Yiming Qiu
A Simple and Effective Framework for Symmetric Consistent Indexing in Large-Scale Dense Retrieval
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Dense retrieval has become the industry standard in large-scale information retrieval systems due to its high efficiency and competitive accuracy. Its core relies on a coarse-to-fine hierarchical architecture that enables rapid candidate selection and precise semantic matching, achieving millisecond-level response over billion-scale corpora. This capability makes it essential not only in traditional search and recommendation scenarios but also in the emerging paradigm of generative recommendation driven by large language models, where semantic IDs-themselves a form of coarse-to-fine representation-play a foundational role. However, the widely adopted dual-tower encoding architecture introduces inherent challenges, primarily representational space misalignment and retrieval index inconsistency, which degrade matching accuracy, retrieval stability, and performance on long-tail queries. These issues are further magnified in semantic ID generation, ultimately limiting the performance ceiling of downstream generative models. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a simple and effective framework named SCI comprising two synergistic modules: a symmetric representation alignment module that employs an innovative input-swapping mechanism to unify the dual-tower representation space without adding parameters, and an consistent indexing with dual-tower synergy module that redesigns retrieval paths using a dual-view indexing strategy to maintain consistency from training to inference. The framework is systematic, lightweight, and engineering-friendly, requiring minimal overhead while fully supporting billion-scale deployment. We provide theoretical guarantees for our approach, with its effectiveness validated by results across public datasets and real-world e-commerce datasets.
Cloud Infrastructure Management in the Age of AI Agents
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Cloud infrastructure is the cornerstone of the modern IT industry. However, managing this infrastructure effectively requires considerable manual effort from the DevOps engineering team. We make a case for developing AI agents powered by large language models (LLMs) to automate cloud infrastructure management tasks. In a preliminary study, we investigate the potential for AI agents to use different cloud/user interfaces such as software development kits (SDK), command line interfaces (CLI), Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) platforms, and web portals. We report takeaways on their effectiveness on different management tasks, and identify research challenges and potential solutions.
EXP-Bench: Can AI Conduct AI Research Experiments?
May 30, 2025



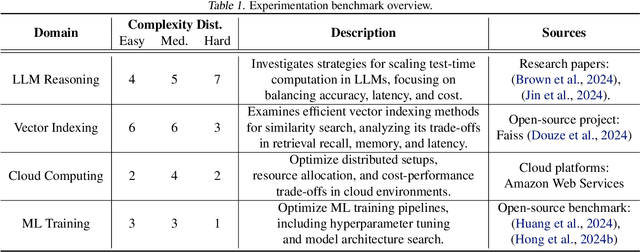
Abstract:Automating AI research holds immense potential for accelerating scientific progress, yet current AI agents struggle with the complexities of rigorous, end-to-end experimentation. We introduce EXP-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to systematically evaluate AI agents on complete research experiments sourced from influential AI publications. Given a research question and incomplete starter code, EXP-Bench challenges AI agents to formulate hypotheses, design and implement experimental procedures, execute them, and analyze results. To enable the creation of such intricate and authentic tasks with high-fidelity, we design a semi-autonomous pipeline to extract and structure crucial experimental details from these research papers and their associated open-source code. With the pipeline, EXP-Bench curated 461 AI research tasks from 51 top-tier AI research papers. Evaluations of leading LLM-based agents, such as OpenHands and IterativeAgent on EXP-Bench demonstrate partial capabilities: while scores on individual experimental aspects such as design or implementation correctness occasionally reach 20-35%, the success rate for complete, executable experiments was a mere 0.5%. By identifying these bottlenecks and providing realistic step-by-step experiment procedures, EXP-Bench serves as a vital tool for future AI agents to improve their ability to conduct AI research experiments. EXP-Bench is open-sourced at https://github.com/Just-Curieous/Curie/tree/main/benchmark/exp_bench.
Curie: Toward Rigorous and Automated Scientific Experimentation with AI Agents
Feb 26, 2025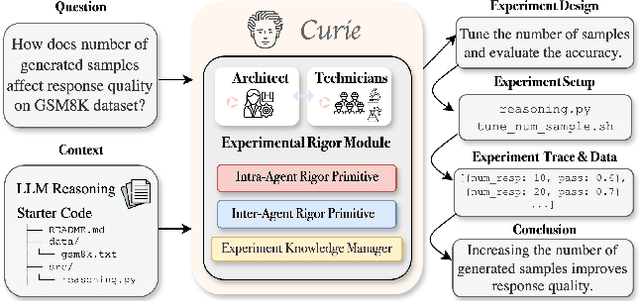
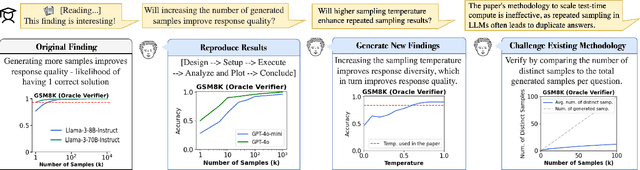
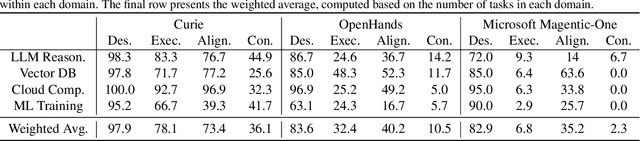
Abstract:Scientific experimentation, a cornerstone of human progress, demands rigor in reliability, methodical control, and interpretability to yield meaningful results. Despite the growing capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in automating different aspects of the scientific process, automating rigorous experimentation remains a significant challenge. To address this gap, we propose Curie, an AI agent framework designed to embed rigor into the experimentation process through three key components: an intra-agent rigor module to enhance reliability, an inter-agent rigor module to maintain methodical control, and an experiment knowledge module to enhance interpretability. To evaluate Curie, we design a novel experimental benchmark composed of 46 questions across four computer science domains, derived from influential research papers, and widely adopted open-source projects. Compared to the strongest baseline tested, we achieve a 3.4$\times$ improvement in correctly answering experimental questions. Curie is open-sourced at https://github.com/Just-Curieous/Curie.
Generative Retrieval with Preference Optimization for E-commerce Search
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:Generative retrieval introduces a groundbreaking paradigm to document retrieval by directly generating the identifier of a pertinent document in response to a specific query. This paradigm has demonstrated considerable benefits and potential, particularly in representation and generalization capabilities, within the context of large language models. However, it faces significant challenges in E-commerce search scenarios, including the complexity of generating detailed item titles from brief queries, the presence of noise in item titles with weak language order, issues with long-tail queries, and the interpretability of results. To address these challenges, we have developed an innovative framework for E-commerce search, called generative retrieval with preference optimization. This framework is designed to effectively learn and align an autoregressive model with target data, subsequently generating the final item through constraint-based beam search. By employing multi-span identifiers to represent raw item titles and transforming the task of generating titles from queries into the task of generating multi-span identifiers from queries, we aim to simplify the generation process. The framework further aligns with human preferences using click data and employs a constrained search method to identify key spans for retrieving the final item, thereby enhancing result interpretability. Our extensive experiments show that this framework achieves competitive performance on a real-world dataset, and online A/B tests demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness in improving conversion gains.
Optimizing E-commerce Search: Toward a Generalizable and Rank-Consistent Pre-Ranking Model
May 09, 2024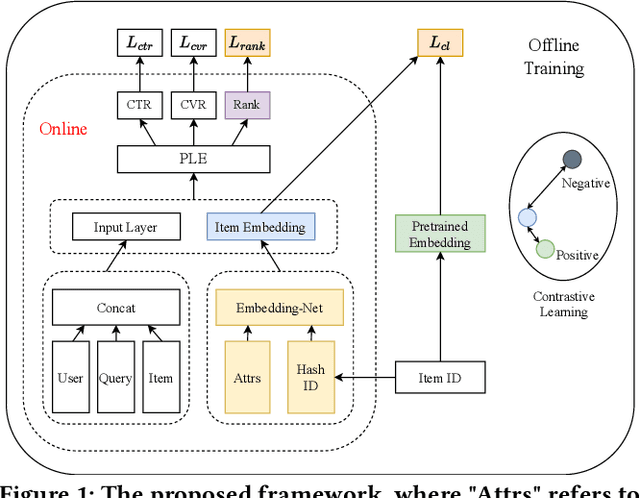
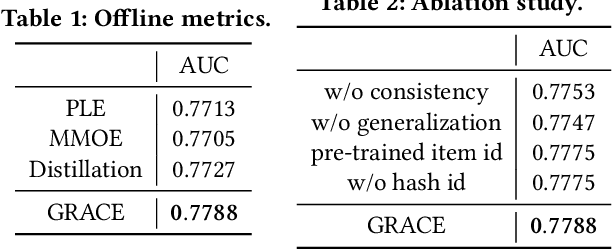
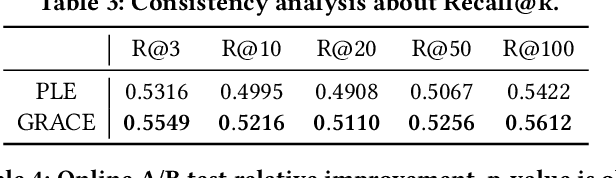
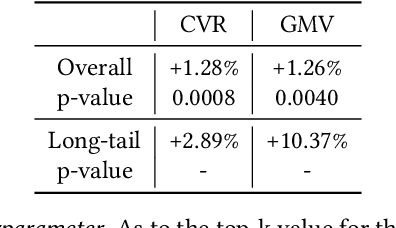
Abstract:In large e-commerce platforms, search systems are typically composed of a series of modules, including recall, pre-ranking, and ranking phases. The pre-ranking phase, serving as a lightweight module, is crucial for filtering out the bulk of products in advance for the downstream ranking module. Industrial efforts on optimizing the pre-ranking model have predominantly focused on enhancing ranking consistency, model structure, and generalization towards long-tail items. Beyond these optimizations, meeting the system performance requirements presents a significant challenge. Contrasting with existing industry works, we propose a novel method: a Generalizable and RAnk-ConsistEnt Pre-Ranking Model (GRACE), which achieves: 1) Ranking consistency by introducing multiple binary classification tasks that predict whether a product is within the top-k results as estimated by the ranking model, which facilitates the addition of learning objectives on common point-wise ranking models; 2) Generalizability through contrastive learning of representation for all products by pre-training on a subset of ranking product embeddings; 3) Ease of implementation in feature construction and online deployment. Our extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements in both offline metrics and online A/B test: a 0.75% increase in AUC and a 1.28% increase in CVR.
Differentiable Retrieval Augmentation via Generative Language Modeling for E-commerce Query Intent Classification
Aug 21, 2023Abstract:Retrieval augmentation, which enhances downstream models by a knowledge retriever and an external corpus instead of by merely increasing the number of model parameters, has been successfully applied to many natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as text classification, question answering and so on. However, existing methods that separately or asynchronously train the retriever and downstream model mainly due to the non-differentiability between the two parts, usually lead to degraded performance compared to end-to-end joint training. In this paper, we propose Differentiable Retrieval Augmentation via Generative lANguage modeling(Dragan), to address this problem by a novel differentiable reformulation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method on a challenging NLP task in e-commerce search, namely query intent classification. Both the experimental results and ablation study show that the proposed method significantly and reasonably improves the state-of-the-art baselines on both offline evaluation and online A/B test.
A Multi-Granularity Matching Attention Network for Query Intent Classification in E-commerce Retrieval
Mar 28, 2023



Abstract:Query intent classification, which aims at assisting customers to find desired products, has become an essential component of the e-commerce search. Existing query intent classification models either design more exquisite models to enhance the representation learning of queries or explore label-graph and multi-task to facilitate models to learn external information. However, these models cannot capture multi-granularity matching features from queries and categories, which makes them hard to mitigate the gap in the expression between informal queries and categories. This paper proposes a Multi-granularity Matching Attention Network (MMAN), which contains three modules: a self-matching module, a char-level matching module, and a semantic-level matching module to comprehensively extract features from the query and a query-category interaction matrix. In this way, the model can eliminate the difference in expression between queries and categories for query intent classification. We conduct extensive offline and online A/B experiments, and the results show that the MMAN significantly outperforms the strong baselines, which shows the superiority and effectiveness of MMAN. MMAN has been deployed in production and brings great commercial value for our company.
Pre-training Tasks for User Intent Detection and Embedding Retrieval in E-commerce Search
Aug 22, 2022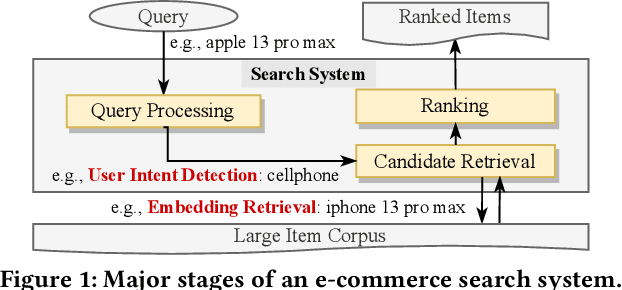

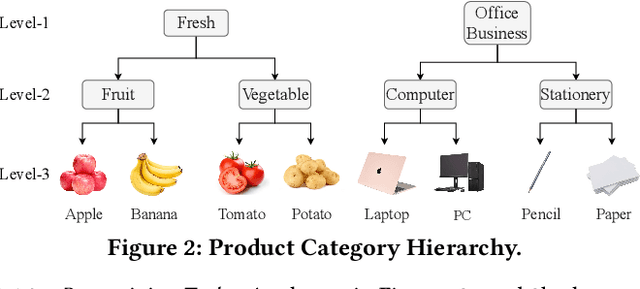
Abstract:BERT-style models pre-trained on the general corpus (e.g., Wikipedia) and fine-tuned on specific task corpus, have recently emerged as breakthrough techniques in many NLP tasks: question answering, text classification, sequence labeling and so on. However, this technique may not always work, especially for two scenarios: a corpus that contains very different text from the general corpus Wikipedia, or a task that learns embedding spacial distribution for a specific purpose (e.g., approximate nearest neighbor search). In this paper, to tackle the above two scenarios that we have encountered in an industrial e-commerce search system, we propose customized and novel pre-training tasks for two critical modules: user intent detection and semantic embedding retrieval. The customized pre-trained models after fine-tuning, being less than 10% of BERT-base's size in order to be feasible for cost-efficient CPU serving, significantly improve the other baseline models: 1) no pre-training model and 2) fine-tuned model from the official pre-trained BERT using general corpus, on both offline datasets and online system. We have open sourced our datasets for the sake of reproducibility and future works.
Givens Coordinate Descent Methods for Rotation Matrix Learning in Trainable Embedding Indexes
Mar 09, 2022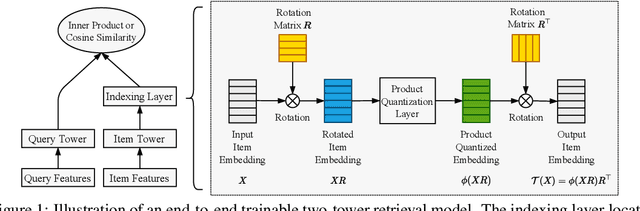
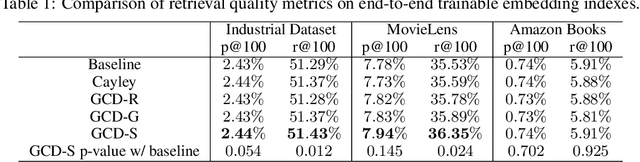
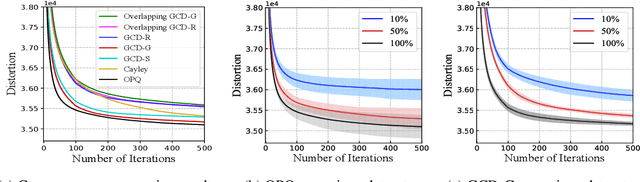
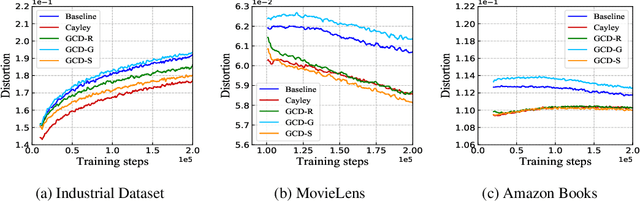
Abstract:Product quantization (PQ) coupled with a space rotation, is widely used in modern approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search systems to significantly compress the disk storage for embeddings and speed up the inner product computation. Existing rotation learning methods, however, minimize quantization distortion for fixed embeddings, which are not applicable to an end-to-end training scenario where embeddings are updated constantly. In this paper, based on geometric intuitions from Lie group theory, in particular the special orthogonal group $SO(n)$, we propose a family of block Givens coordinate descent algorithms to learn rotation matrix that are provably convergent on any convex objectives. Compared to the state-of-the-art SVD method, the Givens algorithms are much more parallelizable, reducing runtime by orders of magnitude on modern GPUs, and converge more stably according to experimental studies. They further improve upon vanilla product quantization significantly in an end-to-end training scenario.
* published in ICLR 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge