Enqiang Xu
Advancing Re-Ranking with Multimodal Fusion and Target-Oriented Auxiliary Tasks in E-Commerce Search
Aug 11, 2024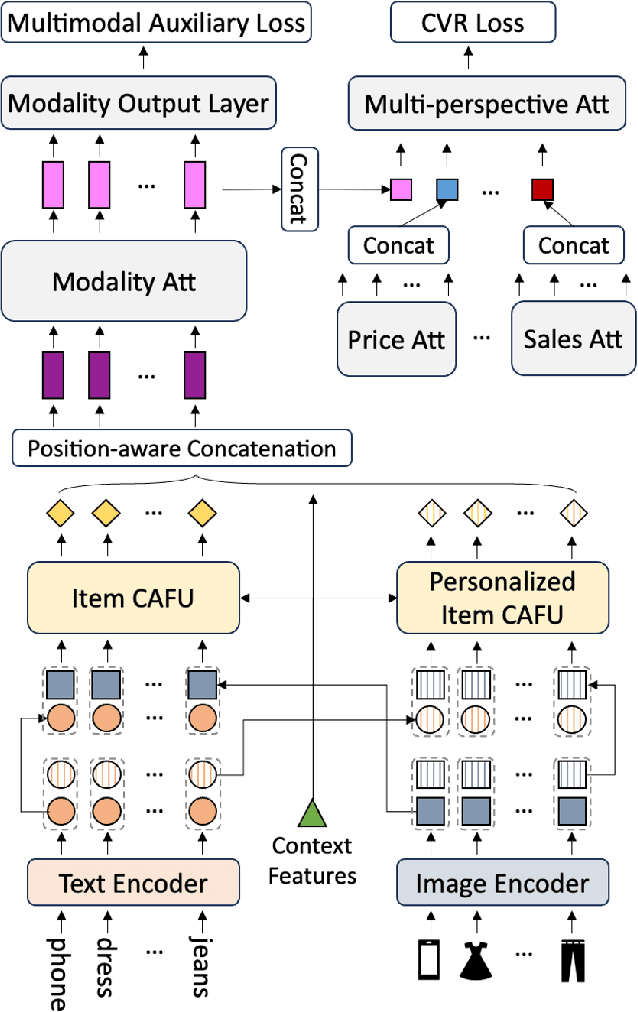
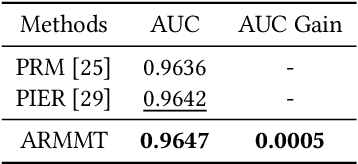

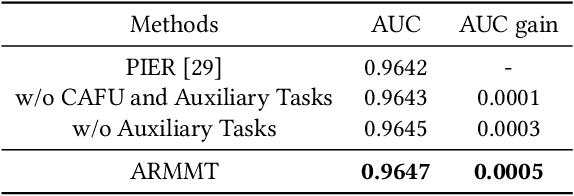
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of e-commerce, the effectiveness of search re-ranking models is crucial for enhancing user experience and driving conversion rates. Despite significant advancements in feature representation and model architecture, the integration of multimodal information remains underexplored. This study addresses this gap by investigating the computation and fusion of textual and visual information in the context of re-ranking. We propose \textbf{A}dvancing \textbf{R}e-Ranking with \textbf{M}ulti\textbf{m}odal Fusion and \textbf{T}arget-Oriented Auxiliary Tasks (ARMMT), which integrates an attention-based multimodal fusion technique and an auxiliary ranking-aligned task to enhance item representation and improve targeting capabilities. This method not only enriches the understanding of product attributes but also enables more precise and personalized recommendations. Experimental evaluations on JD.com's search platform demonstrate that ARMMT achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal information integration, evidenced by a 0.22\% increase in the Conversion Rate (CVR), significantly contributing to Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV). This pioneering approach has the potential to revolutionize e-commerce re-ranking, leading to elevated user satisfaction and business growth.
MODRL-TA:A Multi-Objective Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Traffic Allocation in E-Commerce Search
Jul 22, 2024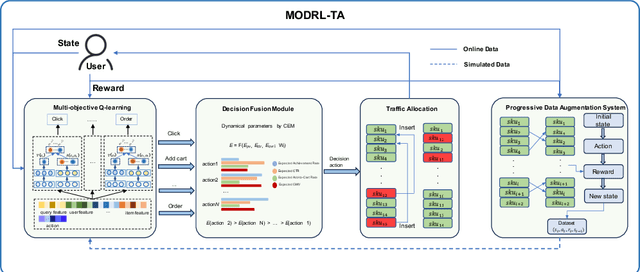
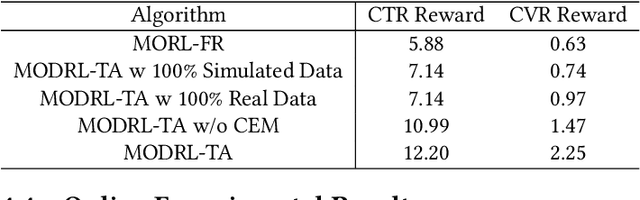
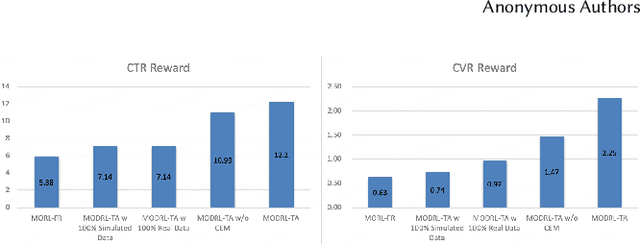
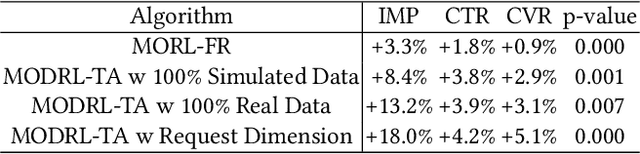
Abstract:Traffic allocation is a process of redistributing natural traffic to products by adjusting their positions in the post-search phase, aimed at effectively fostering merchant growth, precisely meeting customer demands, and ensuring the maximization of interests across various parties within e-commerce platforms. Existing methods based on learning to rank neglect the long-term value of traffic allocation, whereas approaches of reinforcement learning suffer from balancing multiple objectives and the difficulties of cold starts within realworld data environments. To address the aforementioned issues, this paper propose a multi-objective deep reinforcement learning framework consisting of multi-objective Q-learning (MOQ), a decision fusion algorithm (DFM) based on the cross-entropy method(CEM), and a progressive data augmentation system(PDA). Specifically. MOQ constructs ensemble RL models, each dedicated to an objective, such as click-through rate, conversion rate, etc. These models individually determine the position of items as actions, aiming to estimate the long-term value of multiple objectives from an individual perspective. Then we employ DFM to dynamically adjust weights among objectives to maximize long-term value, addressing temporal dynamics in objective preferences in e-commerce scenarios. Initially, PDA trained MOQ with simulated data from offline logs. As experiments progressed, it strategically integrated real user interaction data, ultimately replacing the simulated dataset to alleviate distributional shifts and the cold start problem. Experimental results on real-world online e-commerce systems demonstrate the significant improvements of MODRL-TA, and we have successfully deployed MODRL-TA on an e-commerce search platform.
Optimizing E-commerce Search: Toward a Generalizable and Rank-Consistent Pre-Ranking Model
May 09, 2024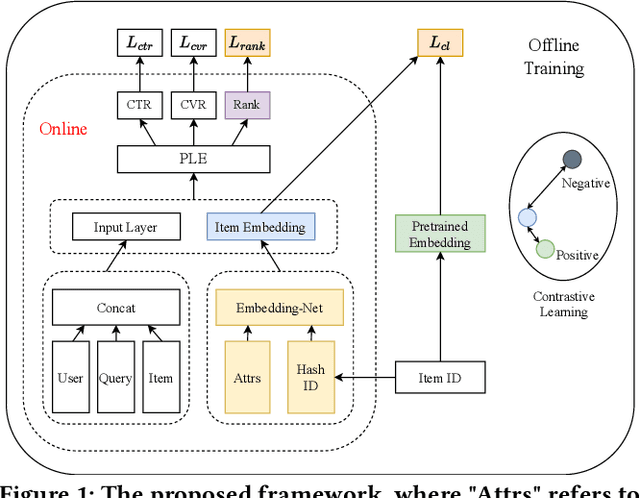
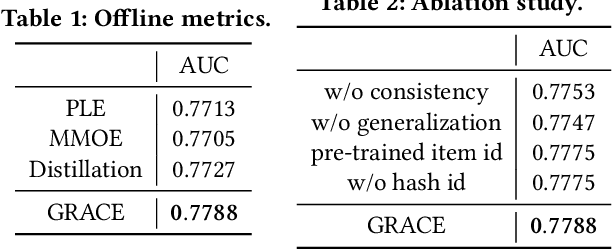
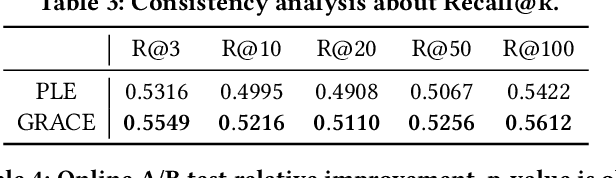
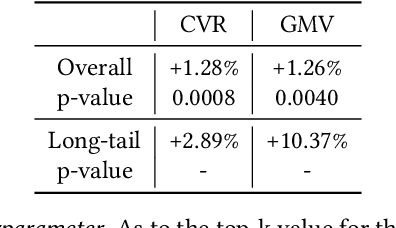
Abstract:In large e-commerce platforms, search systems are typically composed of a series of modules, including recall, pre-ranking, and ranking phases. The pre-ranking phase, serving as a lightweight module, is crucial for filtering out the bulk of products in advance for the downstream ranking module. Industrial efforts on optimizing the pre-ranking model have predominantly focused on enhancing ranking consistency, model structure, and generalization towards long-tail items. Beyond these optimizations, meeting the system performance requirements presents a significant challenge. Contrasting with existing industry works, we propose a novel method: a Generalizable and RAnk-ConsistEnt Pre-Ranking Model (GRACE), which achieves: 1) Ranking consistency by introducing multiple binary classification tasks that predict whether a product is within the top-k results as estimated by the ranking model, which facilitates the addition of learning objectives on common point-wise ranking models; 2) Generalizability through contrastive learning of representation for all products by pre-training on a subset of ranking product embeddings; 3) Ease of implementation in feature construction and online deployment. Our extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements in both offline metrics and online A/B test: a 0.75% increase in AUC and a 1.28% increase in CVR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge