Juan Rafael Orozco-Arroyave
Towards Inclusive ASR: Investigating Voice Conversion for Dysarthric Speech Recognition in Low-Resource Languages
May 20, 2025Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) for dysarthric speech remains challenging due to data scarcity, particularly in non-English languages. To address this, we fine-tune a voice conversion model on English dysarthric speech (UASpeech) to encode both speaker characteristics and prosodic distortions, then apply it to convert healthy non-English speech (FLEURS) into non-English dysarthric-like speech. The generated data is then used to fine-tune a multilingual ASR model, Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS), for improved dysarthric speech recognition. Evaluation on PC-GITA (Spanish), EasyCall (Italian), and SSNCE (Tamil) demonstrates that VC with both speaker and prosody conversion significantly outperforms the off-the-shelf MMS performance and conventional augmentation techniques such as speed and tempo perturbation. Objective and subjective analyses of the generated data further confirm that the generated speech simulates dysarthric characteristics.
A Speech-to-Video Synthesis Approach Using Spatio-Temporal Diffusion for Vocal Tract MRI
Mar 15, 2025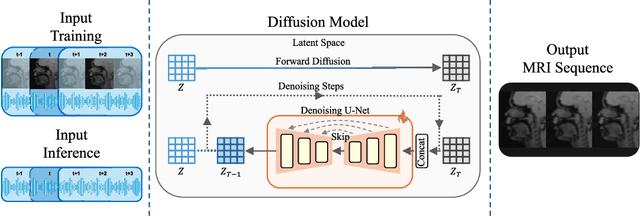
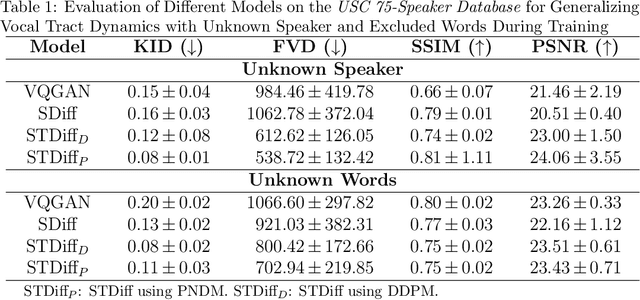
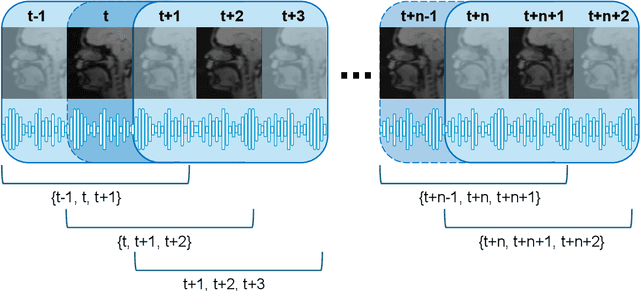

Abstract:Understanding the relationship between vocal tract motion during speech and the resulting acoustic signal is crucial for aided clinical assessment and developing personalized treatment and rehabilitation strategies. Toward this goal, we introduce an audio-to-video generation framework for creating Real Time/cine-Magnetic Resonance Imaging (RT-/cine-MRI) visuals of the vocal tract from speech signals. Our framework first preprocesses RT-/cine-MRI sequences and speech samples to achieve temporal alignment, ensuring synchronization between visual and audio data. We then employ a modified stable diffusion model, integrating structural and temporal blocks, to effectively capture movement characteristics and temporal dynamics in the synchronized data. This process enables the generation of MRI sequences from new speech inputs, improving the conversion of audio into visual data. We evaluated our framework on healthy controls and tongue cancer patients by analyzing and comparing the vocal tract movements in synthesized videos. Our framework demonstrated adaptability to new speech inputs and effective generalization. In addition, positive human evaluations confirmed its effectiveness, with realistic and accurate visualizations, suggesting its potential for outpatient therapy and personalized simulation of vocal tract visualizations.
Bilingual Dual-Head Deep Model for Parkinson's Disease Detection from Speech
Mar 13, 2025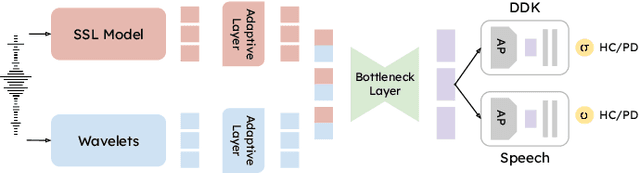
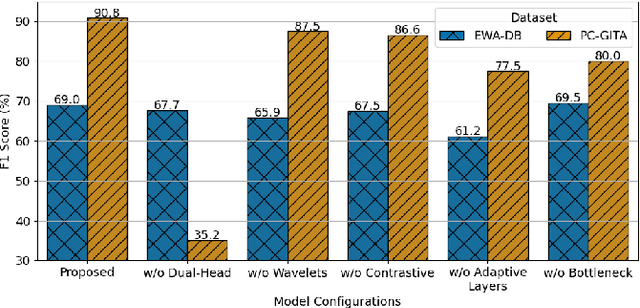
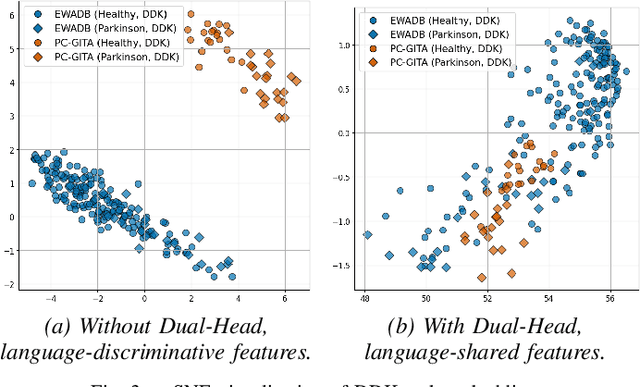
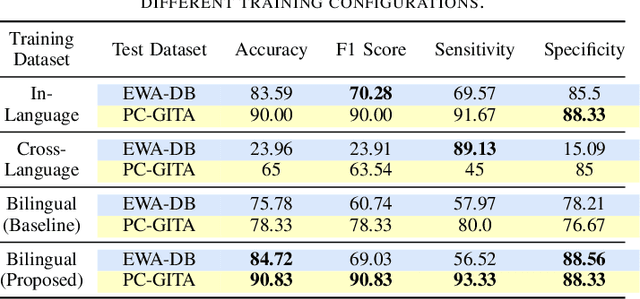
Abstract:This work aims to tackle the Parkinson's disease (PD) detection problem from the speech signal in a bilingual setting by proposing an ad-hoc dual-head deep neural architecture for type-based binary classification. One head is specialized for diadochokinetic patterns. The other head looks for natural speech patterns present in continuous spoken utterances. Only one of the two heads is operative accordingly to the nature of the input. Speech representations are extracted from self-supervised learning (SSL) models and wavelet transforms. Adaptive layers, convolutional bottlenecks, and contrastive learning are exploited to reduce variations across languages. Our solution is assessed against two distinct datasets, EWA-DB, and PC-GITA, which cover Slovak and Spanish languages, respectively. Results indicate that conventional models trained on a single language dataset struggle with cross-linguistic generalization, and naive combinations of datasets are suboptimal. In contrast, our model improves generalization on both languages, simultaneously.
Differential privacy for protecting patient data in speech disorder detection using deep learning
Sep 27, 2024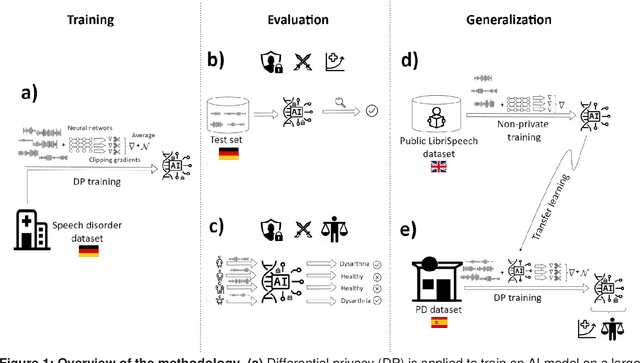
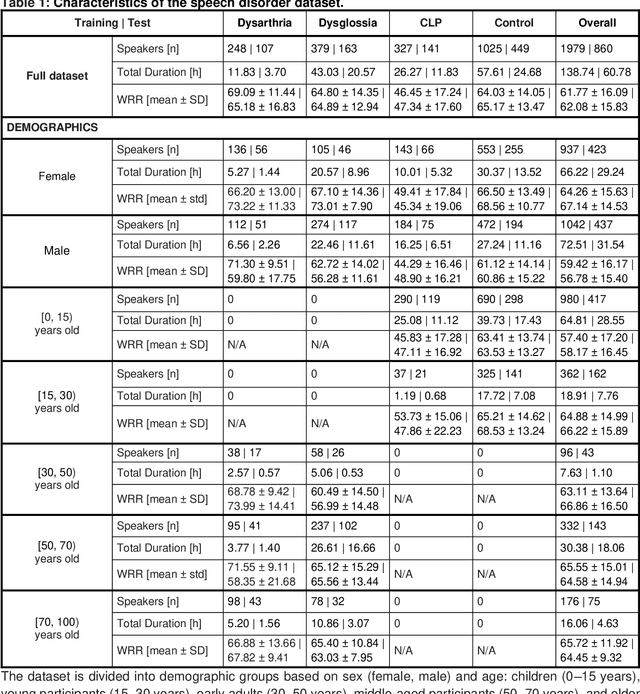
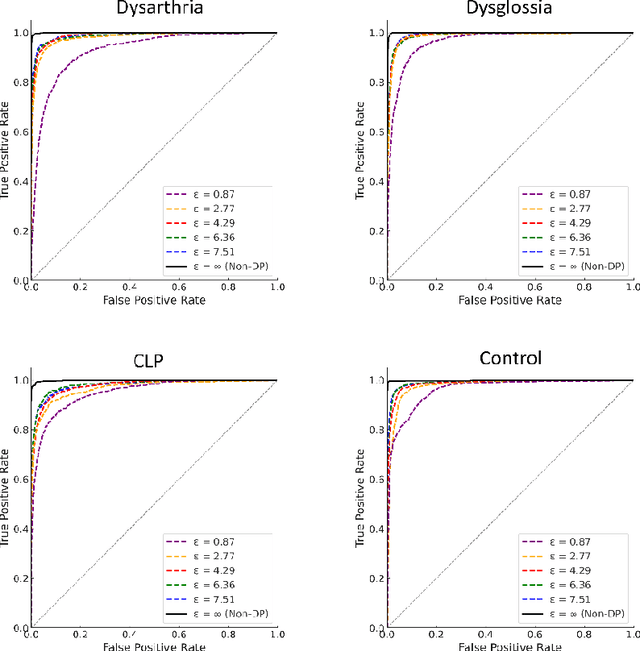
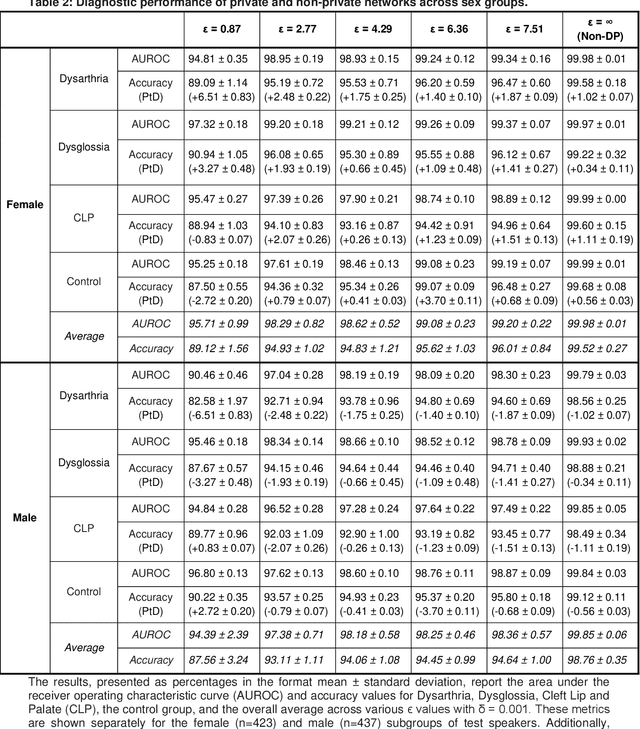
Abstract:Speech pathology has impacts on communication abilities and quality of life. While deep learning-based models have shown potential in diagnosing these disorders, the use of sensitive data raises critical privacy concerns. Although differential privacy (DP) has been explored in the medical imaging domain, its application in pathological speech analysis remains largely unexplored despite the equally critical privacy concerns. This study is the first to investigate DP's impact on pathological speech data, focusing on the trade-offs between privacy, diagnostic accuracy, and fairness. Using a large, real-world dataset of 200 hours of recordings from 2,839 German-speaking participants, we observed a maximum accuracy reduction of 3.85% when training with DP with a privacy budget, denoted by {\epsilon}, of 7.51. To generalize our findings, we validated our approach on a smaller dataset of Spanish-speaking Parkinson's disease patients, demonstrating that careful pretraining on large-scale task-specific datasets can maintain or even improve model accuracy under DP constraints. We also conducted a comprehensive fairness analysis, revealing that reasonable privacy levels (2<{\epsilon}<10) do not introduce significant gender bias, though age-related disparities may require further attention. Our results suggest that DP can effectively balance privacy and utility in speech disorder detection, but also highlight the unique challenges in the speech domain, particularly regarding the privacy-fairness trade-off. This provides a foundation for future work to refine DP methodologies and address fairness across diverse patient groups in real-world deployments.
Exploiting Foundation Models and Speech Enhancement for Parkinson's Disease Detection from Speech in Real-World Operative Conditions
Jun 23, 2024



Abstract:This work is concerned with devising a robust Parkinson's (PD) disease detector from speech in real-world operating conditions using (i) foundational models, and (ii) speech enhancement (SE) methods. To this end, we first fine-tune several foundational-based models on the standard PC-GITA (s-PC-GITA) clean data. Our results demonstrate superior performance to previously proposed models. Second, we assess the generalization capability of the PD models on the extended PC-GITA (e-PC-GITA) recordings, collected in real-world operative conditions, and observe a severe drop in performance moving from ideal to real-world conditions. Third, we align training and testing conditions applaying off-the-shelf SE techniques on e-PC-GITA, and a significant boost in performance is observed only for the foundational-based models. Finally, combining the two best foundational-based models trained on s-PC-GITA, namely WavLM Base and Hubert Base, yielded top performance on the enhanced e-PC-GITA.
Federated learning for secure development of AI models for Parkinson's disease detection using speech from different languages
May 18, 2023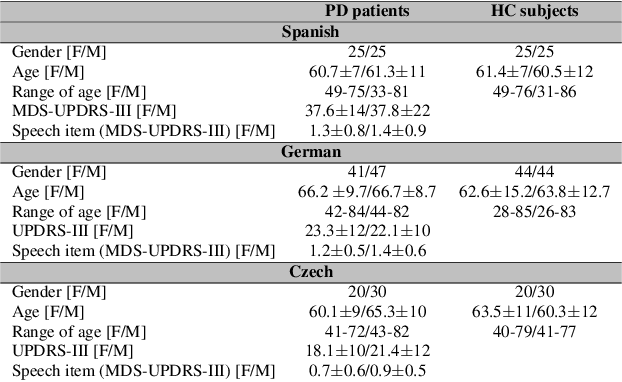
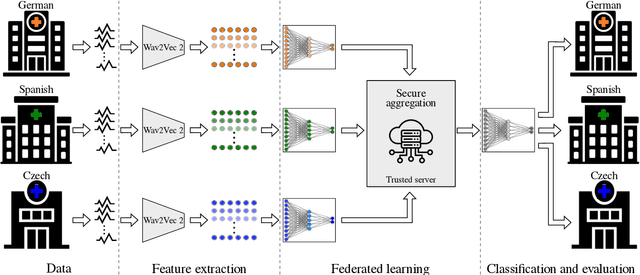
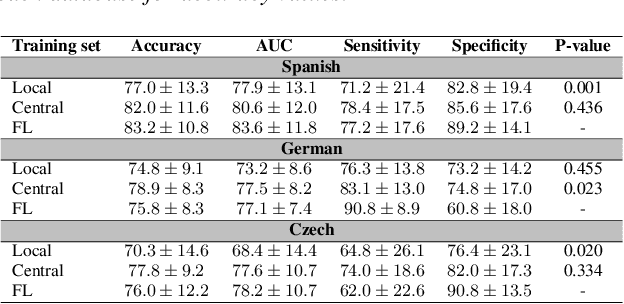
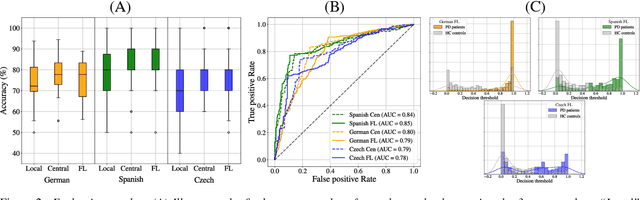
Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurological disorder impacting a person's speech. Among automatic PD assessment methods, deep learning models have gained particular interest. Recently, the community has explored cross-pathology and cross-language models which can improve diagnostic accuracy even further. However, strict patient data privacy regulations largely prevent institutions from sharing patient speech data with each other. In this paper, we employ federated learning (FL) for PD detection using speech signals from 3 real-world language corpora of German, Spanish, and Czech, each from a separate institution. Our results indicate that the FL model outperforms all the local models in terms of diagnostic accuracy, while not performing very differently from the model based on centrally combined training sets, with the advantage of not requiring any data sharing among collaborators. This will simplify inter-institutional collaborations, resulting in enhancement of patient outcomes.
Representation Learning Strategies to Model Pathological Speech: Effect of Multiple Spectral Resolutions
Sep 17, 2022


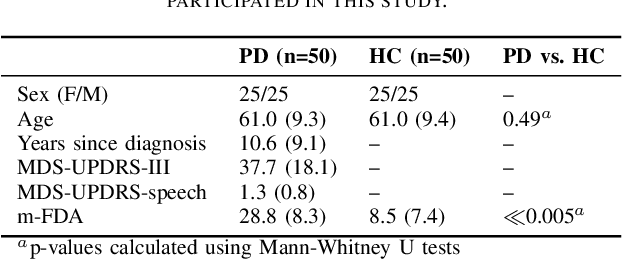
Abstract:This paper considers a representation learning strategy to model speech signals from patients with Parkinson's disease and cleft lip and palate. In particular, it compares different parametrized representation types such as wideband and narrowband spectrograms, and wavelet-based scalograms, with the goal of quantifying the representation capacity of each. Methods for quantification include the ability of the proposed model to classify different pathologies and the associated disease severity. Additionally, this paper proposes a novel fusion strategy called multi-spectral fusion that combines wideband and narrowband spectral resolutions using a representation learning strategy based on autoencoders. The proposed models are able to classify the speech from Parkinson's disease patients with accuracy up to 95\%. The proposed models were also able to asses the dysarthria severity of Parkinson's disease patients with a Spearman correlation up to 0.75. These results outperform those observed in literature where the same problem was addressed with the same corpus.
Self-Supervised Speech Representations Preserve Speech Characteristics while Anonymizing Voices
Apr 04, 2022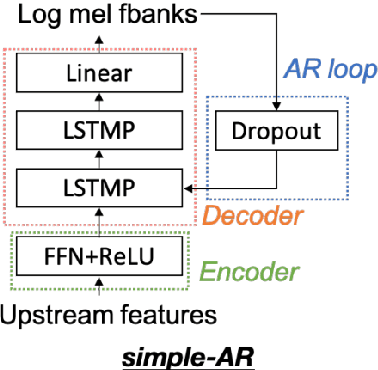
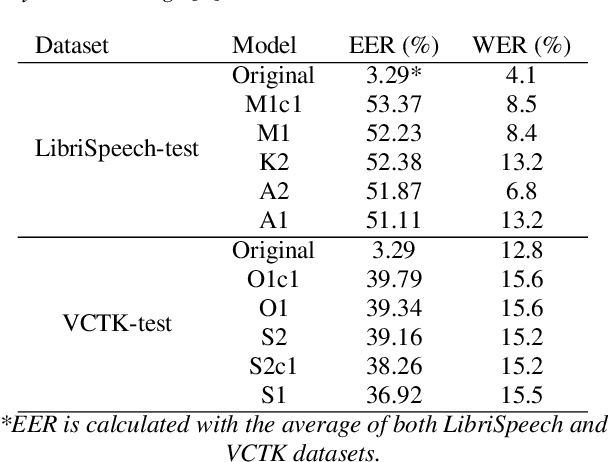

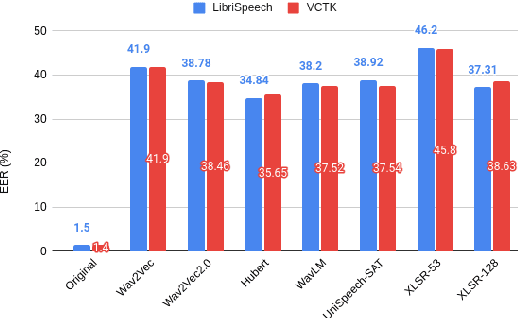
Abstract:Collecting speech data is an important step in training speech recognition systems and other speech-based machine learning models. However, the issue of privacy protection is an increasing concern that must be addressed. The current study investigates the use of voice conversion as a method for anonymizing voices. In particular, we train several voice conversion models using self-supervised speech representations including Wav2Vec2.0, Hubert and UniSpeech. Converted voices retain a low word error rate within 1% of the original voice. Equal error rate increases from 1.52% to 46.24% on the LibriSpeech test set and from 3.75% to 45.84% on speakers from the VCTK corpus which signifies degraded performance on speaker verification. Lastly, we conduct experiments on dysarthric speech data to show that speech features relevant to articulation, prosody, phonation and phonology can be extracted from anonymized voices for discriminating between healthy and pathological speech.
Cross-lingual Self-Supervised Speech Representations for Improved Dysarthric Speech Recognition
Apr 04, 2022



Abstract:State-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems perform well on healthy speech. However, the performance on impaired speech still remains an issue. The current study explores the usefulness of using Wav2Vec self-supervised speech representations as features for training an ASR system for dysarthric speech. Dysarthric speech recognition is particularly difficult as several aspects of speech such as articulation, prosody and phonation can be impaired. Specifically, we train an acoustic model with features extracted from Wav2Vec, Hubert, and the cross-lingual XLSR model. Results suggest that speech representations pretrained on large unlabelled data can improve word error rate (WER) performance. In particular, features from the multilingual model led to lower WERs than filterbanks (Fbank) or models trained on a single language. Improvements were observed in English speakers with cerebral palsy caused dysarthria (UASpeech corpus), Spanish speakers with Parkinsonian dysarthria (PC-GITA corpus) and Italian speakers with paralysis-based dysarthria (EasyCall corpus). Compared to using Fbank features, XLSR-based features reduced WERs by 6.8%, 22.0%, and 7.0% for the UASpeech, PC-GITA, and EasyCall corpus, respectively.
Common Phone: A Multilingual Dataset for Robust Acoustic Modelling
Jan 31, 2022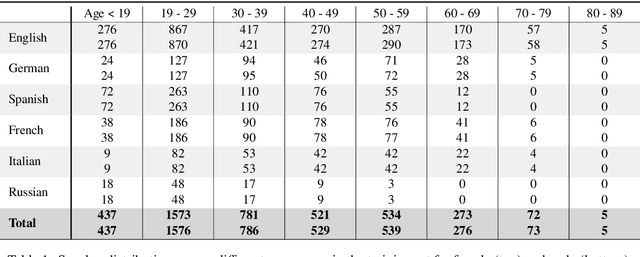

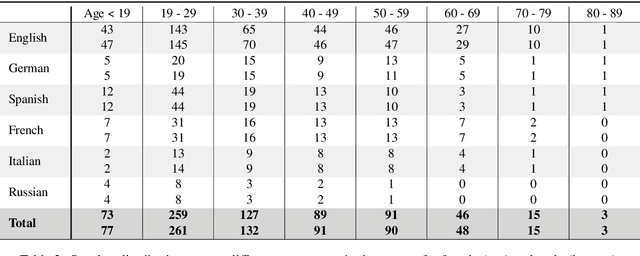
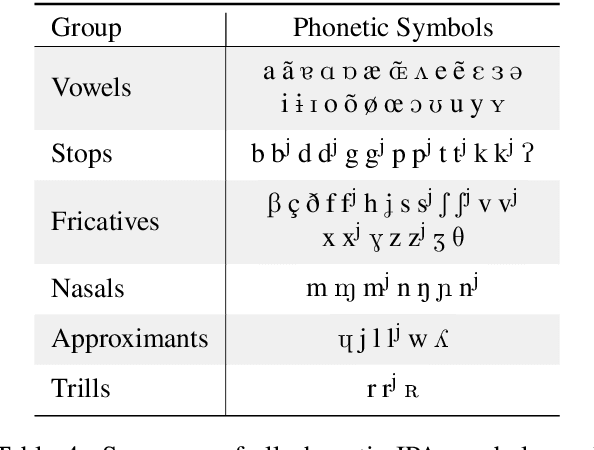
Abstract:Current state of the art acoustic models can easily comprise more than 100 million parameters. This growing complexity demands larger training datasets to maintain a decent generalization of the final decision function. An ideal dataset is not necessarily large in size, but large with respect to the amount of unique speakers, utilized hardware and varying recording conditions. This enables a machine learning model to explore as much of the domain-specific input space as possible during parameter estimation. This work introduces Common Phone, a gender-balanced, multilingual corpus recorded from more than 11.000 contributors via Mozilla's Common Voice project. It comprises around 116 hours of speech enriched with automatically generated phonetic segmentation. A Wav2Vec 2.0 acoustic model was trained with the Common Phone to perform phonetic symbol recognition and validate the quality of the generated phonetic annotation. The architecture achieved a PER of 18.1 % on the entire test set, computed with all 101 unique phonetic symbols, showing slight differences between the individual languages. We conclude that Common Phone provides sufficient variability and reliable phonetic annotation to help bridging the gap between research and application of acoustic models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge