Maria Schuster
Perceptual Implications of Automatic Anonymization in Pathological Speech
May 01, 2025Abstract:Automatic anonymization techniques are essential for ethical sharing of pathological speech data, yet their perceptual consequences remain understudied. This study presents the first comprehensive human-centered analysis of anonymized pathological speech, using a structured perceptual protocol involving ten native and non-native German listeners with diverse linguistic, clinical, and technical backgrounds. Listeners evaluated anonymized-original utterance pairs from 180 speakers spanning Cleft Lip and Palate, Dysarthria, Dysglossia, Dysphonia, and age-matched healthy controls. Speech was anonymized using state-of-the-art automatic methods (equal error rates in the range of 30-40%). Listeners completed Turing-style discrimination and quality rating tasks under zero-shot (single-exposure) and few-shot (repeated-exposure) conditions. Discrimination accuracy was high overall (91% zero-shot; 93% few-shot), but varied by disorder (repeated-measures ANOVA: p=0.007), ranging from 96% (Dysarthria) to 86% (Dysphonia). Anonymization consistently reduced perceived quality (from 83% to 59%, p<0.001), with pathology-specific degradation patterns (one-way ANOVA: p=0.005). Native listeners rated original speech slightly higher than non-native listeners (Delta=4%, p=0.199), but this difference nearly disappeared after anonymization (Delta=1%, p=0.724). No significant gender-based bias was observed. Critically, human perceptual outcomes did not correlate with automatic privacy or clinical utility metrics. These results underscore the need for listener-informed, disorder- and context-specific anonymization strategies that preserve privacy while maintaining interpretability, communicative functions, and diagnostic utility, especially for vulnerable populations such as children.
Differential privacy for protecting patient data in speech disorder detection using deep learning
Sep 27, 2024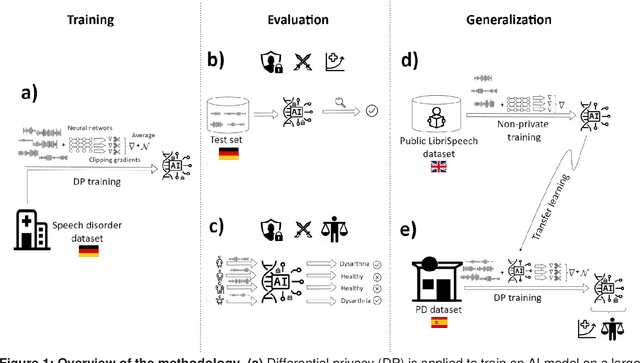
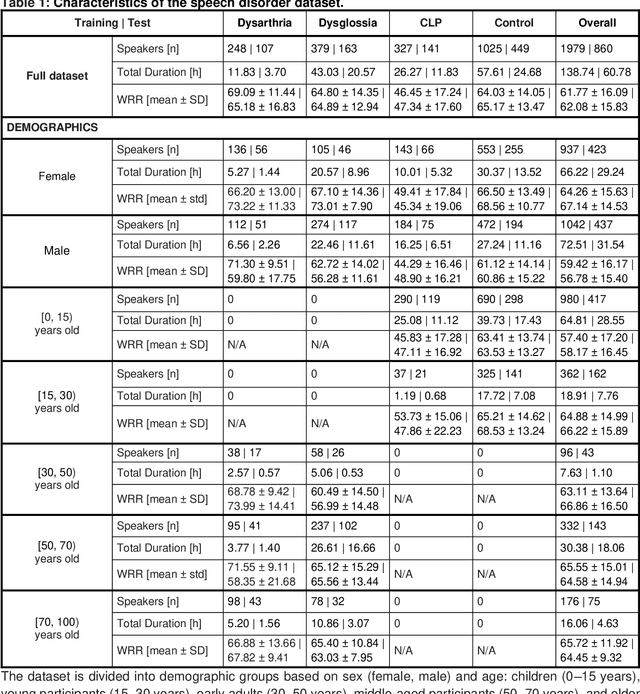
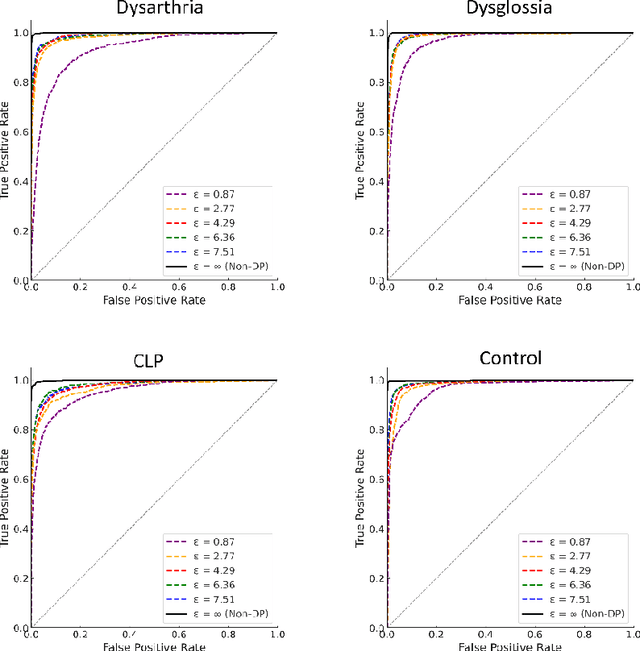
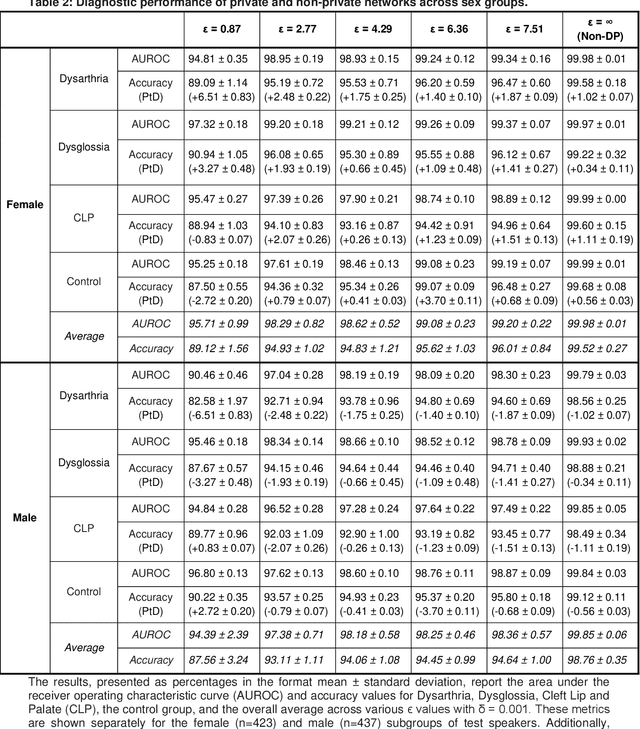
Abstract:Speech pathology has impacts on communication abilities and quality of life. While deep learning-based models have shown potential in diagnosing these disorders, the use of sensitive data raises critical privacy concerns. Although differential privacy (DP) has been explored in the medical imaging domain, its application in pathological speech analysis remains largely unexplored despite the equally critical privacy concerns. This study is the first to investigate DP's impact on pathological speech data, focusing on the trade-offs between privacy, diagnostic accuracy, and fairness. Using a large, real-world dataset of 200 hours of recordings from 2,839 German-speaking participants, we observed a maximum accuracy reduction of 3.85% when training with DP with a privacy budget, denoted by {\epsilon}, of 7.51. To generalize our findings, we validated our approach on a smaller dataset of Spanish-speaking Parkinson's disease patients, demonstrating that careful pretraining on large-scale task-specific datasets can maintain or even improve model accuracy under DP constraints. We also conducted a comprehensive fairness analysis, revealing that reasonable privacy levels (2<{\epsilon}<10) do not introduce significant gender bias, though age-related disparities may require further attention. Our results suggest that DP can effectively balance privacy and utility in speech disorder detection, but also highlight the unique challenges in the speech domain, particularly regarding the privacy-fairness trade-off. This provides a foundation for future work to refine DP methodologies and address fairness across diverse patient groups in real-world deployments.
Speaker- and Text-Independent Estimation of Articulatory Movements and Phoneme Alignments from Speech
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel combination of two tasks, previously treated separately: acoustic-to-articulatory speech inversion (AAI) and phoneme-to-articulatory (PTA) motion estimation. We refer to this joint task as acoustic phoneme-to-articulatory speech inversion (APTAI) and explore two different approaches, both working speaker- and text-independently during inference. We use a multi-task learning setup, with the end-to-end goal of taking raw speech as input and estimating the corresponding articulatory movements, phoneme sequence, and phoneme alignment. While both proposed approaches share these same requirements, they differ in their way of achieving phoneme-related predictions: one is based on frame classification, the other on a two-staged training procedure and forced alignment. We reach competitive performance of 0.73 mean correlation for the AAI task and achieve up to approximately 87% frame overlap compared to a state-of-the-art text-dependent phoneme force aligner.
The Impact of Speech Anonymization on Pathology and Its Limits
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Integration of speech into healthcare has intensified privacy concerns due to its potential as a non-invasive biomarker containing individual biometric information. In response, speaker anonymization aims to conceal personally identifiable information while retaining crucial linguistic content. However, the application of anonymization techniques to pathological speech, a critical area where privacy is especially vital, has not been extensively examined. This study investigates anonymization's impact on pathological speech across over 2,700 speakers from multiple German institutions, focusing on privacy, pathological utility, and demographic fairness. We explore both training-based and signal processing-based anonymization methods, and document substantial privacy improvements across disorders-evidenced by equal error rate increases up to 1933%, with minimal overall impact on utility. Specific disorders such as Dysarthria, Dysphonia, and Cleft Lip and Palate experienced minimal utility changes, while Dysglossia showed slight improvements. Our findings underscore that the impact of anonymization varies substantially across different disorders. This necessitates disorder-specific anonymization strategies to optimally balance privacy with diagnostic utility. Additionally, our fairness analysis revealed consistent anonymization effects across most of the demographics. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of anonymization in pathological speech for enhancing privacy, while also highlighting the importance of customized approaches to account for inversion attacks.
Is Speech Pathology a Biomarker in Automatic Speaker Verification?
Apr 13, 2022



Abstract:With the advancements in deep learning (DL) and an increasing interest in data-driven speech processing methods, a major challenge for speech data scientists in the healthcare domain is the anonymization of pathological speech, which is a required step to be able to make them accessible as a public training resource. In this paper, we investigate pathological speech data and compare their speaker verifiability with that of healthy individuals. We utilize a large pathological speech corpus of more than 2,000 test subjects with various speech and voice disorders from different ages and apply DL-based automatic speaker verification (ASV) techniques. As a result, we obtained a mean equal error rate (EER) of 0.86% with a standard deviation of 0.16%, which is a factor of three lower than comparable healthy speech databases. We further perform detailed analyses of external influencing factors on ASV such as age, pathology, recording environment, and utterance length, to explore their respective effect. Our findings indicate that speech pathology is a potential biomarker in ASV. This is potentially of high interest for the anonymization of pathological speech data.
Disentangled Latent Speech Representation for Automatic Pathological Intelligibility Assessment
Apr 08, 2022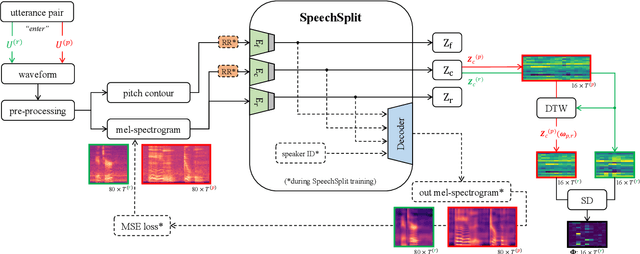
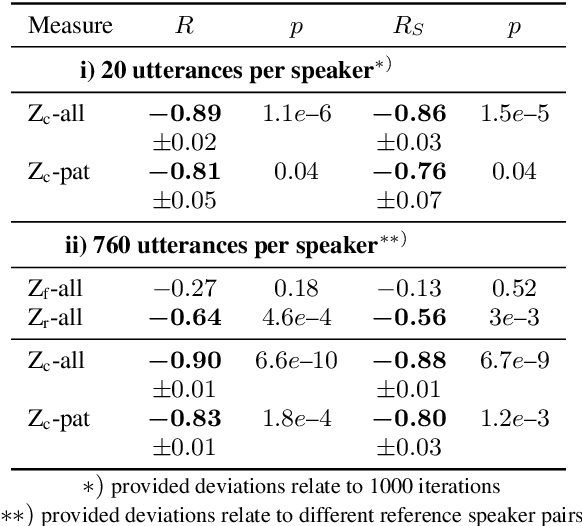
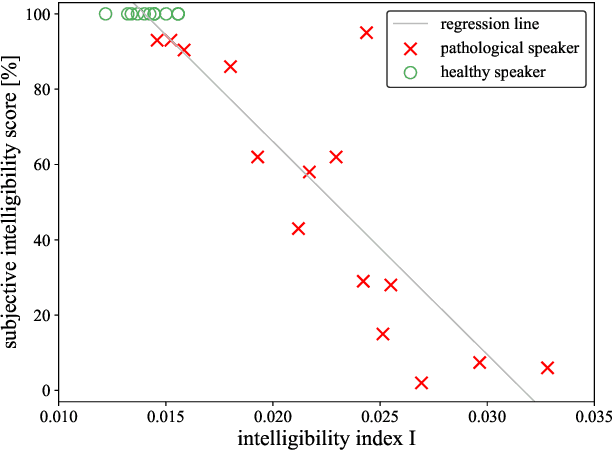
Abstract:Speech intelligibility assessment plays an important role in the therapy of patients suffering from pathological speech disorders. Automatic and objective measures are desirable to assist therapists in their traditionally subjective and labor-intensive assessments. In this work, we investigate a novel approach for obtaining such a measure using the divergence in disentangled latent speech representations of a parallel utterance pair, obtained from a healthy reference and a pathological speaker. Experiments on an English database of Cerebral Palsy patients, using all available utterances per speaker, show high and significant correlation values (R = -0.9) with subjective intelligibility measures, while having only minimal deviation (+-0.01) across four different reference speaker pairs. We also demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method (R = -0.89 deviating +-0.02 over 1000 iterations) by considering a significantly smaller amount of utterances per speaker. Our results are among the first to show that disentangled speech representations can be used for automatic pathological speech intelligibility assessment, resulting in a reference speaker pair invariant method, applicable in scenarios with only few utterances available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge