Elmar Nöth
Towards Inclusive ASR: Investigating Voice Conversion for Dysarthric Speech Recognition in Low-Resource Languages
May 20, 2025Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) for dysarthric speech remains challenging due to data scarcity, particularly in non-English languages. To address this, we fine-tune a voice conversion model on English dysarthric speech (UASpeech) to encode both speaker characteristics and prosodic distortions, then apply it to convert healthy non-English speech (FLEURS) into non-English dysarthric-like speech. The generated data is then used to fine-tune a multilingual ASR model, Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS), for improved dysarthric speech recognition. Evaluation on PC-GITA (Spanish), EasyCall (Italian), and SSNCE (Tamil) demonstrates that VC with both speaker and prosody conversion significantly outperforms the off-the-shelf MMS performance and conventional augmentation techniques such as speed and tempo perturbation. Objective and subjective analyses of the generated data further confirm that the generated speech simulates dysarthric characteristics.
Personalized Fine-Tuning with Controllable Synthetic Speech from LLM-Generated Transcripts for Dysarthric Speech Recognition
May 19, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present our submission to the Speech Accessibility Project challenge for dysarthric speech recognition. We integrate parameter-efficient fine-tuning with latent audio representations to improve an encoder-decoder ASR system. Synthetic training data is generated by fine-tuning Parler-TTS to mimic dysarthric speech, using LLM-generated prompts for corpus-consistent target transcripts. Personalization with x-vectors consistently reduces word error rates (WERs) over non-personalized fine-tuning. AdaLoRA adapters outperform full fine-tuning and standard low-rank adaptation, achieving relative WER reductions of ~23% and ~22%, respectively. Further improvements (~5% WER reduction) come from incorporating wav2vec 2.0-based audio representations. Training with synthetic dysarthric speech yields up to ~7% relative WER improvement over personalized fine-tuning alone.
A Speech-to-Video Synthesis Approach Using Spatio-Temporal Diffusion for Vocal Tract MRI
Mar 15, 2025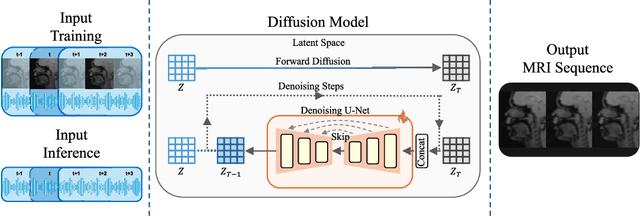
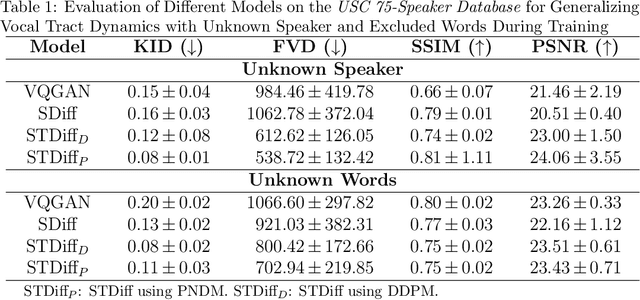
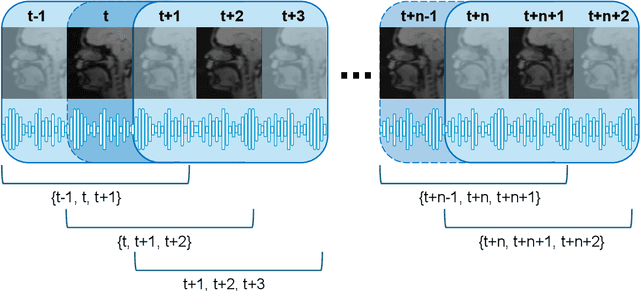

Abstract:Understanding the relationship between vocal tract motion during speech and the resulting acoustic signal is crucial for aided clinical assessment and developing personalized treatment and rehabilitation strategies. Toward this goal, we introduce an audio-to-video generation framework for creating Real Time/cine-Magnetic Resonance Imaging (RT-/cine-MRI) visuals of the vocal tract from speech signals. Our framework first preprocesses RT-/cine-MRI sequences and speech samples to achieve temporal alignment, ensuring synchronization between visual and audio data. We then employ a modified stable diffusion model, integrating structural and temporal blocks, to effectively capture movement characteristics and temporal dynamics in the synchronized data. This process enables the generation of MRI sequences from new speech inputs, improving the conversion of audio into visual data. We evaluated our framework on healthy controls and tongue cancer patients by analyzing and comparing the vocal tract movements in synthesized videos. Our framework demonstrated adaptability to new speech inputs and effective generalization. In addition, positive human evaluations confirmed its effectiveness, with realistic and accurate visualizations, suggesting its potential for outpatient therapy and personalized simulation of vocal tract visualizations.
Large Language Models for Dysfluency Detection in Stuttered Speech
Jun 16, 2024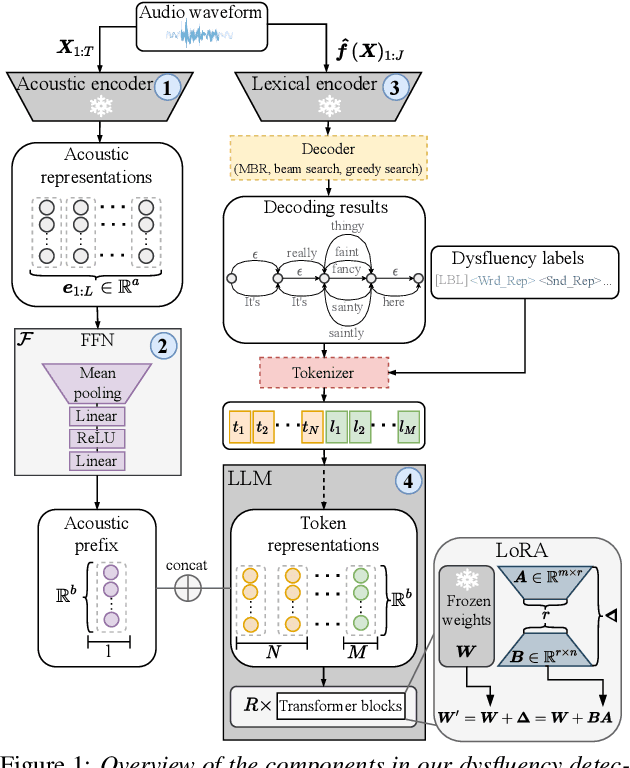
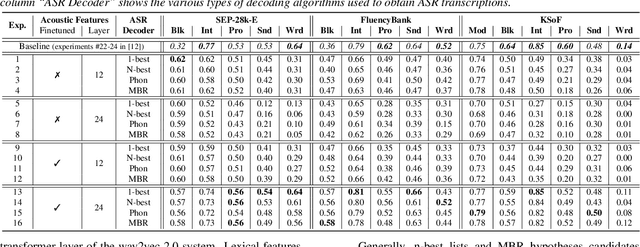
Abstract:Accurately detecting dysfluencies in spoken language can help to improve the performance of automatic speech and language processing components and support the development of more inclusive speech and language technologies. Inspired by the recent trend towards the deployment of large language models (LLMs) as universal learners and processors of non-lexical inputs, such as audio and video, we approach the task of multi-label dysfluency detection as a language modeling problem. We present hypotheses candidates generated with an automatic speech recognition system and acoustic representations extracted from an audio encoder model to an LLM, and finetune the system to predict dysfluency labels on three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech. The experimental results show that our system effectively combines acoustic and lexical information and achieves competitive results on the multi-label stuttering detection task.
Classifying Dementia in the Presence of Depression: A Cross-Corpus Study
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Automated dementia screening enables early detection and intervention, reducing costs to healthcare systems and increasing quality of life for those affected. Depression has shared symptoms with dementia, adding complexity to diagnoses. The research focus so far has been on binary classification of dementia (DEM) and healthy controls (HC) using speech from picture description tests from a single dataset. In this work, we apply established baseline systems to discriminate cognitive impairment in speech from the semantic Verbal Fluency Test and the Boston Naming Test using text, audio and emotion embeddings in a 3-class classification problem (HC vs. MCI vs. DEM). We perform cross-corpus and mixed-corpus experiments on two independently recorded German datasets to investigate generalization to larger populations and different recording conditions. In a detailed error analysis, we look at depression as a secondary diagnosis to understand what our classifiers actually learn.
A Stutter Seldom Comes Alone -- Cross-Corpus Stuttering Detection as a Multi-label Problem
May 30, 2023Abstract:Most stuttering detection and classification research has viewed stuttering as a multi-class classification problem or a binary detection task for each dysfluency type; however, this does not match the nature of stuttering, in which one dysfluency seldom comes alone but rather co-occurs with others. This paper explores multi-language and cross-corpus end-to-end stuttering detection as a multi-label problem using a modified wav2vec 2.0 system with an attention-based classification head and multi-task learning. We evaluate the method using combinations of three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech, one containing speech modified by fluency shaping. The experimental results and an error analysis show that multi-label stuttering detection systems trained on cross-corpus and multi-language data achieve competitive results but performance on samples with multiple labels stays below over-all detection results.
Dysfluencies Seldom Come Alone -- Detection as a Multi-Label Problem
Oct 28, 2022


Abstract:Specially adapted speech recognition models are necessary to handle stuttered speech. For these to be used in a targeted manner, stuttered speech must be reliably detected. Recent works have treated stuttering as a multi-class classification problem or viewed detecting each dysfluency type as an isolated task; that does not capture the nature of stuttering, where one dysfluency seldom comes alone, i.e., co-occurs with others. This work explores an approach based on a modified wav2vec 2.0 system for end-to-end stuttering detection and classification as a multi-label problem. The method is evaluated on combinations of three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech, yielding state-of-the-art results for stuttering detection on the SEP-28k-Extended dataset. Experimental results provide evidence for the transferability of features and the generalizability of the method across datasets and languages.
The Importance of Speech Stimuli for Pathologic Speech Classification
Oct 28, 2022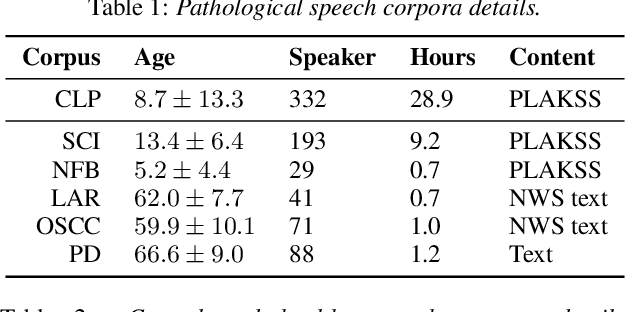
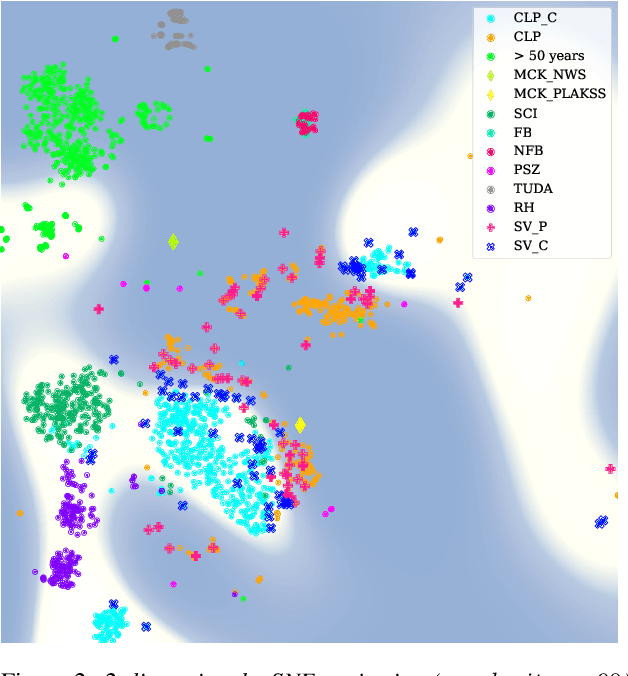
Abstract:Current findings show that pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 models can be successfully used as feature extractors to discriminate on speaker-based tasks. We demonstrate that latent representations extracted at different layers of a pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 system can be effectively used for binary classification of various types of pathologic speech. We examine the pathologies laryngectomy, oral squamous cell carcinoma, parkinson's disease and cleft lip and palate for this purpose. The results show that a distinction between pathological and healthy voices, especially with latent representations from the lower layers, performs well with the lowest accuracy from 77.2% for parkinson's disease to 100% for laryngectomy classification. However, cross-pathology and cross-healthy tests show that the trained classifiers seem to be biased. The recognition rates vary considerably if there is a mismatch between training and out-of-domain test data, e.g., in age, spoken content or acoustic conditions.
Multi-class Detection of Pathological Speech with Latent Features: How does it perform on unseen data?
Oct 27, 2022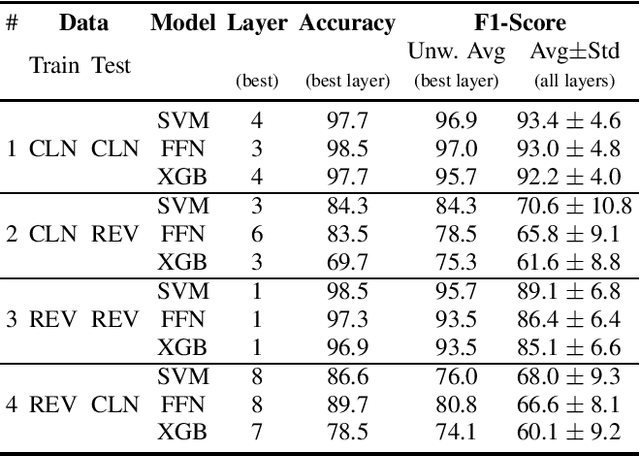

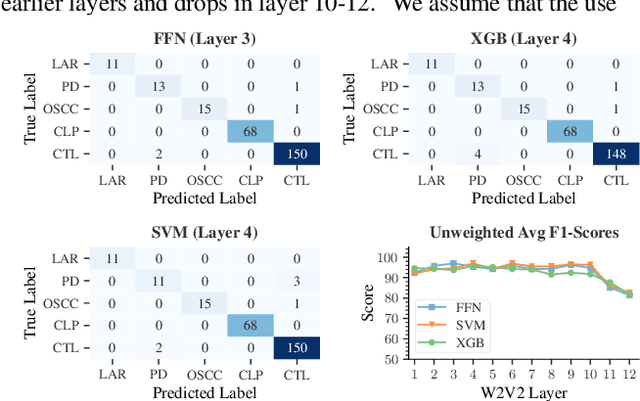
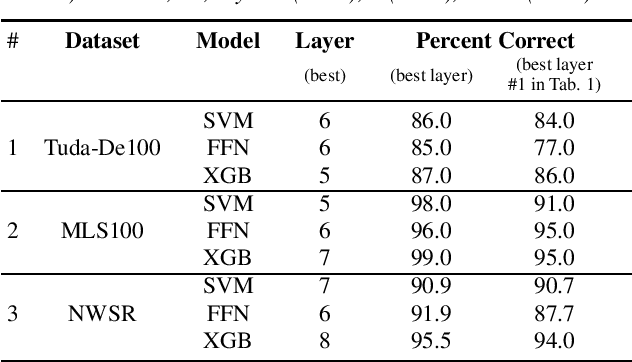
Abstract:The detection of pathologies from speech features is usually defined as a binary classification task with one class representing a specific pathology and the other class representing healthy speech. In this work, we train neural networks, large margin classifiers, and tree boosting machines to distinguish between four different pathologies: Parkinson's disease, laryngeal cancer, cleft lip and palate, and oral squamous cell carcinoma. We demonstrate that latent representations extracted at different layers of a pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 system can be effectively used to classify these types of pathological voices. We evaluate the robustness of our classifiers by adding room impulse responses to the test data and by applying them to unseen speech corpora. Our approach achieves unweighted average F1-Scores between 74.1% and 96.4%, depending on the model and the noise conditions used. The systems generalize and perform well on unseen data of healthy speakers sampled from a variety of different sources.
Representation Learning Strategies to Model Pathological Speech: Effect of Multiple Spectral Resolutions
Sep 17, 2022


Abstract:This paper considers a representation learning strategy to model speech signals from patients with Parkinson's disease and cleft lip and palate. In particular, it compares different parametrized representation types such as wideband and narrowband spectrograms, and wavelet-based scalograms, with the goal of quantifying the representation capacity of each. Methods for quantification include the ability of the proposed model to classify different pathologies and the associated disease severity. Additionally, this paper proposes a novel fusion strategy called multi-spectral fusion that combines wideband and narrowband spectral resolutions using a representation learning strategy based on autoencoders. The proposed models are able to classify the speech from Parkinson's disease patients with accuracy up to 95\%. The proposed models were also able to asses the dysarthria severity of Parkinson's disease patients with a Spearman correlation up to 0.75. These results outperform those observed in literature where the same problem was addressed with the same corpus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge