Hui Zheng
Self-supervised Multiplex Consensus Mamba for General Image Fusion
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Image fusion integrates complementary information from different modalities to generate high-quality fused images, thereby enhancing downstream tasks such as object detection and semantic segmentation. Unlike task-specific techniques that primarily focus on consolidating inter-modal information, general image fusion needs to address a wide range of tasks while improving performance without increasing complexity. To achieve this, we propose SMC-Mamba, a Self-supervised Multiplex Consensus Mamba framework for general image fusion. Specifically, the Modality-Agnostic Feature Enhancement (MAFE) module preserves fine details through adaptive gating and enhances global representations via spatial-channel and frequency-rotational scanning. The Multiplex Consensus Cross-modal Mamba (MCCM) module enables dynamic collaboration among experts, reaching a consensus to efficiently integrate complementary information from multiple modalities. The cross-modal scanning within MCCM further strengthens feature interactions across modalities, facilitating seamless integration of critical information from both sources. Additionally, we introduce a Bi-level Self-supervised Contrastive Learning Loss (BSCL), which preserves high-frequency information without increasing computational overhead while simultaneously boosting performance in downstream tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) image fusion algorithms in tasks such as infrared-visible, medical, multi-focus, and multi-exposure fusion, as well as downstream visual tasks.
BrainStratify: Coarse-to-Fine Disentanglement of Intracranial Neural Dynamics
May 26, 2025Abstract:Decoding speech directly from neural activity is a central goal in brain-computer interface (BCI) research. In recent years, exciting advances have been made through the growing use of intracranial field potential recordings, such as stereo-ElectroEncephaloGraphy (sEEG) and ElectroCorticoGraphy (ECoG). These neural signals capture rich population-level activity but present key challenges: (i) task-relevant neural signals are sparsely distributed across sEEG electrodes, and (ii) they are often entangled with task-irrelevant neural signals in both sEEG and ECoG. To address these challenges, we introduce a unified Coarse-to-Fine neural disentanglement framework, BrainStratify, which includes (i) identifying functional groups through spatial-context-guided temporal-spatial modeling, and (ii) disentangling distinct neural dynamics within the target functional group using Decoupled Product Quantization (DPQ). We evaluate BrainStratify on two open-source sEEG datasets and one (epidural) ECoG dataset, spanning tasks like vocal production and speech perception. Extensive experiments show that BrainStratify, as a unified framework for decoding speech from intracranial neural signals, significantly outperforms previous decoding methods. Overall, by combining data-driven stratification with neuroscience-inspired modularity, BrainStratify offers a robust and interpretable solution for speech decoding from intracranial recordings.
Pan-LUT: Efficient Pan-sharpening via Learnable Look-Up Tables
Mar 31, 2025
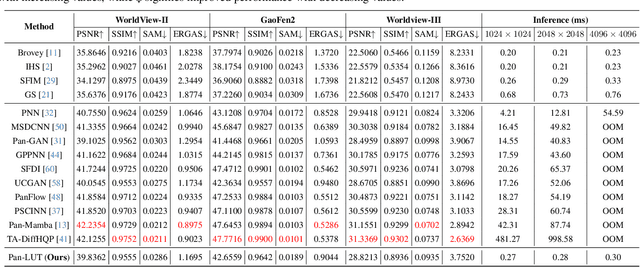
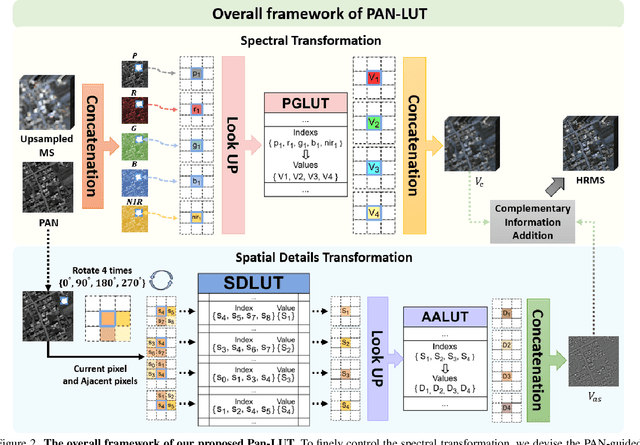
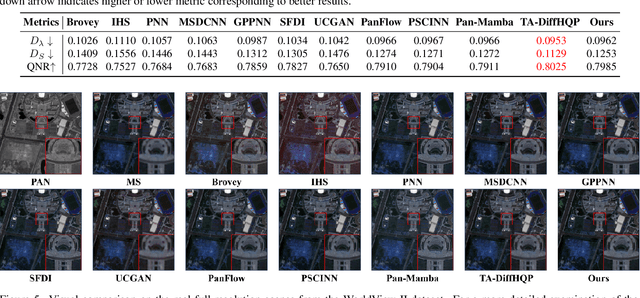
Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based pan-sharpening algorithms have achieved notable advancements over traditional methods. However, many deep learning-based approaches incur substantial computational overhead during inference, especially with high-resolution images. This excessive computational demand limits the applicability of these methods in real-world scenarios, particularly in the absence of dedicated computing devices such as GPUs and TPUs. To address these challenges, we propose Pan-LUT, a novel learnable look-up table (LUT) framework for pan-sharpening that strikes a balance between performance and computational efficiency for high-resolution remote sensing images. To finely control the spectral transformation, we devise the PAN-guided look-up table (PGLUT) for channel-wise spectral mapping. To effectively capture fine-grained spatial details and adaptively learn local contexts, we introduce the spatial details look-up table (SDLUT) and adaptive aggregation look-up table (AALUT). Our proposed method contains fewer than 300K parameters and processes a 8K resolution image in under 1 ms using a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU, demonstrating significantly faster performance compared to other methods. Experiments reveal that Pan-LUT efficiently processes large remote sensing images in a lightweight manner, bridging the gap to real-world applications. Furthermore, our model surpasses SOTA methods in full-resolution scenes under real-world conditions, highlighting its effectiveness and efficiency.
High-Precision Fabric Defect Detection via Adaptive Shape Convolutions and Large Kernel Spatial Modeling
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Detecting fabric defects in the textile industry remains a challenging task due to the diverse and complex nature of defect patterns. Traditional methods often suffer from slow inference speeds, limited accuracy, and inadequate recognition rates, particularly in scenarios involving intricate or subtle defects. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Fab-ASLKS, an advanced fabric defect detection framework built upon the YOLOv8s architecture. Fab-ASLKS incorporates two key modules: (1) the Adaptive Shape Convolution Module (ASCM), which leverages adaptive shape convolution within the Neck to enhance feature fusion and improve efficiency by extending the capabilities of the standard C2f structure, and (2) the Large Kernel Shift Convolution Module (LKSCM), designed to emulate large kernel effects within the Backbone, enabling superior spatial information extraction. These modules collaboratively optimize feature extraction and information integration across the network. Extensive experiments conducted on the Tianchi fabric defect detection dataset demonstrate that Fab-ASLKS achieves a 5% improvement in mAP@50 over the baseline, showcasing its capability to deliver high precision and efficiency.
Training-Free Large Model Priors for Multiple-in-One Image Restoration
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Image restoration aims to reconstruct the latent clear images from their degraded versions. Despite the notable achievement, existing methods predominantly focus on handling specific degradation types and thus require specialized models, impeding real-world applications in dynamic degradation scenarios. To address this issue, we propose Large Model Driven Image Restoration framework (LMDIR), a novel multiple-in-one image restoration paradigm that leverages the generic priors from large multi-modal language models (MMLMs) and the pretrained diffusion models. In detail, LMDIR integrates three key prior knowledges: 1) global degradation knowledge from MMLMs, 2) scene-aware contextual descriptions generated by MMLMs, and 3) fine-grained high-quality reference images synthesized by diffusion models guided by MMLM descriptions. Standing on above priors, our architecture comprises a query-based prompt encoder, degradation-aware transformer block injecting global degradation knowledge, content-aware transformer block incorporating scene description, and reference-based transformer block incorporating fine-grained image priors. This design facilitates single-stage training paradigm to address various degradations while supporting both automatic and user-guided restoration. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our designed method outperforms state-of-the-art competitors on multiple evaluation benchmarks.
Du-IN: Discrete units-guided mask modeling for decoding speech from Intracranial Neural signals
May 19, 2024Abstract:Invasive brain-computer interfaces have garnered significant attention due to their high performance. The current intracranial stereoElectroEncephaloGraphy (sEEG) foundation models typically build univariate representations based on a single channel. Some of them further use Transformer to model the relationship among channels. However, due to the locality and specificity of brain computation, their performance on more difficult tasks, e.g., speech decoding, which demands intricate processing in specific brain regions, is yet to be fully investigated. We hypothesize that building multi-variate representations within certain brain regions can better capture the specific neural processing. To explore this hypothesis, we collect a well-annotated Chinese word-reading sEEG dataset, targeting language-related brain networks, over 12 subjects. Leveraging this benchmark dataset, we developed the Du-IN model that can extract contextual embeddings from specific brain regions through discrete codebook-guided mask modeling. Our model achieves SOTA performance on the downstream 61-word classification task, surpassing all baseline models. Model comparison and ablation analysis reveal that our design choices, including (i) multi-variate representation by fusing channels in vSMC and STG regions and (ii) self-supervision by discrete codebook-guided mask modeling, significantly contribute to these performances. Collectively, our approach, inspired by neuroscience findings, capitalizing on multi-variate neural representation from specific brain regions, is suitable for invasive brain modeling. It marks a promising neuro-inspired AI approach in BCI.
Universal Sleep Decoder: Aligning awake and sleep neural representation across subjects
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Decoding memory content from brain activity during sleep has long been a goal in neuroscience. While spontaneous reactivation of memories during sleep in rodents is known to support memory consolidation and offline learning, capturing memory replay in humans is challenging due to the absence of well-annotated sleep datasets and the substantial differences in neural patterns between wakefulness and sleep. To address these challenges, we designed a novel cognitive neuroscience experiment and collected a comprehensive, well-annotated electroencephalography (EEG) dataset from 52 subjects during both wakefulness and sleep. Leveraging this benchmark dataset, we developed the Universal Sleep Decoder (USD) to align neural representations between wakefulness and sleep across subjects. Our model achieves up to 16.6% top-1 zero-shot accuracy on unseen subjects, comparable to decoding performances using individual sleep data. Furthermore, fine-tuning USD on test subjects enhances decoding accuracy to 25.9% top-1 accuracy, a substantial improvement over the baseline chance of 6.7%. Model comparison and ablation analyses reveal that our design choices, including the use of (i) an additional contrastive objective to integrate awake and sleep neural signals and (ii) the pretrain-finetune paradigm to incorporate different subjects, significantly contribute to these performances. Collectively, our findings and methodologies represent a significant advancement in the field of sleep decoding.
Network-based Isoform Quantification with RNA-Seq Data for Cancer Transcriptome Analysis
Sep 15, 2015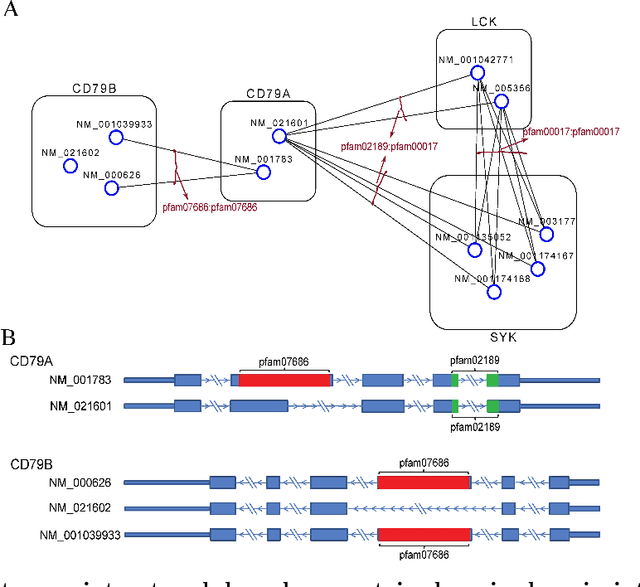


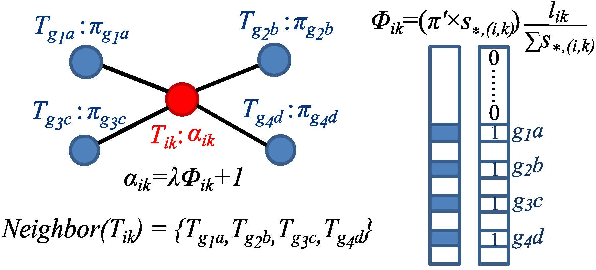
Abstract:High-throughput mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) is widely used for transcript quantification of gene isoforms. Since RNA-Seq data alone is often not sufficient to accurately identify the read origins from the isoforms for quantification, we propose to explore protein domain-domain interactions as prior knowledge for integrative analysis with RNA-seq data. We introduce a Network-based method for RNA-Seq-based Transcript Quantification (Net-RSTQ) to integrate protein domain-domain interaction network with short read alignments for transcript abundance estimation. Based on our observation that the abundances of the neighboring isoforms by domain-domain interactions in the network are positively correlated, Net-RSTQ models the expression of the neighboring transcripts as Dirichlet priors on the likelihood of the observed read alignments against the transcripts in one gene. The transcript abundances of all the genes are then jointly estimated with alternating optimization of multiple EM problems. In simulation Net-RSTQ effectively improved isoform transcript quantifications when isoform co-expressions correlate with their interactions. qRT-PCR results on 25 multi-isoform genes in a stem cell line, an ovarian cancer cell line, and a breast cancer cell line also showed that Net-RSTQ estimated more consistent isoform proportions with RNA-Seq data. In the experiments on the RNA-Seq data in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the transcript abundances estimated by Net-RSTQ are more informative for patient sample classification of ovarian cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer. All experimental results collectively support that Net-RSTQ is a promising approach for isoform quantification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge