Sharon X. Huang
Computer-Aided Layout Generation for Building Design: A Review
Apr 13, 2025
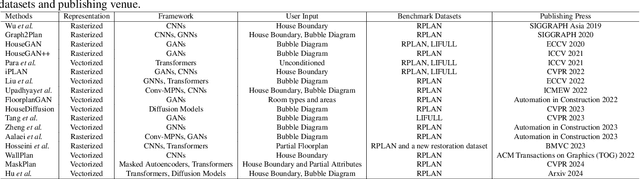
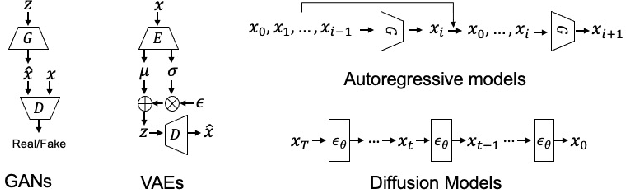
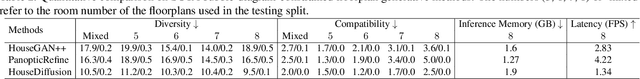
Abstract:Generating realistic building layouts for automatic building design has been studied in both the computer vision and architecture domains. Traditional approaches from the architecture domain, which are based on optimization techniques or heuristic design guidelines, can synthesize desirable layouts, but usually require post-processing and involve human interaction in the design pipeline, making them costly and timeconsuming. The advent of deep generative models has significantly improved the fidelity and diversity of the generated architecture layouts, reducing the workload by designers and making the process much more efficient. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive review of three major research topics of architecture layout design and generation: floorplan layout generation, scene layout synthesis, and generation of some other formats of building layouts. For each topic, we present an overview of the leading paradigms, categorized either by research domains (architecture or machine learning) or by user input conditions or constraints. We then introduce the commonly-adopted benchmark datasets that are used to verify the effectiveness of the methods, as well as the corresponding evaluation metrics. Finally, we identify the well-solved problems and limitations of existing approaches, then propose new perspectives as promising directions for future research in this important research area. A project associated with this survey to maintain the resources is available at awesome-building-layout-generation.
TI2V-Zero: Zero-Shot Image Conditioning for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Text-conditioned image-to-video generation (TI2V) aims to synthesize a realistic video starting from a given image (e.g., a woman's photo) and a text description (e.g., "a woman is drinking water."). Existing TI2V frameworks often require costly training on video-text datasets and specific model designs for text and image conditioning. In this paper, we propose TI2V-Zero, a zero-shot, tuning-free method that empowers a pretrained text-to-video (T2V) diffusion model to be conditioned on a provided image, enabling TI2V generation without any optimization, fine-tuning, or introducing external modules. Our approach leverages a pretrained T2V diffusion foundation model as the generative prior. To guide video generation with the additional image input, we propose a "repeat-and-slide" strategy that modulates the reverse denoising process, allowing the frozen diffusion model to synthesize a video frame-by-frame starting from the provided image. To ensure temporal continuity, we employ a DDPM inversion strategy to initialize Gaussian noise for each newly synthesized frame and a resampling technique to help preserve visual details. We conduct comprehensive experiments on both domain-specific and open-domain datasets, where TI2V-Zero consistently outperforms a recent open-domain TI2V model. Furthermore, we show that TI2V-Zero can seamlessly extend to other tasks such as video infilling and prediction when provided with more images. Its autoregressive design also supports long video generation.
ANCHOR: LLM-driven News Subject Conditioning for Text-to-Image Synthesis
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-Image (T2I) Synthesis has made tremendous strides in enhancing synthesized image quality, but current datasets evaluate model performance only on descriptive, instruction-based prompts. Real-world news image captions take a more pragmatic approach, providing high-level situational and Named-Entity (NE) information and limited physical object descriptions, making them abstractive. To evaluate the ability of T2I models to capture intended subjects from news captions, we introduce the Abstractive News Captions with High-level cOntext Representation (ANCHOR) dataset, containing 70K+ samples sourced from 5 different news media organizations. With Large Language Models (LLM) achieving success in language and commonsense reasoning tasks, we explore the ability of different LLMs to identify and understand key subjects from abstractive captions. Our proposed method Subject-Aware Finetuning (SAFE), selects and enhances the representation of key subjects in synthesized images by leveraging LLM-generated subject weights. It also adapts to the domain distribution of news images and captions through custom Domain Fine-tuning, outperforming current T2I baselines on ANCHOR. By launching the ANCHOR dataset, we hope to motivate research in furthering the Natural Language Understanding (NLU) capabilities of T2I models.
3D-Aware Talking-Head Video Motion Transfer
Nov 05, 2023Abstract:Motion transfer of talking-head videos involves generating a new video with the appearance of a subject video and the motion pattern of a driving video. Current methodologies primarily depend on a limited number of subject images and 2D representations, thereby neglecting to fully utilize the multi-view appearance features inherent in the subject video. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D-aware talking-head video motion transfer network, Head3D, which fully exploits the subject appearance information by generating a visually-interpretable 3D canonical head from the 2D subject frames with a recurrent network. A key component of our approach is a self-supervised 3D head geometry learning module, designed to predict head poses and depth maps from 2D subject video frames. This module facilitates the estimation of a 3D head in canonical space, which can then be transformed to align with driving video frames. Additionally, we employ an attention-based fusion network to combine the background and other details from subject frames with the 3D subject head to produce the synthetic target video. Our extensive experiments on two public talking-head video datasets demonstrate that Head3D outperforms both 2D and 3D prior arts in the practical cross-identity setting, with evidence showing it can be readily adapted to the pose-controllable novel view synthesis task.
NeRF-Enhanced Outpainting for Faithful Field-of-View Extrapolation
Sep 23, 2023Abstract:In various applications, such as robotic navigation and remote visual assistance, expanding the field of view (FOV) of the camera proves beneficial for enhancing environmental perception. Unlike image outpainting techniques aimed solely at generating aesthetically pleasing visuals, these applications demand an extended view that faithfully represents the scene. To achieve this, we formulate a new problem of faithful FOV extrapolation that utilizes a set of pre-captured images as prior knowledge of the scene. To address this problem, we present a simple yet effective solution called NeRF-Enhanced Outpainting (NEO) that uses extended-FOV images generated through NeRF to train a scene-specific image outpainting model. To assess the performance of NEO, we conduct comprehensive evaluations on three photorealistic datasets and one real-world dataset. Extensive experiments on the benchmark datasets showcase the robustness and potential of our method in addressing this challenge. We believe our work lays a strong foundation for future exploration within the research community.
Synthetic Augmentation with Large-scale Unconditional Pre-training
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning based medical image recognition systems often require a substantial amount of training data with expert annotations, which can be expensive and time-consuming to obtain. Recently, synthetic augmentation techniques have been proposed to mitigate the issue by generating realistic images conditioned on class labels. However, the effectiveness of these methods heavily depends on the representation capability of the trained generative model, which cannot be guaranteed without sufficient labeled training data. To further reduce the dependency on annotated data, we propose a synthetic augmentation method called HistoDiffusion, which can be pre-trained on large-scale unlabeled datasets and later applied to a small-scale labeled dataset for augmented training. In particular, we train a latent diffusion model (LDM) on diverse unlabeled datasets to learn common features and generate realistic images without conditional inputs. Then, we fine-tune the model with classifier guidance in latent space on an unseen labeled dataset so that the model can synthesize images of specific categories. Additionally, we adopt a selective mechanism to only add synthetic samples with high confidence of matching to target labels. We evaluate our proposed method by pre-training on three histopathology datasets and testing on a histopathology dataset of colorectal cancer (CRC) excluded from the pre-training datasets. With HistoDiffusion augmentation, the classification accuracy of a backbone classifier is remarkably improved by 6.4% using a small set of the original labels. Our code is available at https://github.com/karenyyy/HistoDiffAug.
Conditional Image-to-Video Generation with Latent Flow Diffusion Models
Mar 24, 2023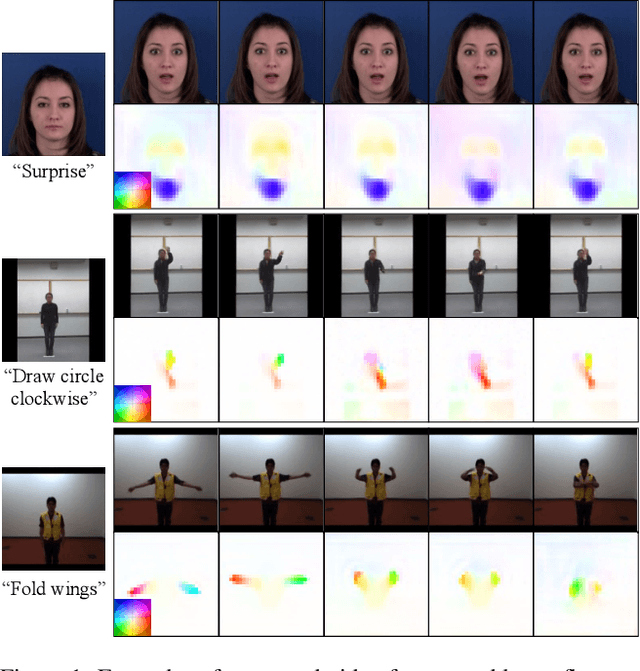
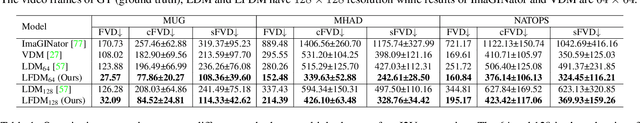
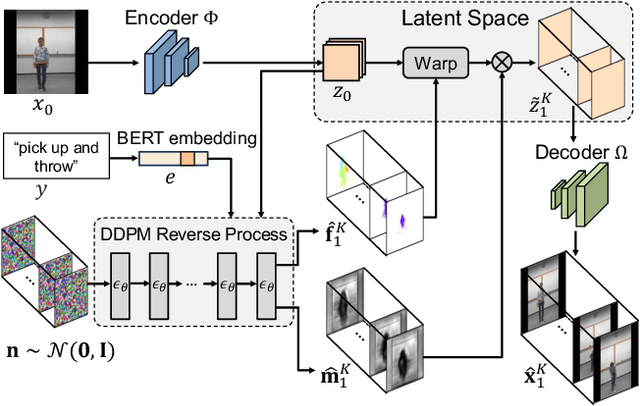

Abstract:Conditional image-to-video (cI2V) generation aims to synthesize a new plausible video starting from an image (e.g., a person's face) and a condition (e.g., an action class label like smile). The key challenge of the cI2V task lies in the simultaneous generation of realistic spatial appearance and temporal dynamics corresponding to the given image and condition. In this paper, we propose an approach for cI2V using novel latent flow diffusion models (LFDM) that synthesize an optical flow sequence in the latent space based on the given condition to warp the given image. Compared to previous direct-synthesis-based works, our proposed LFDM can better synthesize spatial details and temporal motion by fully utilizing the spatial content of the given image and warping it in the latent space according to the generated temporally-coherent flow. The training of LFDM consists of two separate stages: (1) an unsupervised learning stage to train a latent flow auto-encoder for spatial content generation, including a flow predictor to estimate latent flow between pairs of video frames, and (2) a conditional learning stage to train a 3D-UNet-based diffusion model (DM) for temporal latent flow generation. Unlike previous DMs operating in pixel space or latent feature space that couples spatial and temporal information, the DM in our LFDM only needs to learn a low-dimensional latent flow space for motion generation, thus being more computationally efficient. We conduct comprehensive experiments on multiple datasets, where LFDM consistently outperforms prior arts. Furthermore, we show that LFDM can be easily adapted to new domains by simply finetuning the image decoder. Our code is available at https://github.com/nihaomiao/CVPR23_LFDM.
ANNA: Abstractive Text-to-Image Synthesis with Filtered News Captions
Jan 05, 2023



Abstract:Advancements in Text-to-Image synthesis over recent years have focused more on improving the quality of generated samples on datasets with descriptive captions. However, real-world image-caption pairs present in domains such as news data do not use simple and directly descriptive captions. With captions containing information on both the image content and underlying contextual cues, they become abstractive in nature. In this paper, we launch ANNA, an Abstractive News captioNs dAtaset extracted from online news articles in a variety of different contexts. We explore the capabilities of current Text-to-Image synthesis models to generate news domain-specific images using abstractive captions by benchmarking them on ANNA, in both standard training and transfer learning settings. The generated images are judged on the basis of contextual relevance, visual quality, and perceptual similarity to ground-truth image-caption pairs. Through our experiments, we show that techniques such as transfer learning achieve limited success in understanding abstractive captions but still fail to consistently learn the relationships between content and context features.
Cross-identity Video Motion Retargeting with Joint Transformation and Synthesis
Oct 02, 2022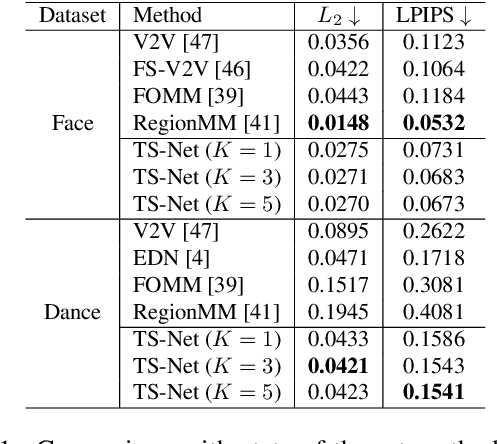
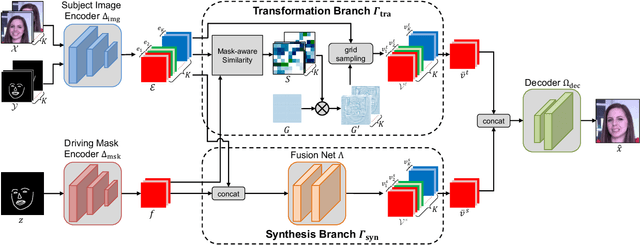
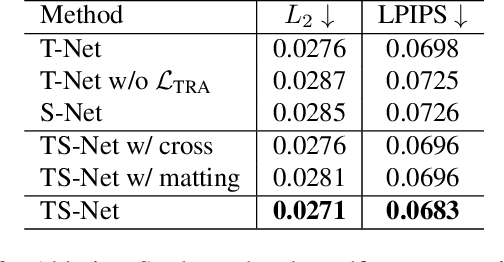
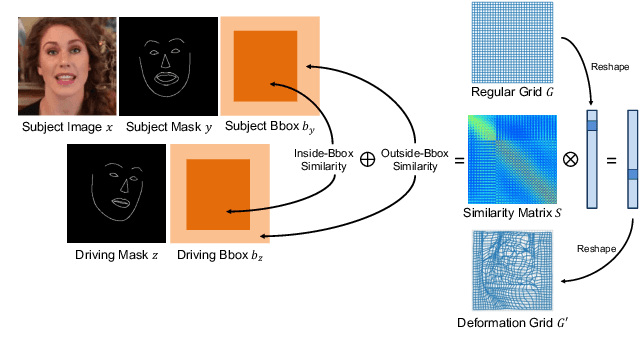
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel dual-branch Transformation-Synthesis network (TS-Net), for video motion retargeting. Given one subject video and one driving video, TS-Net can produce a new plausible video with the subject appearance of the subject video and motion pattern of the driving video. TS-Net consists of a warp-based transformation branch and a warp-free synthesis branch. The novel design of dual branches combines the strengths of deformation-grid-based transformation and warp-free generation for better identity preservation and robustness to occlusion in the synthesized videos. A mask-aware similarity module is further introduced to the transformation branch to reduce computational overhead. Experimental results on face and dance datasets show that TS-Net achieves better performance in video motion retargeting than several state-of-the-art models as well as its single-branch variants. Our code is available at https://github.com/nihaomiao/WACV23_TSNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge