Sebastian P. Bayerl
Infusing Acoustic Pause Context into Text-Based Dementia Assessment
Aug 27, 2024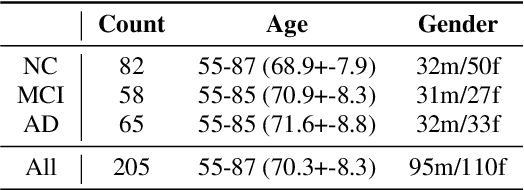
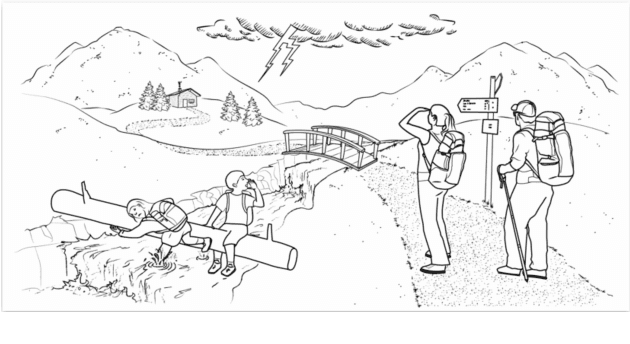
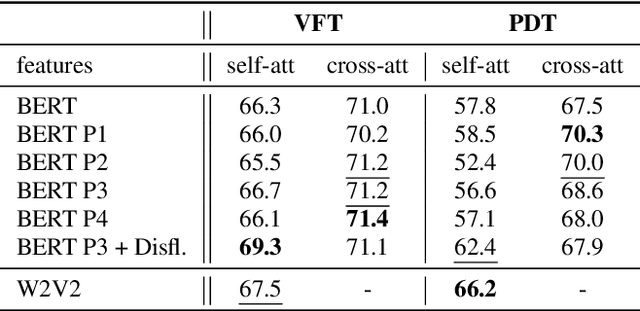
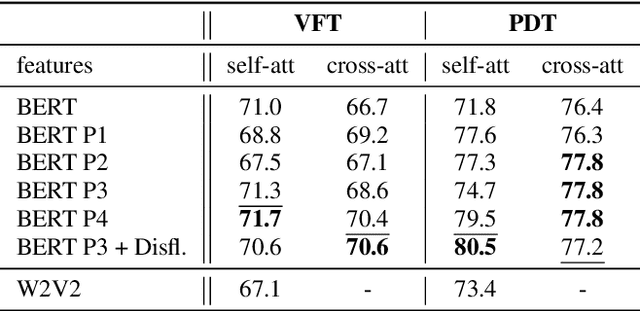
Abstract:Speech pauses, alongside content and structure, offer a valuable and non-invasive biomarker for detecting dementia. This work investigates the use of pause-enriched transcripts in transformer-based language models to differentiate the cognitive states of subjects with no cognitive impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's dementia based on their speech from a clinical assessment. We address three binary classification tasks: Onset, monitoring, and dementia exclusion. The performance is evaluated through experiments on a German Verbal Fluency Test and a Picture Description Test, comparing the model's effectiveness across different speech production contexts. Starting from a textual baseline, we investigate the effect of incorporation of pause information and acoustic context. We show the test should be chosen depending on the task, and similarly, lexical pause information and acoustic cross-attention contribute differently.
Large Language Models for Dysfluency Detection in Stuttered Speech
Jun 16, 2024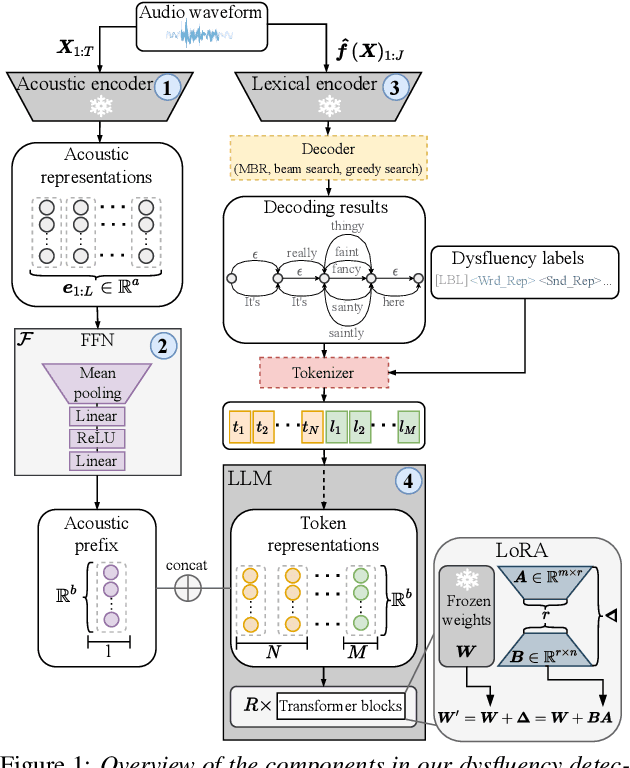
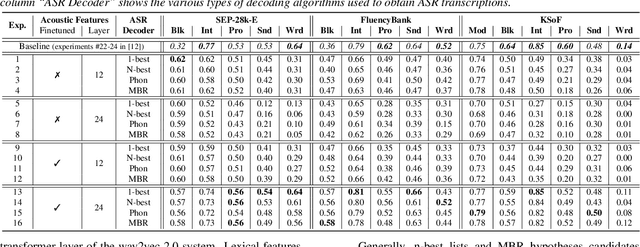
Abstract:Accurately detecting dysfluencies in spoken language can help to improve the performance of automatic speech and language processing components and support the development of more inclusive speech and language technologies. Inspired by the recent trend towards the deployment of large language models (LLMs) as universal learners and processors of non-lexical inputs, such as audio and video, we approach the task of multi-label dysfluency detection as a language modeling problem. We present hypotheses candidates generated with an automatic speech recognition system and acoustic representations extracted from an audio encoder model to an LLM, and finetune the system to predict dysfluency labels on three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech. The experimental results show that our system effectively combines acoustic and lexical information and achieves competitive results on the multi-label stuttering detection task.
Classifying Dementia in the Presence of Depression: A Cross-Corpus Study
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Automated dementia screening enables early detection and intervention, reducing costs to healthcare systems and increasing quality of life for those affected. Depression has shared symptoms with dementia, adding complexity to diagnoses. The research focus so far has been on binary classification of dementia (DEM) and healthy controls (HC) using speech from picture description tests from a single dataset. In this work, we apply established baseline systems to discriminate cognitive impairment in speech from the semantic Verbal Fluency Test and the Boston Naming Test using text, audio and emotion embeddings in a 3-class classification problem (HC vs. MCI vs. DEM). We perform cross-corpus and mixed-corpus experiments on two independently recorded German datasets to investigate generalization to larger populations and different recording conditions. In a detailed error analysis, we look at depression as a secondary diagnosis to understand what our classifiers actually learn.
A Stutter Seldom Comes Alone -- Cross-Corpus Stuttering Detection as a Multi-label Problem
May 30, 2023Abstract:Most stuttering detection and classification research has viewed stuttering as a multi-class classification problem or a binary detection task for each dysfluency type; however, this does not match the nature of stuttering, in which one dysfluency seldom comes alone but rather co-occurs with others. This paper explores multi-language and cross-corpus end-to-end stuttering detection as a multi-label problem using a modified wav2vec 2.0 system with an attention-based classification head and multi-task learning. We evaluate the method using combinations of three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech, one containing speech modified by fluency shaping. The experimental results and an error analysis show that multi-label stuttering detection systems trained on cross-corpus and multi-language data achieve competitive results but performance on samples with multiple labels stays below over-all detection results.
Generative Models for Improved Naturalness, Intelligibility, and Voicing of Whispered Speech
Dec 04, 2022Abstract:This work adapts two recent architectures of generative models and evaluates their effectiveness for the conversion of whispered speech to normal speech. We incorporate the normal target speech into the training criterion of vector-quantized variational autoencoders (VQ-VAEs) and MelGANs, thereby conditioning the systems to recover voiced speech from whispered inputs. Objective and subjective quality measures indicate that both VQ-VAEs and MelGANs can be modified to perform the conversion task. We find that the proposed approaches significantly improve the Mel cepstral distortion (MCD) metric by at least 25% relative to a DiscoGAN baseline. Subjective listening tests suggest that the MelGAN-based system significantly improves naturalness, intelligibility, and voicing compared to the whispered input speech. A novel evaluation measure based on differences between latent speech representations also indicates that our MelGAN-based approach yields improvements relative to the baseline.
Speaker Adaptation for End-To-End Speech Recognition Systems in Noisy Environments
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:We analyze the impact of speaker adaptation in end-to-end architectures based on transformers and wav2vec 2.0 under different noise conditions. We demonstrate that the proven method of concatenating speaker vectors to the acoustic features and supplying them as an auxiliary model input remains a viable option to increase the robustness of end-to-end architectures. By including speaker embeddings obtained from x-vector and ECAPA-TDNN models, we achieve relative word error rate improvements of up to 9.6% on LibriSpeech and up to 14.5% on Switchboard. The effect on transformer-based architectures is approximately inversely proportional to the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and is strongest in heavily noised environments ($SNR=0$). The most substantial benefit of speaker adaption in systems based on wav2vec 2.0 can be achieved under moderate noise conditions ($SNR\geq18$). We also find that x-vectors tend to yield larger improvements than ECAPA-TDNN embeddings.
Dysfluencies Seldom Come Alone -- Detection as a Multi-Label Problem
Oct 28, 2022


Abstract:Specially adapted speech recognition models are necessary to handle stuttered speech. For these to be used in a targeted manner, stuttered speech must be reliably detected. Recent works have treated stuttering as a multi-class classification problem or viewed detecting each dysfluency type as an isolated task; that does not capture the nature of stuttering, where one dysfluency seldom comes alone, i.e., co-occurs with others. This work explores an approach based on a modified wav2vec 2.0 system for end-to-end stuttering detection and classification as a multi-label problem. The method is evaluated on combinations of three datasets containing English and German stuttered speech, yielding state-of-the-art results for stuttering detection on the SEP-28k-Extended dataset. Experimental results provide evidence for the transferability of features and the generalizability of the method across datasets and languages.
The Importance of Speech Stimuli for Pathologic Speech Classification
Oct 28, 2022
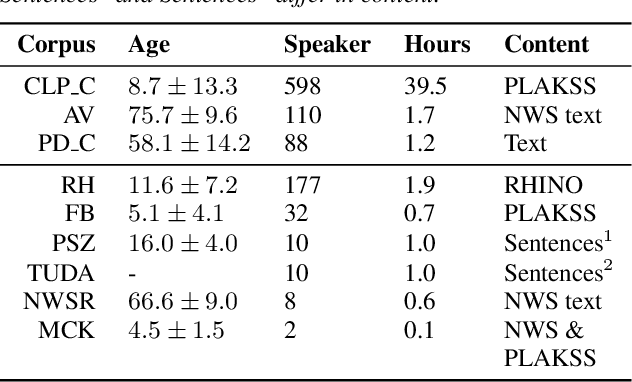
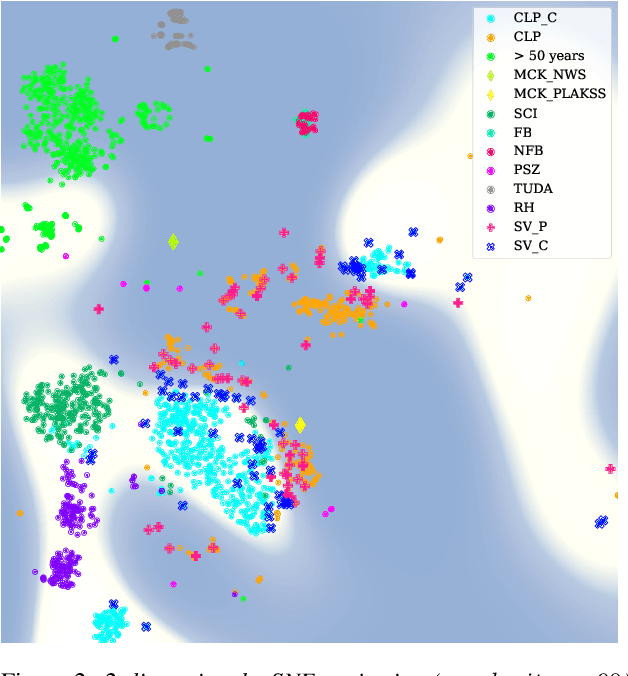
Abstract:Current findings show that pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 models can be successfully used as feature extractors to discriminate on speaker-based tasks. We demonstrate that latent representations extracted at different layers of a pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 system can be effectively used for binary classification of various types of pathologic speech. We examine the pathologies laryngectomy, oral squamous cell carcinoma, parkinson's disease and cleft lip and palate for this purpose. The results show that a distinction between pathological and healthy voices, especially with latent representations from the lower layers, performs well with the lowest accuracy from 77.2% for parkinson's disease to 100% for laryngectomy classification. However, cross-pathology and cross-healthy tests show that the trained classifiers seem to be biased. The recognition rates vary considerably if there is a mismatch between training and out-of-domain test data, e.g., in age, spoken content or acoustic conditions.
Multi-class Detection of Pathological Speech with Latent Features: How does it perform on unseen data?
Oct 27, 2022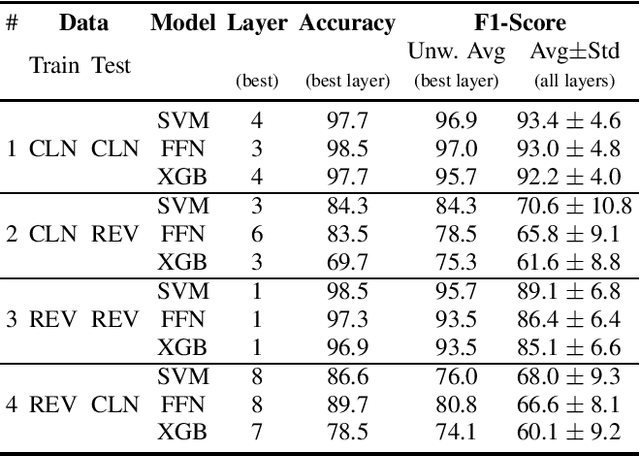

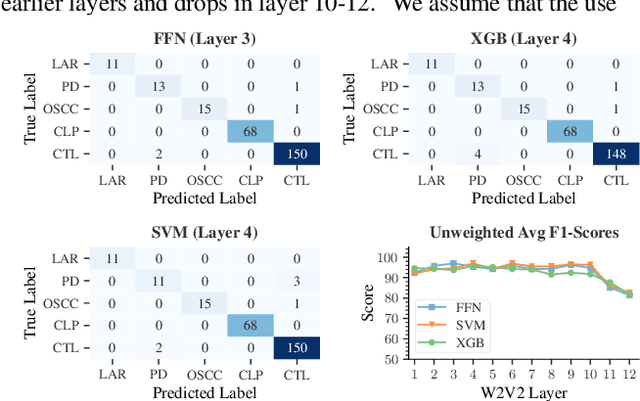
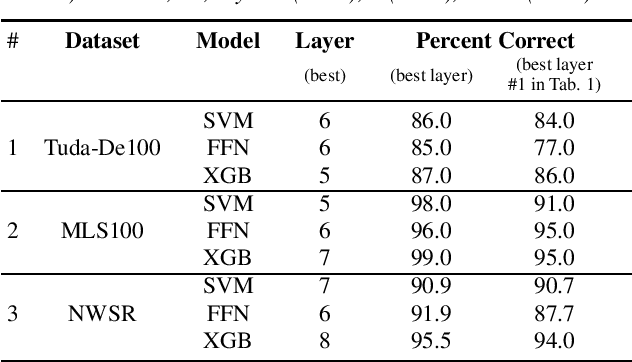
Abstract:The detection of pathologies from speech features is usually defined as a binary classification task with one class representing a specific pathology and the other class representing healthy speech. In this work, we train neural networks, large margin classifiers, and tree boosting machines to distinguish between four different pathologies: Parkinson's disease, laryngeal cancer, cleft lip and palate, and oral squamous cell carcinoma. We demonstrate that latent representations extracted at different layers of a pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 system can be effectively used to classify these types of pathological voices. We evaluate the robustness of our classifiers by adding room impulse responses to the test data and by applying them to unseen speech corpora. Our approach achieves unweighted average F1-Scores between 74.1% and 96.4%, depending on the model and the noise conditions used. The systems generalize and perform well on unseen data of healthy speakers sampled from a variety of different sources.
What can Speech and Language Tell us About the Working Alliance in Psychotherapy
Jun 27, 2022

Abstract:We are interested in the problem of conversational analysis and its application to the health domain. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a structured approach in psychotherapy, allowing the therapist to help the patient to identify and modify the malicious thoughts, behavior, or actions. This cooperative effort can be evaluated using the Working Alliance Inventory Observer-rated Shortened - a 12 items inventory covering task, goal, and relationship - which has a relevant influence on therapeutic outcomes. In this work, we investigate the relation between this alliance inventory and the spoken conversations (sessions) between the patient and the psychotherapist. We have delivered eight weeks of e-therapy, collected their audio and video call sessions, and manually transcribed them. The spoken conversations have been annotated and evaluated with WAI ratings by professional therapists. We have investigated speech and language features and their association with WAI items. The feature types include turn dynamics, lexical entrainment, and conversational descriptors extracted from the speech and language signals. Our findings provide strong evidence that a subset of these features are strong indicators of working alliance. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first and a novel study to exploit speech and language for characterising working alliance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge