Jinbao Wang
A Lightweight 3D Anomaly Detection Method with Rotationally Invariant Features
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:3D anomaly detection (AD) is a crucial task in computer vision, aiming to identify anomalous points or regions from point cloud data. However, existing methods may encounter challenges when handling point clouds with changes in orientation and position because the resulting features may vary significantly. To address this problem, we propose a novel Rotationally Invariant Features (RIF) framework for 3D AD. Firstly, to remove the adverse effect of variations on point cloud data, we develop a Point Coordinate Mapping (PCM) technique, which maps each point into a rotationally invariant space to maintain consistency of representation. Then, to learn robust and discriminative features, we design a lightweight Convolutional Transform Feature Network (CTF-Net) to extract rotationally invariant features for the memory bank. To improve the ability of the feature extractor, we introduce the idea of transfer learning to pre-train the feature extractor with 3D data augmentation. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves the advanced performance on the Anomaly-ShapeNet dataset, with an average P-AUROC improvement of 17.7\%, and also gains the best performance on the Real3D-AD dataset, with an average P-AUROC improvement of 1.6\%. The strong generalization ability of RIF has been verified by combining it with traditional feature extraction methods on anomaly detection tasks, demonstrating great potential for industrial applications.
ASBench: Image Anomalies Synthesis Benchmark for Anomaly Detection
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection plays a pivotal role in manufacturing quality control, yet its application is constrained by limited abnormal samples and high manual annotation costs. While anomaly synthesis offers a promising solution, existing studies predominantly treat anomaly synthesis as an auxiliary component within anomaly detection frameworks, lacking systematic evaluation of anomaly synthesis algorithms. Current research also overlook crucial factors specific to anomaly synthesis, such as decoupling its impact from detection, quantitative analysis of synthetic data and adaptability across different scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose ASBench, the first comprehensive benchmarking framework dedicated to evaluating anomaly synthesis methods. Our framework introduces four critical evaluation dimensions: (i) the generalization performance across different datasets and pipelines (ii) the ratio of synthetic to real data (iii) the correlation between intrinsic metrics of synthesis images and anomaly detection performance metrics , and (iv) strategies for hybrid anomaly synthesis methods. Through extensive experiments, ASBench not only reveals limitations in current anomaly synthesis methods but also provides actionable insights for future research directions in anomaly synthesis
Enhancing Noise Robustness of Parkinson's Disease Telemonitoring via Contrastive Feature Augmentation
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorder. PD telemonitoring emerges as a novel assessment modality enabling self-administered at-home tests of Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) scores, enhancing accessibility for PD patients. However, three types of noise would occur during measurements: (1) patient-induced measurement inaccuracies, (2) environmental noise, and (3) data packet loss during transmission, resulting in higher prediction errors. To address these challenges, NoRo, a noise-robust UPDRS prediction framework is proposed. First, the original speech features are grouped into ordered bins, based on the continuous values of a selected feature, to construct contrastive pairs. Second, the contrastive pairs are employed to train a multilayer perceptron encoder for generating noise-robust features. Finally, these features are concatenated with the original features as the augmented features, which are then fed into the UPDRS prediction models. Notably, we further introduces a novel evaluation approach with customizable noise injection module, and extensive experiments show that NoRo can successfully enhance the noise robustness of UPDRS prediction across various downstream prediction models under different noisy environments.
LabelGS: Label-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting for 3D Scene Segmentation
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a novel explicit representation for 3D scenes, offering both high-fidelity reconstruction and efficient rendering. However, 3DGS lacks 3D segmentation ability, which limits its applicability in tasks that require scene understanding. The identification and isolating of specific object components is crucial. To address this limitation, we propose Label-aware 3D Gaussian Splatting (LabelGS), a method that augments the Gaussian representation with object label.LabelGS introduces cross-view consistent semantic masks for 3D Gaussians and employs a novel Occlusion Analysis Model to avoid overfitting occlusion during optimization, Main Gaussian Labeling model to lift 2D semantic prior to 3D Gaussian and Gaussian Projection Filter to avoid Gaussian label conflict. Our approach achieves effective decoupling of Gaussian representations and refines the 3DGS optimization process through a random region sampling strategy, significantly improving efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LabelGS outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods, including Feature-3DGS, in the 3D scene segmentation task. Notably, LabelGS achieves a remarkable 22X speedup in training compared to Feature-3DGS, at a resolution of 1440X1080. Our code will be at https://github.com/garrisonz/LabelGS.
Mentor3AD: Feature Reconstruction-based 3D Anomaly Detection via Multi-modality Mentor Learning
May 27, 2025Abstract:Multimodal feature reconstruction is a promising approach for 3D anomaly detection, leveraging the complementary information from dual modalities. We further advance this paradigm by utilizing multi-modal mentor learning, which fuses intermediate features to further distinguish normal from feature differences. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method called Mentor3AD, which utilizes multi-modal mentor learning. By leveraging the shared features of different modalities, Mentor3AD can extract more effective features and guide feature reconstruction, ultimately improving detection performance. Specifically, Mentor3AD includes a Mentor of Fusion Module (MFM) that merges features extracted from RGB and 3D modalities to create a mentor feature. Additionally, we have designed a Mentor of Guidance Module (MGM) to facilitate cross-modal reconstruction, supported by the mentor feature. Lastly, we introduce a Voting Module (VM) to more accurately generate the final anomaly score. Extensive comparative and ablation studies on MVTec 3D-AD and Eyecandies have verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Examining the Source of Defects from a Mechanical Perspective for 3D Anomaly Detection
May 09, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we go beyond identifying anomalies only in structural terms and think about better anomaly detection motivated by anomaly causes. Most anomalies are regarded as the result of unpredictable defective forces from internal and external sources, and their opposite forces are sought to correct the anomalies. We introduced a Mechanics Complementary framework for 3D anomaly detection (MC4AD) to generate internal and external Corrective forces for each point. A Diverse Anomaly-Generation (DA-Gen) module is first proposed to simulate various anomalies. Then, we present a Corrective Force Prediction Network (CFP-Net) with complementary representations for point-level representation to simulate the different contributions of internal and external corrective forces. A combined loss was proposed, including a new symmetric loss and an overall loss, to constrain the corrective forces properly. As a highlight, we consider 3D anomaly detection in industry more comprehensively, creating a hierarchical quality control strategy based on a three-way decision and contributing a dataset named Anomaly-IntraVariance with intraclass variance to evaluate the model. On the proposed and existing five datasets, we obtained nine state-of-the-art performers with the minimum parameters and the fastest inference speed. The source is available at https://github.com/hzzzzzhappy/MC4AD
MC3D-AD: A Unified Geometry-aware Reconstruction Model for Multi-category 3D Anomaly Detection
May 04, 2025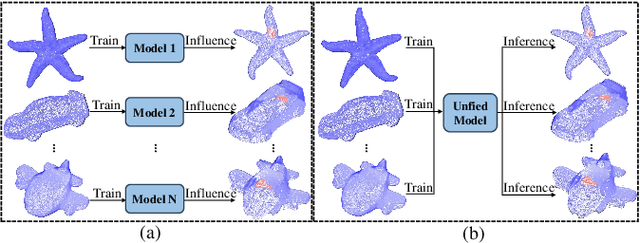
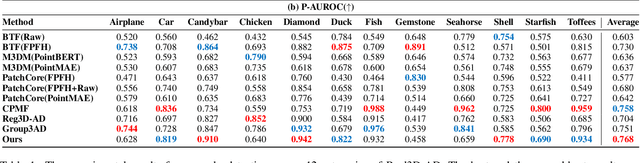
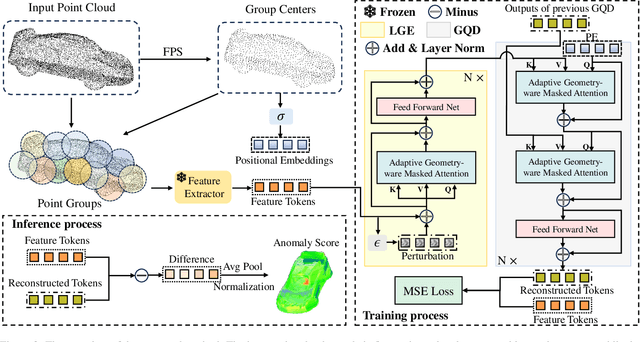
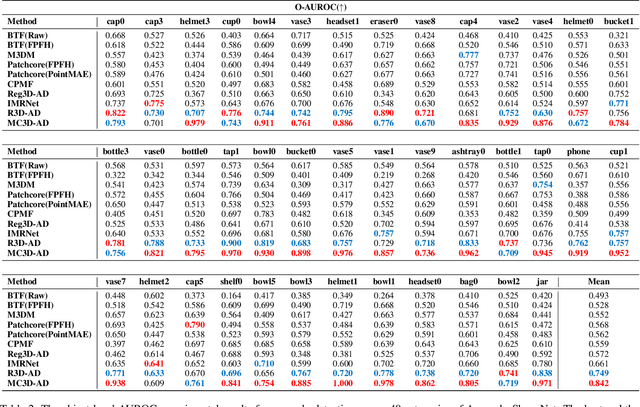
Abstract:3D Anomaly Detection (AD) is a promising means of controlling the quality of manufactured products. However, existing methods typically require carefully training a task-specific model for each category independently, leading to high cost, low efficiency, and weak generalization. Therefore, this paper presents a novel unified model for Multi-Category 3D Anomaly Detection (MC3D-AD) that aims to utilize both local and global geometry-aware information to reconstruct normal representations of all categories. First, to learn robust and generalized features of different categories, we propose an adaptive geometry-aware masked attention module that extracts geometry variation information to guide mask attention. Then, we introduce a local geometry-aware encoder reinforced by the improved mask attention to encode group-level feature tokens. Finally, we design a global query decoder that utilizes point cloud position embeddings to improve the decoding process and reconstruction ability. This leads to local and global geometry-aware reconstructed feature tokens for the AD task. MC3D-AD is evaluated on two publicly available Real3D-AD and Anomaly-ShapeNet datasets, and exhibits significant superiority over current state-of-the-art single-category methods, achieving 3.1\% and 9.3\% improvement in object-level AUROC over Real3D-AD and Anomaly-ShapeNet, respectively. The source code will be released upon acceptance.
Fence Theorem: Towards Dual-Objective Semantic-Structure Isolation in Preprocessing Phase for 3D Anomaly Detection
Mar 04, 2025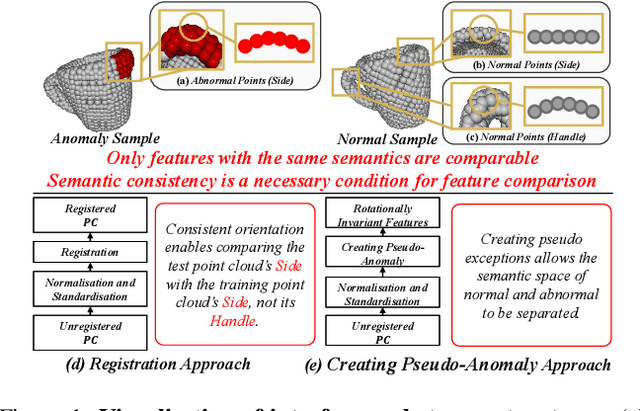
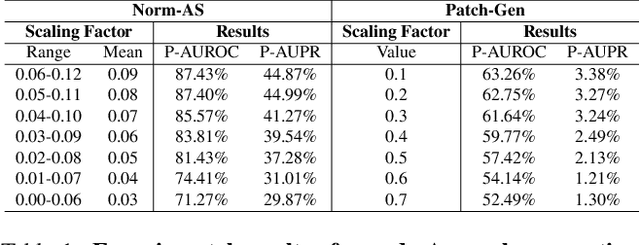
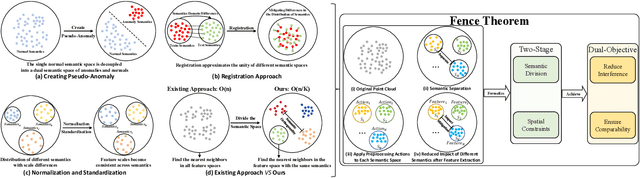

Abstract:3D anomaly detection (AD) is prominent but difficult due to lacking a unified theoretical foundation for preprocessing design. We establish the Fence Theorem, formalizing preprocessing as a dual-objective semantic isolator: (1) mitigating cross-semantic interference to the greatest extent feasible and (2) confining anomaly judgments to aligned semantic spaces wherever viable, thereby establishing intra-semantic comparability. Any preprocessing approach achieves this goal through a two-stage process of Emantic-Division and Spatial-Constraints stage. Through systematic deconstruction, we theoretically and experimentally subsume existing preprocessing methods under this theorem via tripartite evidence: qualitative analyses, quantitative studies, and mathematical proofs. Guided by the Fence Theorem, we implement Patch3D, consisting of Patch-Cutting and Patch-Matching modules, to segment semantic spaces and consolidate similar ones while independently modeling normal features within each space. Experiments on Anomaly-ShapeNet and Real3D-AD with different settings demonstrate that progressively finer-grained semantic alignment in preprocessing directly enhances point-level AD accuracy, providing inverse validation of the theorem's causal logic.
Learning with Open-world Noisy Data via Class-independent Margin in Dual Representation Space
Jan 19, 2025



Abstract:Learning with Noisy Labels (LNL) aims to improve the model generalization when facing data with noisy labels, and existing methods generally assume that noisy labels come from known classes, called closed-set noise. However, in real-world scenarios, noisy labels from similar unknown classes, i.e., open-set noise, may occur during the training and inference stage. Such open-world noisy labels may significantly impact the performance of LNL methods. In this study, we propose a novel dual-space joint learning method to robustly handle the open-world noise. To mitigate model overfitting on closed-set and open-set noises, a dual representation space is constructed by two networks. One is a projection network that learns shared representations in the prototype space, while the other is a One-Vs-All (OVA) network that makes predictions using unique semantic representations in the class-independent space. Then, bi-level contrastive learning and consistency regularization are introduced in two spaces to enhance the detection capability for data with unknown classes. To benefit from the memorization effects across different types of samples, class-independent margin criteria are designed for sample identification, which selects clean samples, weights closed-set noise, and filters open-set noise effectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and achieves an average accuracy improvement of 4.55\% and an AUROC improvement of 6.17\% on CIFAR80N.
DEGSTalk: Decomposed Per-Embedding Gaussian Fields for Hair-Preserving Talking Face Synthesis
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Accurately synthesizing talking face videos and capturing fine facial features for individuals with long hair presents a significant challenge. To tackle these challenges in existing methods, we propose a decomposed per-embedding Gaussian fields (DEGSTalk), a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)-based talking face synthesis method for generating realistic talking faces with long hairs. Our DEGSTalk employs Deformable Pre-Embedding Gaussian Fields, which dynamically adjust pre-embedding Gaussian primitives using implicit expression coefficients. This enables precise capture of dynamic facial regions and subtle expressions. Additionally, we propose a Dynamic Hair-Preserving Portrait Rendering technique to enhance the realism of long hair motions in the synthesized videos. Results show that DEGSTalk achieves improved realism and synthesis quality compared to existing approaches, particularly in handling complex facial dynamics and hair preservation. Our code will be publicly available at https://github.com/CVI-SZU/DEGSTalk.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge