Jiachen Liu
Sci-Reasoning: A Dataset Decoding AI Innovation Patterns
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:While AI innovation accelerates rapidly, the intellectual process behind breakthroughs -- how researchers identify gaps, synthesize prior work, and generate insights -- remains poorly understood. The lack of structured data on scientific reasoning hinders systematic analysis and development of AI research agents. We introduce Sci-Reasoning, the first dataset capturing the intellectual synthesis behind high-quality AI research. Using community-validated quality signals and an LLM-accelerated, human-verified pipeline, we trace Oral and Spotlight papers across NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR (2023-2025) to its key predecessors, articulating specific reasoning links in a structured format. Our analysis identifies 15 distinct thinking patterns, with three dominant strategies accounting for 52.7%: Gap-Driven Reframing (24.2%), Cross-Domain Synthesis (18.0%), and Representation Shift (10.5%). The most powerful innovation recipes combine multiple patterns: Gap-Driven Reframing + Representation Shift, Cross-Domain Synthesis + Representation Shift, and Gap-Driven Reframing + Cross-Domain Synthesis. This dataset enables quantitative studies of scientific progress and provides structured reasoning trajectories for training the next generation AI research agents.
M-SEVIQ: A Multi-band Stereo Event Visual-Inertial Quadruped-based Dataset for Perception under Rapid Motion and Challenging Illumination
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Agile locomotion in legged robots poses significant challenges for visual perception. Traditional frame-based cameras often fail in these scenarios for producing blurred images, particularly under low-light conditions. In contrast, event cameras capture changes in brightness asynchronously, offering low latency, high temporal resolution, and high dynamic range. These advantages make them suitable for robust perception during rapid motion and under challenging illumination. However, existing event camera datasets exhibit limitations in stereo configurations and multi-band sensing domains under various illumination conditions. To address this gap, we present M-SEVIQ, a multi-band stereo event visual and inertial quadruped dataset collected using a Unitree Go2 equipped with stereo event cameras, a frame-based camera, an inertial measurement unit (IMU), and joint encoders. This dataset contains more than 30 real-world sequences captured across different velocity levels, illumination wavelengths, and lighting conditions. In addition, comprehensive calibration data, including intrinsic, extrinsic, and temporal alignments, are provided to facilitate accurate sensor fusion and benchmarking. Our M-SEVIQ can be used to support research in agile robot perception, sensor fusion, semantic segmentation and multi-modal vision in challenging environments.
EXP-Bench: Can AI Conduct AI Research Experiments?
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Automating AI research holds immense potential for accelerating scientific progress, yet current AI agents struggle with the complexities of rigorous, end-to-end experimentation. We introduce EXP-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to systematically evaluate AI agents on complete research experiments sourced from influential AI publications. Given a research question and incomplete starter code, EXP-Bench challenges AI agents to formulate hypotheses, design and implement experimental procedures, execute them, and analyze results. To enable the creation of such intricate and authentic tasks with high-fidelity, we design a semi-autonomous pipeline to extract and structure crucial experimental details from these research papers and their associated open-source code. With the pipeline, EXP-Bench curated 461 AI research tasks from 51 top-tier AI research papers. Evaluations of leading LLM-based agents, such as OpenHands and IterativeAgent on EXP-Bench demonstrate partial capabilities: while scores on individual experimental aspects such as design or implementation correctness occasionally reach 20-35%, the success rate for complete, executable experiments was a mere 0.5%. By identifying these bottlenecks and providing realistic step-by-step experiment procedures, EXP-Bench serves as a vital tool for future AI agents to improve their ability to conduct AI research experiments. EXP-Bench is open-sourced at https://github.com/Just-Curieous/Curie/tree/main/benchmark/exp_bench.
The ML.ENERGY Benchmark: Toward Automated Inference Energy Measurement and Optimization
May 09, 2025Abstract:As the adoption of Generative AI in real-world services grow explosively, energy has emerged as a critical bottleneck resource. However, energy remains a metric that is often overlooked, under-explored, or poorly understood in the context of building ML systems. We present the ML.ENERGY Benchmark, a benchmark suite and tool for measuring inference energy consumption under realistic service environments, and the corresponding ML.ENERGY Leaderboard, which have served as a valuable resource for those hoping to understand and optimize the energy consumption of their generative AI services. In this paper, we explain four key design principles for benchmarking ML energy we have acquired over time, and then describe how they are implemented in the ML.ENERGY Benchmark. We then highlight results from the latest iteration of the benchmark, including energy measurements of 40 widely used model architectures across 6 different tasks, case studies of how ML design choices impact energy consumption, and how automated optimization recommendations can lead to significant (sometimes more than 40%) energy savings without changing what is being computed by the model. The ML.ENERGY Benchmark is open-source and can be easily extended to various customized models and application scenarios.
Evaluation Framework for AI Systems in "the Wild"
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) models have become vital across industries, yet current evaluation methods have not adapted to their widespread use. Traditional evaluations often rely on benchmarks and fixed datasets, frequently failing to reflect real-world performance, which creates a gap between lab-tested outcomes and practical applications. This white paper proposes a comprehensive framework for how we should evaluate real-world GenAI systems, emphasizing diverse, evolving inputs and holistic, dynamic, and ongoing assessment approaches. The paper offers guidance for practitioners on how to design evaluation methods that accurately reflect real-time capabilities, and provides policymakers with recommendations for crafting GenAI policies focused on societal impacts, rather than fixed performance numbers or parameter sizes. We advocate for holistic frameworks that integrate performance, fairness, and ethics and the use of continuous, outcome-oriented methods that combine human and automated assessments while also being transparent to foster trust among stakeholders. Implementing these strategies ensures GenAI models are not only technically proficient but also ethically responsible and impactful.
Computer-Aided Layout Generation for Building Design: A Review
Apr 13, 2025
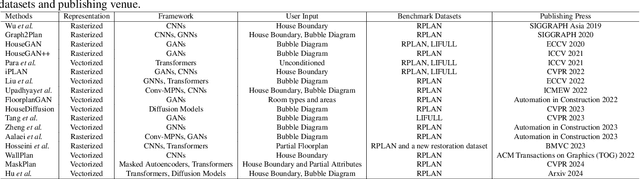
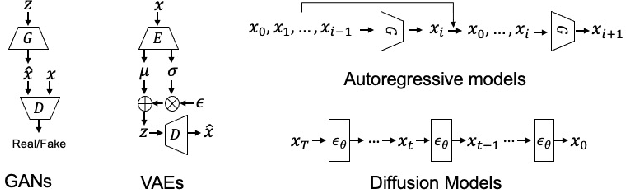
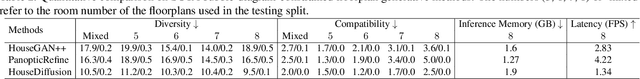
Abstract:Generating realistic building layouts for automatic building design has been studied in both the computer vision and architecture domains. Traditional approaches from the architecture domain, which are based on optimization techniques or heuristic design guidelines, can synthesize desirable layouts, but usually require post-processing and involve human interaction in the design pipeline, making them costly and timeconsuming. The advent of deep generative models has significantly improved the fidelity and diversity of the generated architecture layouts, reducing the workload by designers and making the process much more efficient. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive review of three major research topics of architecture layout design and generation: floorplan layout generation, scene layout synthesis, and generation of some other formats of building layouts. For each topic, we present an overview of the leading paradigms, categorized either by research domains (architecture or machine learning) or by user input conditions or constraints. We then introduce the commonly-adopted benchmark datasets that are used to verify the effectiveness of the methods, as well as the corresponding evaluation metrics. Finally, we identify the well-solved problems and limitations of existing approaches, then propose new perspectives as promising directions for future research in this important research area. A project associated with this survey to maintain the resources is available at awesome-building-layout-generation.
Curie: Toward Rigorous and Automated Scientific Experimentation with AI Agents
Feb 26, 2025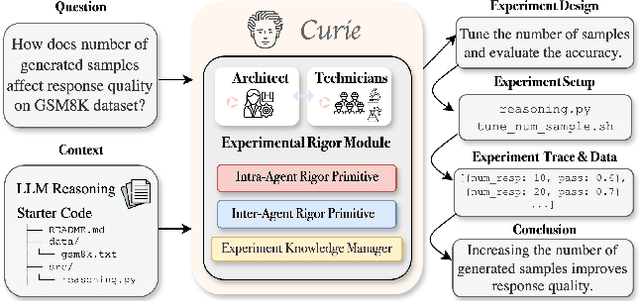
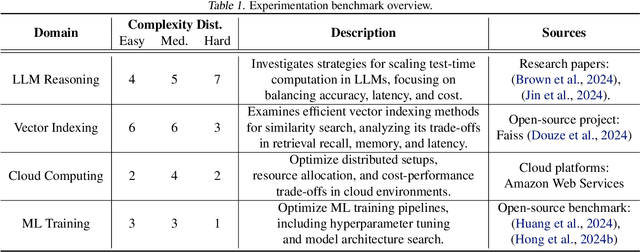
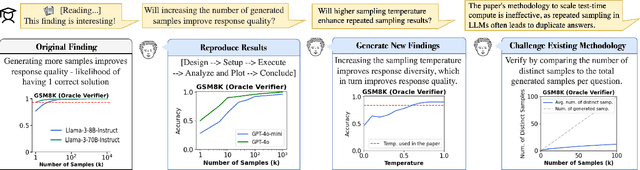
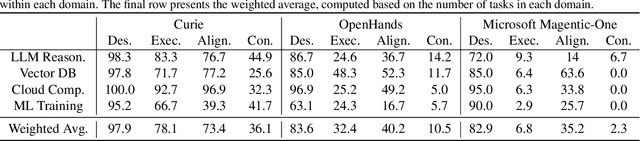
Abstract:Scientific experimentation, a cornerstone of human progress, demands rigor in reliability, methodical control, and interpretability to yield meaningful results. Despite the growing capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in automating different aspects of the scientific process, automating rigorous experimentation remains a significant challenge. To address this gap, we propose Curie, an AI agent framework designed to embed rigor into the experimentation process through three key components: an intra-agent rigor module to enhance reliability, an inter-agent rigor module to maintain methodical control, and an experiment knowledge module to enhance interpretability. To evaluate Curie, we design a novel experimental benchmark composed of 46 questions across four computer science domains, derived from influential research papers, and widely adopted open-source projects. Compared to the strongest baseline tested, we achieve a 3.4$\times$ improvement in correctly answering experimental questions. Curie is open-sourced at https://github.com/Just-Curieous/Curie.
MonoPlane: Exploiting Monocular Geometric Cues for Generalizable 3D Plane Reconstruction
Nov 02, 2024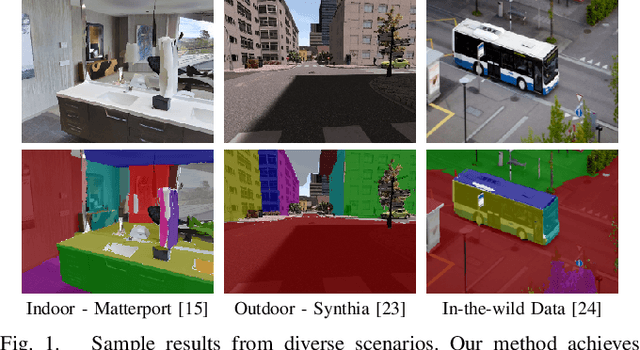
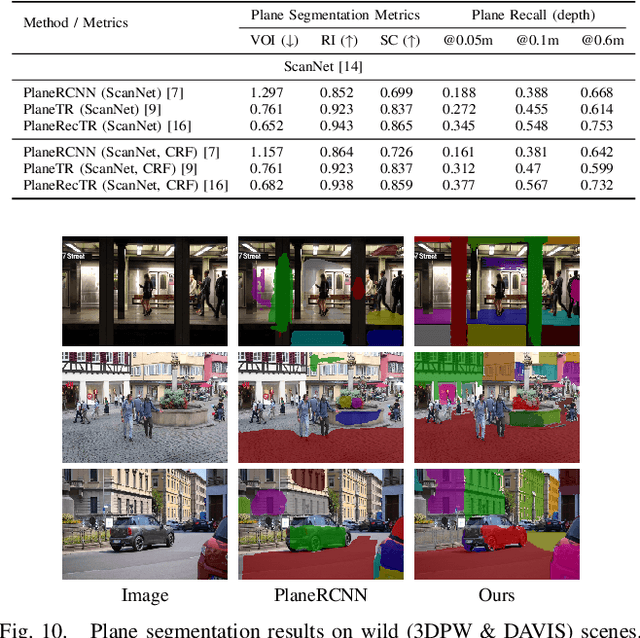

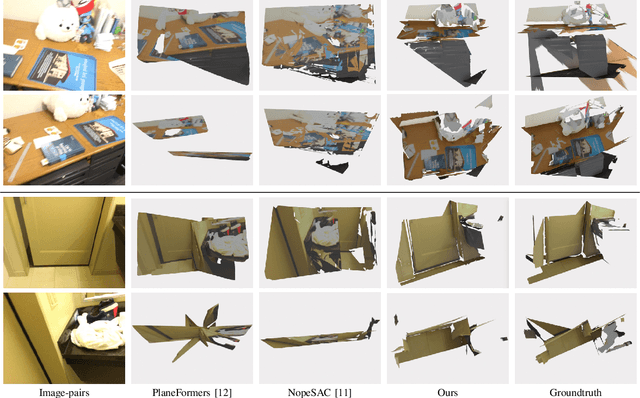
Abstract:This paper presents a generalizable 3D plane detection and reconstruction framework named MonoPlane. Unlike previous robust estimator-based works (which require multiple images or RGB-D input) and learning-based works (which suffer from domain shift), MonoPlane combines the best of two worlds and establishes a plane reconstruction pipeline based on monocular geometric cues, resulting in accurate, robust and scalable 3D plane detection and reconstruction in the wild. Specifically, we first leverage large-scale pre-trained neural networks to obtain the depth and surface normals from a single image. These monocular geometric cues are then incorporated into a proximity-guided RANSAC framework to sequentially fit each plane instance. We exploit effective 3D point proximity and model such proximity via a graph within RANSAC to guide the plane fitting from noisy monocular depths, followed by image-level multi-plane joint optimization to improve the consistency among all plane instances. We further design a simple but effective pipeline to extend this single-view solution to sparse-view 3D plane reconstruction. Extensive experiments on a list of datasets demonstrate our superior zero-shot generalizability over baselines, achieving state-of-the-art plane reconstruction performance in a transferring setting. Our code is available at https://github.com/thuzhaowang/MonoPlane .
HairDiffusion: Vivid Multi-Colored Hair Editing via Latent Diffusion
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Hair editing is a critical image synthesis task that aims to edit hair color and hairstyle using text descriptions or reference images, while preserving irrelevant attributes (e.g., identity, background, cloth). Many existing methods are based on StyleGAN to address this task. However, due to the limited spatial distribution of StyleGAN, it struggles with multiple hair color editing and facial preservation. Considering the advancements in diffusion models, we utilize Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) for hairstyle editing. Our approach introduces Multi-stage Hairstyle Blend (MHB), effectively separating control of hair color and hairstyle in diffusion latent space. Additionally, we train a warping module to align the hair color with the target region. To further enhance multi-color hairstyle editing, we fine-tuned a CLIP model using a multi-color hairstyle dataset. Our method not only tackles the complexity of multi-color hairstyles but also addresses the challenge of preserving original colors during diffusion editing. Extensive experiments showcase the superiority of our method in editing multi-color hairstyles while preserving facial attributes given textual descriptions and reference images.
Empowering Backbone Models for Visual Text Generation with Input Granularity Control and Glyph-Aware Training
Oct 06, 2024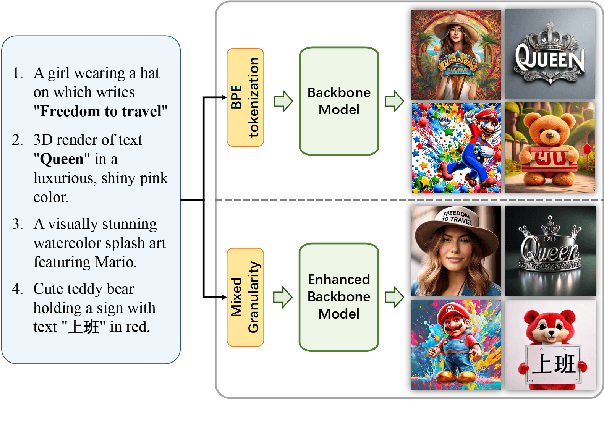
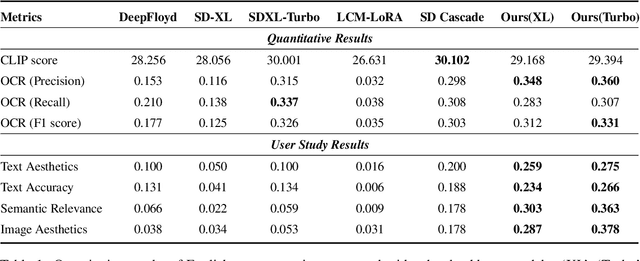
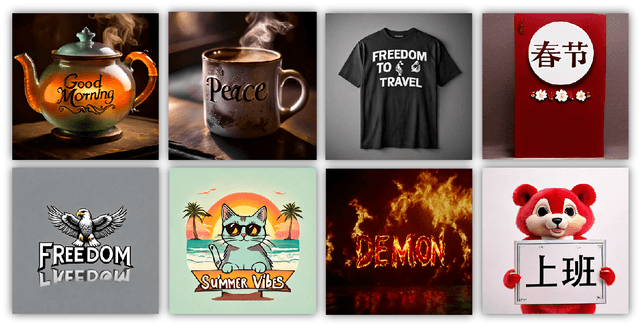

Abstract:Diffusion-based text-to-image models have demonstrated impressive achievements in diversity and aesthetics but struggle to generate images with legible visual texts. Existing backbone models have limitations such as misspelling, failing to generate texts, and lack of support for Chinese text, but their development shows promising potential. In this paper, we propose a series of methods, aiming to empower backbone models to generate visual texts in English and Chinese. We first conduct a preliminary study revealing that Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) tokenization and the insufficient learning of cross-attention modules restrict the performance of the backbone models. Based on these observations, we make the following improvements: (1) We design a mixed granularity input strategy to provide more suitable text representations; (2) We propose to augment the conventional training objective with three glyph-aware training losses, which enhance the learning of cross-attention modules and encourage the model to focus on visual texts. Through experiments, we demonstrate that our methods can effectively empower backbone models to generate semantic relevant, aesthetically appealing, and accurate visual text images, while maintaining their fundamental image generation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge