Yunbo Xu
Disentangling Foreground and Background for vision-Language Navigation via Online Augmentation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Following language instructions, vision-language navigation (VLN) agents are tasked with navigating unseen environments. While augmenting multifaceted visual representations has propelled advancements in VLN, the significance of foreground and background in visual observations remains underexplored. Intuitively, foreground regions provide semantic cues, whereas the background encompasses spatial connectivity information. Inspired on this insight, we propose a Consensus-driven Online Feature Augmentation strategy (COFA) with alternative foreground and background features to facilitate the navigable generalization. Specifically, we first leverage semantically-enhanced landmark identification to disentangle foreground and background as candidate augmented features. Subsequently, a consensus-driven online augmentation strategy encourages the agent to consolidate two-stage voting results on feature preferences according to diverse instructions and navigational locations. Experiments on REVERIE and R2R demonstrate that our online foreground-background augmentation boosts the generalization of baseline and attains state-of-the-art performance.
Agent Journey Beyond RGB: Unveiling Hybrid Semantic-Spatial Environmental Representations for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 10, 2024


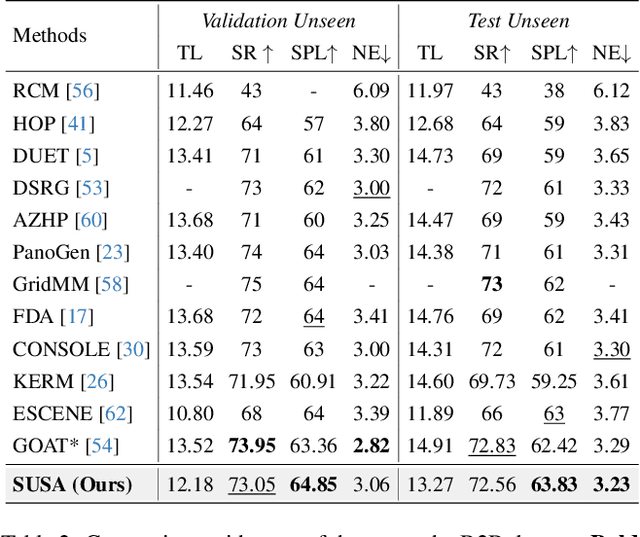
Abstract:Navigating unseen environments based on natural language instructions remains difficult for egocentric agents in Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN). While recent advancements have yielded promising outcomes, they primarily rely on RGB images for environmental representation, often overlooking the underlying semantic knowledge and spatial cues. Intuitively, humans inherently ground textual semantics within the spatial layout during indoor navigation. Inspired by this, we propose a versatile Semantic Understanding and Spatial Awareness (SUSA) architecture to facilitate navigation. SUSA includes a Textual Semantic Understanding (TSU) module, which narrows the modality gap between instructions and environments by generating and associating the descriptions of environmental landmarks in the agent's immediate surroundings. Additionally, a Depth-based Spatial Perception (DSP) module incrementally constructs a depth exploration map, enabling a more nuanced comprehension of environmental layouts. Experimental results demonstrate that SUSA hybrid semantic-spatial representations effectively enhance navigation performance, setting new state-of-the-art performance across three VLN benchmarks (REVERIE, R2R, and SOON). The source code will be publicly available.
DAT: Dialogue-Aware Transformer with Modality-Group Fusion for Human Engagement Estimation
Oct 11, 2024
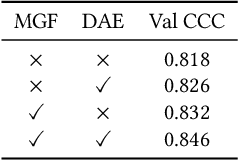
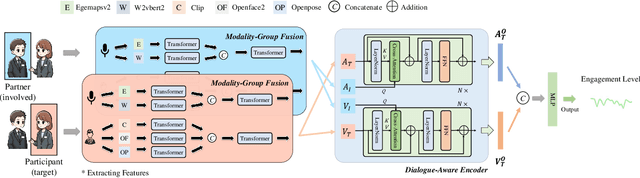

Abstract:Engagement estimation plays a crucial role in understanding human social behaviors, attracting increasing research interests in fields such as affective computing and human-computer interaction. In this paper, we propose a Dialogue-Aware Transformer framework (DAT) with Modality-Group Fusion (MGF), which relies solely on audio-visual input and is language-independent, for estimating human engagement in conversations. Specifically, our method employs a modality-group fusion strategy that independently fuses audio and visual features within each modality for each person before inferring the entire audio-visual content. This strategy significantly enhances the model's performance and robustness. Additionally, to better estimate the target participant's engagement levels, the introduced Dialogue-Aware Transformer considers both the participant's behavior and cues from their conversational partners. Our method was rigorously tested in the Multi-Domain Engagement Estimation Challenge held by MultiMediate'24, demonstrating notable improvements in engagement-level regression precision over the baseline model. Notably, our approach achieves a CCC score of 0.76 on the NoXi Base test set and an average CCC of 0.64 across the NoXi Base, NoXi-Add, and MPIIGI test sets.
Seeing is Believing? Enhancing Vision-Language Navigation using Visual Perturbations
Sep 09, 2024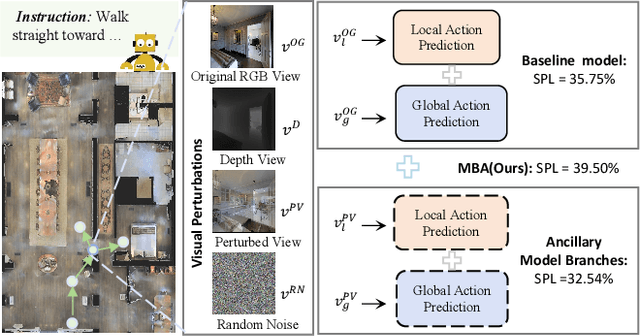

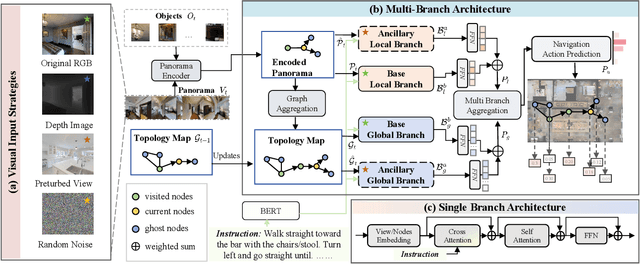

Abstract:Autonomous navigation for an embodied agent guided by natural language instructions remains a formidable challenge in vision-and-language navigation (VLN). Despite remarkable recent progress in learning fine-grained and multifarious visual representations, the tendency to overfit to the training environments leads to unsatisfactory generalization performance. In this work, we present a versatile Multi-Branch Architecture (MBA) aimed at exploring and exploiting diverse visual inputs. Specifically, we introduce three distinct visual variants: ground-truth depth images, visual inputs integrated with incongruent views, and those infused with random noise to enrich the diversity of visual input representation and prevent overfitting to the original RGB observations. To adaptively fuse these varied inputs, the proposed MBA extend a base agent model into a multi-branch variant, where each branch processes a different visual input. Surprisingly, even random noise can further enhance navigation performance in unseen environments. Extensive experiments conducted on three VLN benchmarks (R2R, REVERIE, SOON) demonstrate that our proposed method equals or even surpasses state-of-the-art results. The source code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge