Jingzhi Li
SMA: Who Said That? Auditing Membership Leakage in Semi-Black-box RAG Controlling
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and its Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MRAG) significantly improve the knowledge coverage and contextual understanding of Large Language Models (LLMs) by introducing external knowledge sources. However, retrieval and multimodal fusion obscure content provenance, rendering existing membership inference methods unable to reliably attribute generated outputs to pre-training, external retrieval, or user input, thus undermining privacy leakage accountability To address these challenges, we propose the first Source-aware Membership Audit (SMA) that enables fine-grained source attribution of generated content in a semi-black-box setting with retrieval control capabilities.To address the environmental constraints of semi-black-box auditing, we further design an attribution estimation mechanism based on zero-order optimization, which robustly approximates the true influence of input tokens on the output through large-scale perturbation sampling and ridge regression modeling. In addition, SMA introduces a cross-modal attribution technique that projects image inputs into textual descriptions via MLLMs, enabling token-level attribution in the text modality, which for the first time facilitates membership inference on image retrieval traces in MRAG systems. This work shifts the focus of membership inference from 'whether the data has been memorized' to 'where the content is sourced from', offering a novel perspective for auditing data provenance in complex generative systems.
FaceInsight: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Face Perception
Apr 22, 2025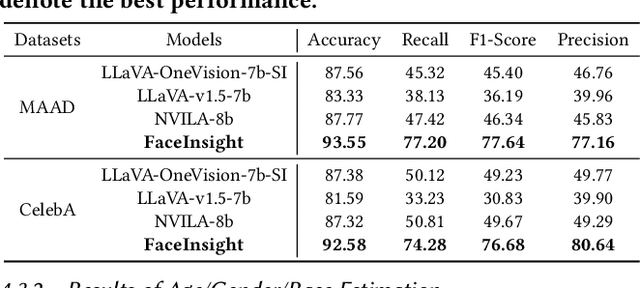
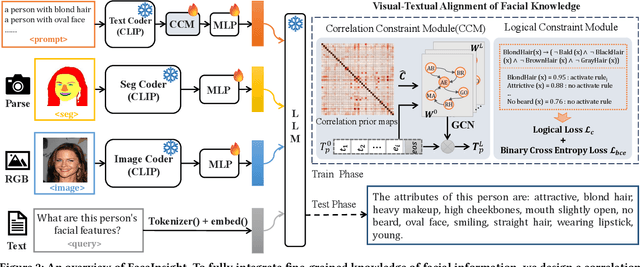
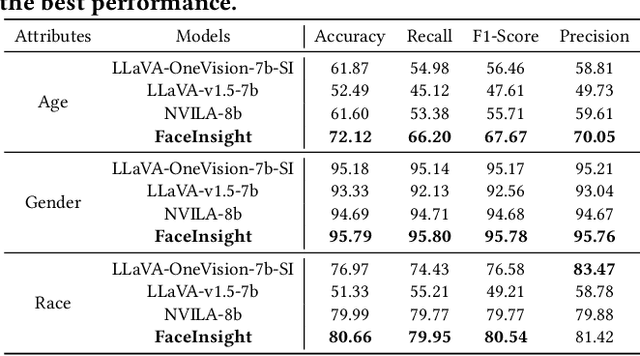
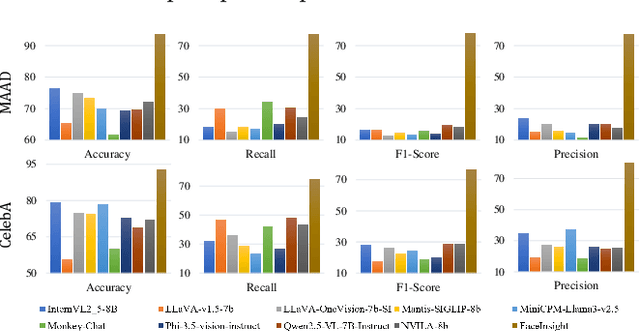
Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in understanding general visual content. However, these general-domain MLLMs perform poorly in face perception tasks, often producing inaccurate or misleading responses to face-specific queries. To address this gap, we propose FaceInsight, the versatile face perception MLLM that provides fine-grained facial information. Our approach introduces visual-textual alignment of facial knowledge to model both uncertain dependencies and deterministic relationships among facial information, mitigating the limitations of language-driven reasoning. Additionally, we incorporate face segmentation maps as an auxiliary perceptual modality, enriching the visual input with localized structural cues to enhance semantic understanding. Comprehensive experiments and analyses across three face perception tasks demonstrate that FaceInsight consistently outperforms nine compared MLLMs under both training-free and fine-tuned settings.
Generalized Semantic Contrastive Learning via Embedding Side Information for Few-Shot Object Detection
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:The objective of few-shot object detection (FSOD) is to detect novel objects with few training samples. The core challenge of this task is how to construct a generalized feature space for novel categories with limited data on the basis of the base category space, which could adapt the learned detection model to unknown scenarios. However, limited by insufficient samples for novel categories, two issues still exist: (1) the features of the novel category are easily implicitly represented by the features of the base category, leading to inseparable classifier boundaries, (2) novel categories with fewer data are not enough to fully represent the distribution, where the model fine-tuning is prone to overfitting. To address these issues, we introduce the side information to alleviate the negative influences derived from the feature space and sample viewpoints and formulate a novel generalized feature representation learning method for FSOD. Specifically, we first utilize embedding side information to construct a knowledge matrix to quantify the semantic relationship between the base and novel categories. Then, to strengthen the discrimination between semantically similar categories, we further develop contextual semantic supervised contrastive learning which embeds side information. Furthermore, to prevent overfitting problems caused by sparse samples, a side-information guided region-aware masked module is introduced to augment the diversity of samples, which finds and abandons biased information that discriminates between similar categories via counterfactual explanation, and refines the discriminative representation space further. Extensive experiments using ResNet and ViT backbones on PASCAL VOC, MS COCO, LVIS V1, FSOD-1K, and FSVOD-500 benchmarks demonstrate that our model outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving the ability of FSOD in most shots/splits.
Less is More: Efficient Black-box Attribution via Minimal Interpretable Subset Selection
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:To develop a trustworthy AI system, which aim to identify the input regions that most influence the models decisions. The primary task of existing attribution methods lies in efficiently and accurately identifying the relationships among input-prediction interactions. Particularly when the input data is discrete, such as images, analyzing the relationship between inputs and outputs poses a significant challenge due to the combinatorial explosion. In this paper, we propose a novel and efficient black-box attribution mechanism, LiMA (Less input is More faithful for Attribution), which reformulates the attribution of important regions as an optimization problem for submodular subset selection. First, to accurately assess interactions, we design a submodular function that quantifies subset importance and effectively captures their impact on decision outcomes. Then, efficiently ranking input sub-regions by their importance for attribution, we improve optimization efficiency through a novel bidirectional greedy search algorithm. LiMA identifies both the most and least important samples while ensuring an optimal attribution boundary that minimizes errors. Extensive experiments on eight foundation models demonstrate that our method provides faithful interpretations with fewer regions and exhibits strong generalization, shows an average improvement of 36.3% in Insertion and 39.6% in Deletion. Our method also outperforms the naive greedy search in attribution efficiency, being 1.6 times faster. Furthermore, when explaining the reasons behind model prediction errors, the average highest confidence achieved by our method is, on average, 86.1% higher than that of state-of-the-art attribution algorithms. The code is available at https://github.com/RuoyuChen10/LIMA.
ReCap: Better Gaussian Relighting with Cross-Environment Captures
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Accurate 3D objects relighting in diverse unseen environments is crucial for realistic virtual object placement. Due to the albedo-lighting ambiguity, existing methods often fall short in producing faithful relights. Without proper constraints, observed training views can be explained by numerous combinations of lighting and material attributes, lacking physical correspondence with the actual environment maps used for relighting. In this work, we present ReCap, treating cross-environment captures as multi-task target to provide the missing supervision that cuts through the entanglement. Specifically, ReCap jointly optimizes multiple lighting representations that share a common set of material attributes. This naturally harmonizes a coherent set of lighting representations around the mutual material attributes, exploiting commonalities and differences across varied object appearances. Such coherence enables physically sound lighting reconstruction and robust material estimation - both essential for accurate relighting. Together with a streamlined shading function and effective post-processing, ReCap outperforms the leading competitor by 3.4 dB in PSNR on an expanded relighting benchmark.
Interpreting Object-level Foundation Models via Visual Precision Search
Nov 25, 2024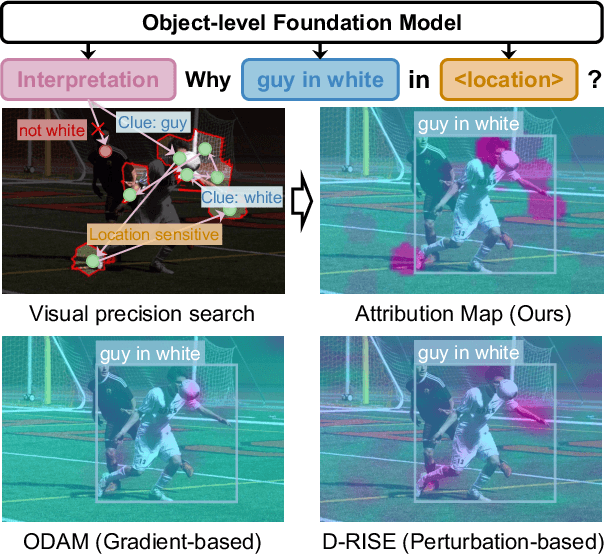
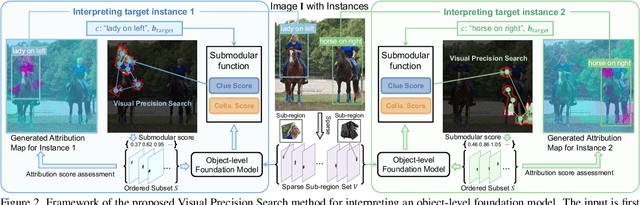
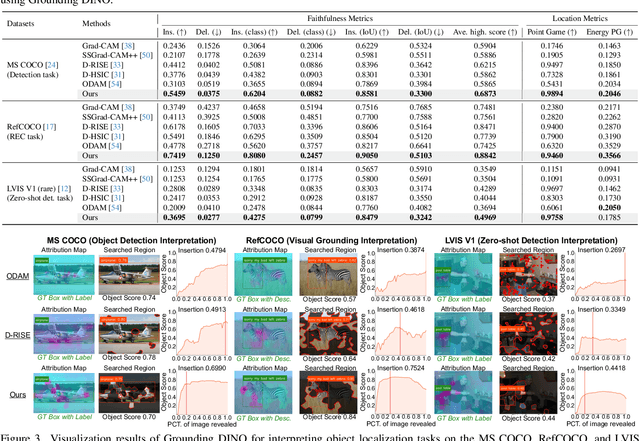
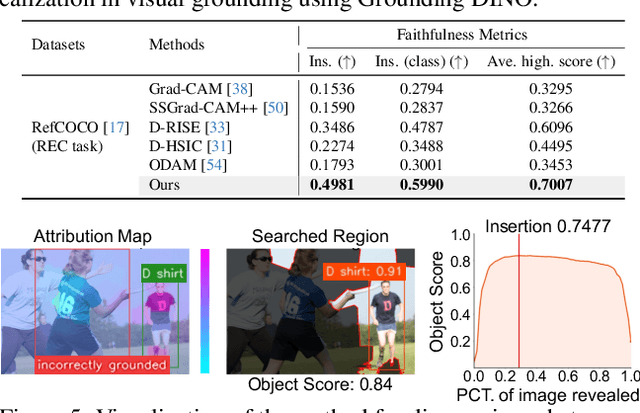
Abstract:Advances in multimodal pre-training have propelled object-level foundation models, such as Grounding DINO and Florence-2, in tasks like visual grounding and object detection. However, interpreting these models\' decisions has grown increasingly challenging. Existing interpretable attribution methods for object-level task interpretation have notable limitations: (1) gradient-based methods lack precise localization due to visual-textual fusion in foundation models, and (2) perturbation-based methods produce noisy saliency maps, limiting fine-grained interpretability. To address these, we propose a Visual Precision Search method that generates accurate attribution maps with fewer regions. Our method bypasses internal model parameters to overcome attribution issues from multimodal fusion, dividing inputs into sparse sub-regions and using consistency and collaboration scores to accurately identify critical decision-making regions. We also conducted a theoretical analysis of the boundary guarantees and scope of applicability of our method. Experiments on RefCOCO, MS COCO, and LVIS show our approach enhances object-level task interpretability over SOTA for Grounding DINO and Florence-2 across various evaluation metrics, with faithfulness gains of 23.7\%, 31.6\%, and 20.1\% on MS COCO, LVIS, and RefCOCO for Grounding DINO, and 102.9\% and 66.9\% on MS COCO and RefCOCO for Florence-2. Additionally, our method can interpret failures in visual grounding and object detection tasks, surpassing existing methods across multiple evaluation metrics. The code will be released at \url{https://github.com/RuoyuChen10/VPS}.
Logit Standardization in Knowledge Distillation
Mar 03, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge distillation involves transferring soft labels from a teacher to a student using a shared temperature-based softmax function. However, the assumption of a shared temperature between teacher and student implies a mandatory exact match between their logits in terms of logit range and variance. This side-effect limits the performance of student, considering the capacity discrepancy between them and the finding that the innate logit relations of teacher are sufficient for student to learn. To address this issue, we propose setting the temperature as the weighted standard deviation of logit and performing a plug-and-play Z-score pre-process of logit standardization before applying softmax and Kullback-Leibler divergence. Our pre-process enables student to focus on essential logit relations from teacher rather than requiring a magnitude match, and can improve the performance of existing logit-based distillation methods. We also show a typical case where the conventional setting of sharing temperature between teacher and student cannot reliably yield the authentic distillation evaluation; nonetheless, this challenge is successfully alleviated by our Z-score. We extensively evaluate our method for various student and teacher models on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet, showing its significant superiority. The vanilla knowledge distillation powered by our pre-process can achieve favorable performance against state-of-the-art methods, and other distillation variants can obtain considerable gain with the assistance of our pre-process.
Less is More: Fewer Interpretable Region via Submodular Subset Selection
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Image attribution algorithms aim to identify important regions that are highly relevant to model decisions. Although existing attribution solutions can effectively assign importance to target elements, they still face the following challenges: 1) existing attribution methods generate inaccurate small regions thus misleading the direction of correct attribution, and 2) the model cannot produce good attribution results for samples with wrong predictions. To address the above challenges, this paper re-models the above image attribution problem as a submodular subset selection problem, aiming to enhance model interpretability using fewer regions. To address the lack of attention to local regions, we construct a novel submodular function to discover more accurate small interpretation regions. To enhance the attribution effect for all samples, we also impose four different constraints on the selection of sub-regions, i.e., confidence, effectiveness, consistency, and collaboration scores, to assess the importance of various subsets. Moreover, our theoretical analysis substantiates that the proposed function is in fact submodular. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method outperforms SOTA methods on two face datasets (Celeb-A and VGG-Face2) and one fine-grained dataset (CUB-200-2011). For correctly predicted samples, the proposed method improves the Deletion and Insertion scores with an average of 4.9% and 2.5% gain relative to HSIC-Attribution. For incorrectly predicted samples, our method achieves gains of 81.0% and 18.4% compared to the HSIC-Attribution algorithm in the average highest confidence and Insertion score respectively. The code is released at https://github.com/RuoyuChen10/SMDL-Attribution.
A Large-scale Multiple-objective Method for Black-box Attack against Object Detection
Sep 16, 2022



Abstract:Recent studies have shown that detectors based on deep models are vulnerable to adversarial examples, even in the black-box scenario where the attacker cannot access the model information. Most existing attack methods aim to minimize the true positive rate, which often shows poor attack performance, as another sub-optimal bounding box may be detected around the attacked bounding box to be the new true positive one. To settle this challenge, we propose to minimize the true positive rate and maximize the false positive rate, which can encourage more false positive objects to block the generation of new true positive bounding boxes. It is modeled as a multi-objective optimization (MOP) problem, of which the generic algorithm can search the Pareto-optimal. However, our task has more than two million decision variables, leading to low searching efficiency. Thus, we extend the standard Genetic Algorithm with Random Subset selection and Divide-and-Conquer, called GARSDC, which significantly improves the efficiency. Moreover, to alleviate the sensitivity to population quality in generic algorithms, we generate a gradient-prior initial population, utilizing the transferability between different detectors with similar backbones. Compared with the state-of-art attack methods, GARSDC decreases by an average 12.0 in the mAP and queries by about 1000 times in extensive experiments. Our codes can be found at https://github.com/LiangSiyuan21/ GARSDC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge