Huimu Wang
A Simple and Effective Framework for Symmetric Consistent Indexing in Large-Scale Dense Retrieval
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Dense retrieval has become the industry standard in large-scale information retrieval systems due to its high efficiency and competitive accuracy. Its core relies on a coarse-to-fine hierarchical architecture that enables rapid candidate selection and precise semantic matching, achieving millisecond-level response over billion-scale corpora. This capability makes it essential not only in traditional search and recommendation scenarios but also in the emerging paradigm of generative recommendation driven by large language models, where semantic IDs-themselves a form of coarse-to-fine representation-play a foundational role. However, the widely adopted dual-tower encoding architecture introduces inherent challenges, primarily representational space misalignment and retrieval index inconsistency, which degrade matching accuracy, retrieval stability, and performance on long-tail queries. These issues are further magnified in semantic ID generation, ultimately limiting the performance ceiling of downstream generative models. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a simple and effective framework named SCI comprising two synergistic modules: a symmetric representation alignment module that employs an innovative input-swapping mechanism to unify the dual-tower representation space without adding parameters, and an consistent indexing with dual-tower synergy module that redesigns retrieval paths using a dual-view indexing strategy to maintain consistency from training to inference. The framework is systematic, lightweight, and engineering-friendly, requiring minimal overhead while fully supporting billion-scale deployment. We provide theoretical guarantees for our approach, with its effectiveness validated by results across public datasets and real-world e-commerce datasets.
Stochastic Trajectory Prediction under Unstructured Constraints
Mar 18, 2025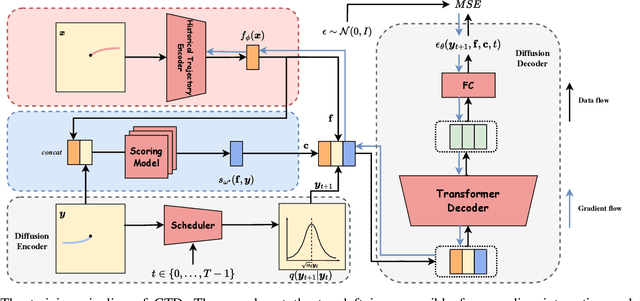
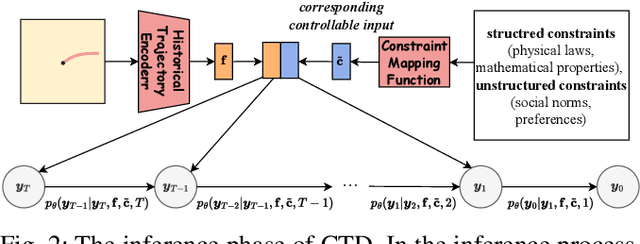
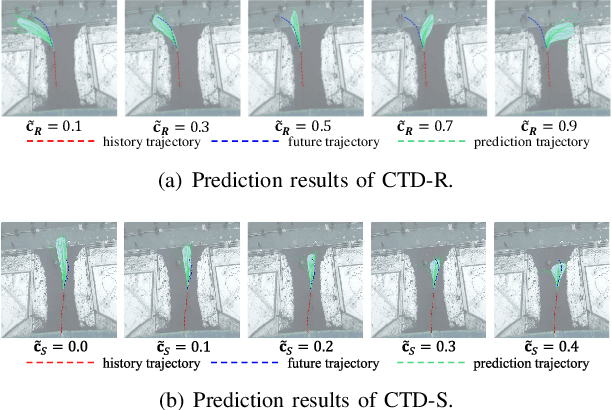
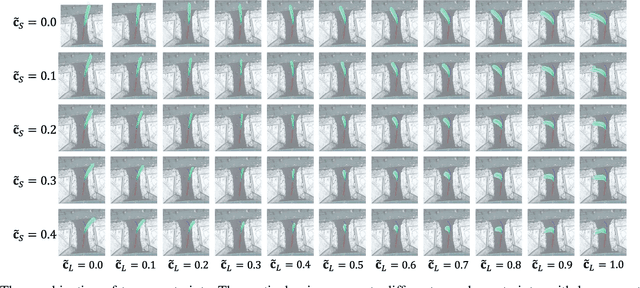
Abstract:Trajectory prediction facilitates effective planning and decision-making, while constrained trajectory prediction integrates regulation into prediction. Recent advances in constrained trajectory prediction focus on structured constraints by constructing optimization objectives. However, handling unstructured constraints is challenging due to the lack of differentiable formal definitions. To address this, we propose a novel method for constrained trajectory prediction using a conditional generative paradigm, named Controllable Trajectory Diffusion (CTD). The key idea is that any trajectory corresponds to a degree of conformity to a constraint. By quantifying this degree and treating it as a condition, a model can implicitly learn to predict trajectories under unstructured constraints. CTD employs a pre-trained scoring model to predict the degree of conformity (i.e., a score), and uses this score as a condition for a conditional diffusion model to generate trajectories. Experimental results demonstrate that CTD achieves high accuracy on the ETH/UCY and SDD benchmarks. Qualitative analysis confirms that CTD ensures adherence to unstructured constraints and can predict trajectories that satisfy combinatorial constraints.
OMoE: Diversifying Mixture of Low-Rank Adaptation by Orthogonal Finetuning
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Building mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture for Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is emerging as a potential direction in parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) for its modular design and remarkable performance. However, simply stacking the number of experts cannot guarantee significant improvement. In this work, we first conduct qualitative analysis to indicate that experts collapse to similar representations in vanilla MoE, limiting the capacity of modular design and computational efficiency. Ulteriorly, Our analysis reveals that the performance of previous MoE variants maybe limited by a lack of diversity among experts. Motivated by these findings, we propose Orthogonal Mixture-of-Experts (OMoE), a resource-efficient MoE variant that trains experts in an orthogonal manner to promote diversity. In OMoE, a Gram-Schmidt process is leveraged to enforce that the experts' representations lie within the Stiefel manifold. By applying orthogonal constraints directly to the architecture, OMoE keeps the learning objective unchanged, without compromising optimality. Our method is simple and alleviates memory bottlenecks, as it incurs minimal experts compared to vanilla MoE models. Experiments on diverse commonsense reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that OMoE can consistently achieve stable and efficient performance improvement when compared with the state-of-the-art methods while significantly reducing the number of required experts.
Breaking the Hourglass Phenomenon of Residual Quantization: Enhancing the Upper Bound of Generative Retrieval
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Generative retrieval (GR) has emerged as a transformative paradigm in search and recommender systems, leveraging numeric-based identifier representations to enhance efficiency and generalization. Notably, methods like TIGER employing Residual Quantization-based Semantic Identifiers (RQ-SID), have shown significant promise in e-commerce scenarios by effectively managing item IDs. However, a critical issue termed the "\textbf{Hourglass}" phenomenon, occurs in RQ-SID, where intermediate codebook tokens become overly concentrated, hindering the full utilization of generative retrieval methods. This paper analyses and addresses this problem by identifying data sparsity and long-tailed distribution as the primary causes. Through comprehensive experiments and detailed ablation studies, we analyze the impact of these factors on codebook utilization and data distribution. Our findings reveal that the "Hourglass" phenomenon substantially impacts the performance of RQ-SID in generative retrieval. We propose effective solutions to mitigate this issue, thereby significantly enhancing the effectiveness of generative retrieval in real-world E-commerce applications.
Generative Retrieval with Preference Optimization for E-commerce Search
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:Generative retrieval introduces a groundbreaking paradigm to document retrieval by directly generating the identifier of a pertinent document in response to a specific query. This paradigm has demonstrated considerable benefits and potential, particularly in representation and generalization capabilities, within the context of large language models. However, it faces significant challenges in E-commerce search scenarios, including the complexity of generating detailed item titles from brief queries, the presence of noise in item titles with weak language order, issues with long-tail queries, and the interpretability of results. To address these challenges, we have developed an innovative framework for E-commerce search, called generative retrieval with preference optimization. This framework is designed to effectively learn and align an autoregressive model with target data, subsequently generating the final item through constraint-based beam search. By employing multi-span identifiers to represent raw item titles and transforming the task of generating titles from queries into the task of generating multi-span identifiers from queries, we aim to simplify the generation process. The framework further aligns with human preferences using click data and employs a constrained search method to identify key spans for retrieving the final item, thereby enhancing result interpretability. Our extensive experiments show that this framework achieves competitive performance on a real-world dataset, and online A/B tests demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness in improving conversion gains.
MODRL-TA:A Multi-Objective Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Traffic Allocation in E-Commerce Search
Jul 22, 2024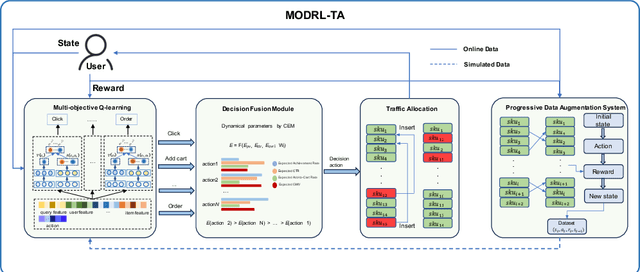
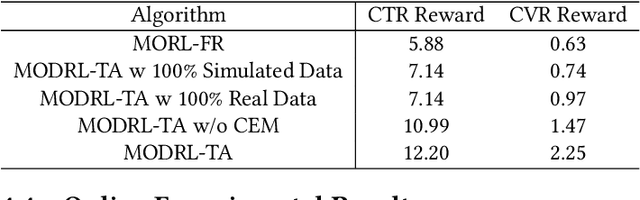
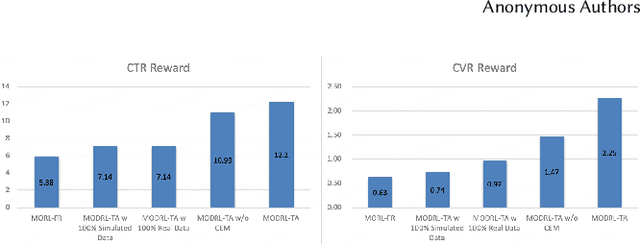
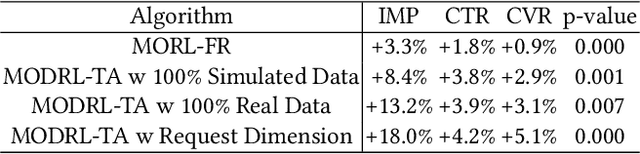
Abstract:Traffic allocation is a process of redistributing natural traffic to products by adjusting their positions in the post-search phase, aimed at effectively fostering merchant growth, precisely meeting customer demands, and ensuring the maximization of interests across various parties within e-commerce platforms. Existing methods based on learning to rank neglect the long-term value of traffic allocation, whereas approaches of reinforcement learning suffer from balancing multiple objectives and the difficulties of cold starts within realworld data environments. To address the aforementioned issues, this paper propose a multi-objective deep reinforcement learning framework consisting of multi-objective Q-learning (MOQ), a decision fusion algorithm (DFM) based on the cross-entropy method(CEM), and a progressive data augmentation system(PDA). Specifically. MOQ constructs ensemble RL models, each dedicated to an objective, such as click-through rate, conversion rate, etc. These models individually determine the position of items as actions, aiming to estimate the long-term value of multiple objectives from an individual perspective. Then we employ DFM to dynamically adjust weights among objectives to maximize long-term value, addressing temporal dynamics in objective preferences in e-commerce scenarios. Initially, PDA trained MOQ with simulated data from offline logs. As experiments progressed, it strategically integrated real user interaction data, ultimately replacing the simulated dataset to alleviate distributional shifts and the cold start problem. Experimental results on real-world online e-commerce systems demonstrate the significant improvements of MODRL-TA, and we have successfully deployed MODRL-TA on an e-commerce search platform.
A Preference-oriented Diversity Model Based on Mutual-information in Re-ranking for E-commerce Search
May 24, 2024Abstract:Re-ranking is a process of rearranging ranking list to more effectively meet user demands by accounting for the interrelationships between items. Existing methods predominantly enhance the precision of search results, often at the expense of diversity, leading to outcomes that may not fulfill the varied needs of users. Conversely, methods designed to promote diversity might compromise the precision of the results, failing to satisfy the users' requirements for accuracy. To alleviate the above problems, this paper proposes a Preference-oriented Diversity Model Based on Mutual-information (PODM-MI), which consider both accuracy and diversity in the re-ranking process. Specifically, PODM-MI adopts Multidimensional Gaussian distributions based on variational inference to capture users' diversity preferences with uncertainty. Then we maximize the mutual information between the diversity preferences of the users and the candidate items using the maximum variational inference lower bound to enhance their correlations. Subsequently, we derive a utility matrix based on the correlations, enabling the adaptive ranking of items in line with user preferences and establishing a balance between the aforementioned objectives. Experimental results on real-world online e-commerce systems demonstrate the significant improvements of PODM-MI, and we have successfully deployed PODM-MI on an e-commerce search platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge