-of-thought prompting for only a small subset of VA samples; these rich textual semantics are then injected by aligning their corresponding embeddings with VA representations through dual-path contrastive learning, further bridging the emotion gap. Extensive experiments on multiple downstream AVER benchmarks show that VAEmo achieves state-of-the-art performance with a compact design, highlighting the benefit of unified cross-modal encoding and emotion-aware semantic guidance for efficient, generalizable VA emotion representations.
PhysioSync: Temporal and Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning Inspired by Physiological Synchronization for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) signals provide a promising and involuntary reflection of brain activity related to emotional states, offering significant advantages over behavioral cues like facial expressions. However, EEG signals are often noisy, affected by artifacts, and vary across individuals, complicating emotion recognition. While multimodal approaches have used Peripheral Physiological Signals (PPS) like GSR to complement EEG, they often overlook the dynamic synchronization and consistent semantics between the modalities. Additionally, the temporal dynamics of emotional fluctuations across different time resolutions in PPS remain underexplored. To address these challenges, we propose PhysioSync, a novel pre-training framework leveraging temporal and cross-modal contrastive learning, inspired by physiological synchronization phenomena. PhysioSync incorporates Cross-Modal Consistency Alignment (CM-CA) to model dynamic relationships between EEG and complementary PPS, enabling emotion-related synchronizations across modalities. Besides, it introduces Long- and Short-Term Temporal Contrastive Learning (LS-TCL) to capture emotional synchronization at different temporal resolutions within modalities. After pre-training, cross-resolution and cross-modal features are hierarchically fused and fine-tuned to enhance emotion recognition. Experiments on DEAP and DREAMER datasets demonstrate PhysioSync's advanced performance under uni-modal and cross-modal conditions, highlighting its effectiveness for EEG-centered emotion recognition.
Video Flow as Time Series: Discovering Temporal Consistency and Variability for VideoQA
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Video Question Answering (VideoQA) is a complex video-language task that demands a sophisticated understanding of both visual content and temporal dynamics. Traditional Transformer-style architectures, while effective in integrating multimodal data, often simplify temporal dynamics through positional encoding and fail to capture non-linear interactions within video sequences. In this paper, we introduce the Temporal Trio Transformer (T3T), a novel architecture that models time consistency and time variability. The T3T integrates three key components: Temporal Smoothing (TS), Temporal Difference (TD), and Temporal Fusion (TF). The TS module employs Brownian Bridge for capturing smooth, continuous temporal transitions, while the TD module identifies and encodes significant temporal variations and abrupt changes within the video content. Subsequently, the TF module synthesizes these temporal features with textual cues, facilitating a deeper contextual understanding and response accuracy. The efficacy of the T3T is demonstrated through extensive testing on multiple VideoQA benchmark datasets. Our results underscore the importance of a nuanced approach to temporal modeling in improving the accuracy and depth of video-based question answering.
Agent Journey Beyond RGB: Unveiling Hybrid Semantic-Spatial Environmental Representations for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 10, 2024


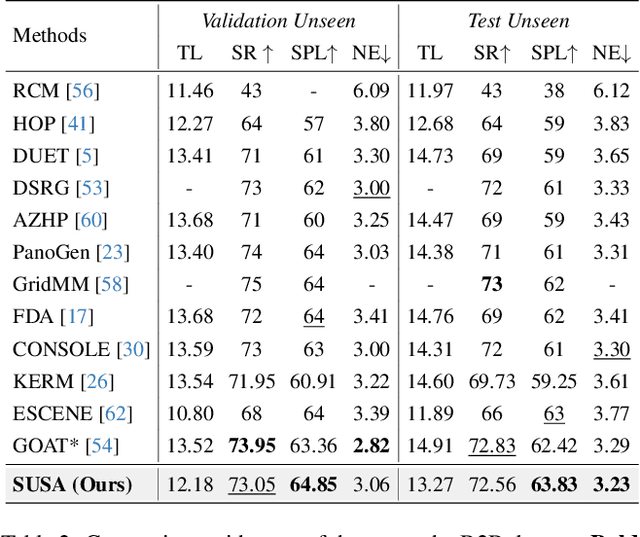
Abstract:Navigating unseen environments based on natural language instructions remains difficult for egocentric agents in Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN). While recent advancements have yielded promising outcomes, they primarily rely on RGB images for environmental representation, often overlooking the underlying semantic knowledge and spatial cues. Intuitively, humans inherently ground textual semantics within the spatial layout during indoor navigation. Inspired by this, we propose a versatile Semantic Understanding and Spatial Awareness (SUSA) architecture to facilitate navigation. SUSA includes a Textual Semantic Understanding (TSU) module, which narrows the modality gap between instructions and environments by generating and associating the descriptions of environmental landmarks in the agent's immediate surroundings. Additionally, a Depth-based Spatial Perception (DSP) module incrementally constructs a depth exploration map, enabling a more nuanced comprehension of environmental layouts. Experimental results demonstrate that SUSA hybrid semantic-spatial representations effectively enhance navigation performance, setting new state-of-the-art performance across three VLN benchmarks (REVERIE, R2R, and SOON). The source code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge