Zixu Lin
Track Any Anomalous Object: A Granular Video Anomaly Detection Pipeline
Jun 05, 2025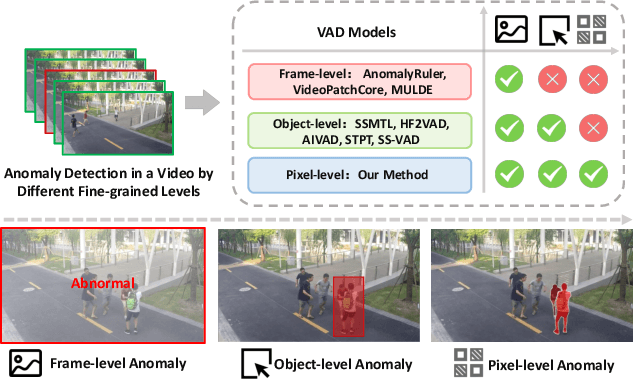
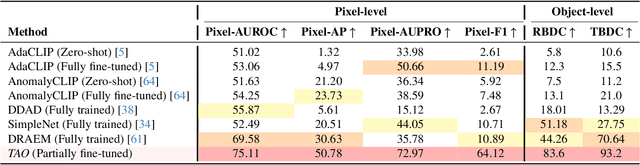
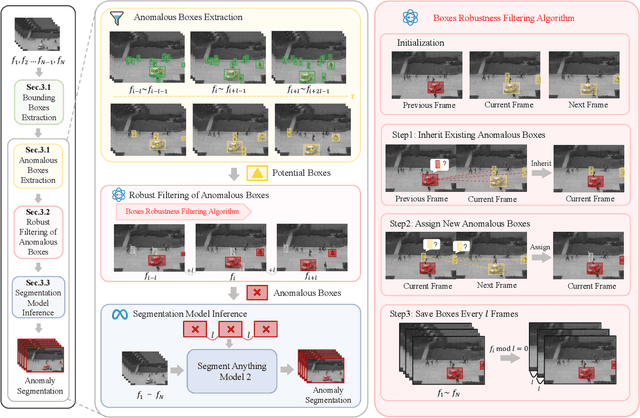

Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) is crucial in scenarios such as surveillance and autonomous driving, where timely detection of unexpected activities is essential. Although existing methods have primarily focused on detecting anomalous objects in videos -- either by identifying anomalous frames or objects -- they often neglect finer-grained analysis, such as anomalous pixels, which limits their ability to capture a broader range of anomalies. To address this challenge, we propose a new framework called Track Any Anomalous Object (TAO), which introduces a granular video anomaly detection pipeline that, for the first time, integrates the detection of multiple fine-grained anomalous objects into a unified framework. Unlike methods that assign anomaly scores to every pixel, our approach transforms the problem into pixel-level tracking of anomalous objects. By linking anomaly scores to downstream tasks such as segmentation and tracking, our method removes the need for threshold tuning and achieves more precise anomaly localization in long and complex video sequences. Experiments demonstrate that TAO sets new benchmarks in accuracy and robustness. Project page available online.
JarvisIR: Elevating Autonomous Driving Perception with Intelligent Image Restoration
Apr 05, 2025



Abstract:Vision-centric perception systems struggle with unpredictable and coupled weather degradations in the wild. Current solutions are often limited, as they either depend on specific degradation priors or suffer from significant domain gaps. To enable robust and autonomous operation in real-world conditions, we propose JarvisIR, a VLM-powered agent that leverages the VLM as a controller to manage multiple expert restoration models. To further enhance system robustness, reduce hallucinations, and improve generalizability in real-world adverse weather, JarvisIR employs a novel two-stage framework consisting of supervised fine-tuning and human feedback alignment. Specifically, to address the lack of paired data in real-world scenarios, the human feedback alignment enables the VLM to be fine-tuned effectively on large-scale real-world data in an unsupervised manner. To support the training and evaluation of JarvisIR, we introduce CleanBench, a comprehensive dataset consisting of high-quality and large-scale instruction-responses pairs, including 150K synthetic entries and 80K real entries. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JarvisIR exhibits superior decision-making and restoration capabilities. Compared with existing methods, it achieves a 50% improvement in the average of all perception metrics on CleanBench-Real. Project page: https://cvpr2025-jarvisir.github.io/.
Pan-LUT: Efficient Pan-sharpening via Learnable Look-Up Tables
Mar 31, 2025
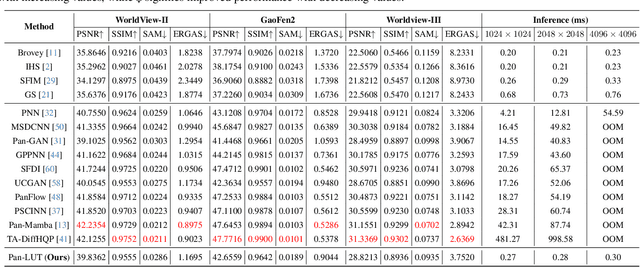
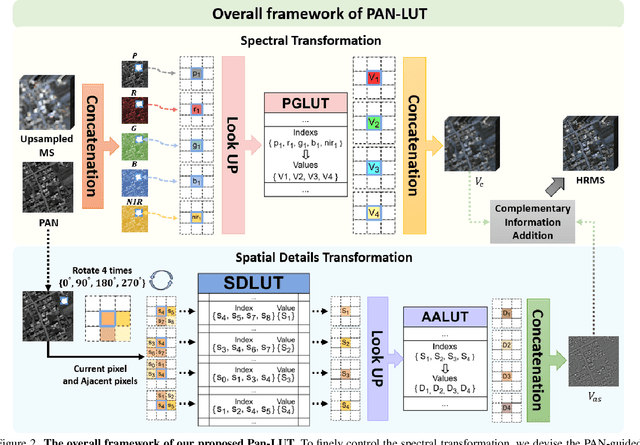
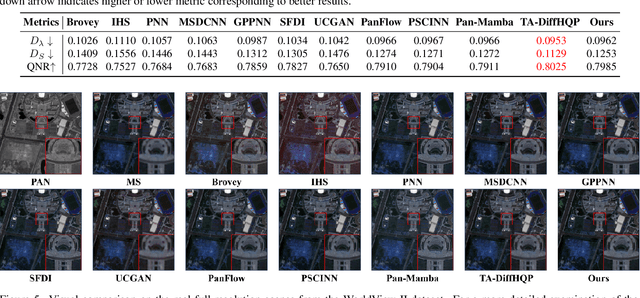
Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based pan-sharpening algorithms have achieved notable advancements over traditional methods. However, many deep learning-based approaches incur substantial computational overhead during inference, especially with high-resolution images. This excessive computational demand limits the applicability of these methods in real-world scenarios, particularly in the absence of dedicated computing devices such as GPUs and TPUs. To address these challenges, we propose Pan-LUT, a novel learnable look-up table (LUT) framework for pan-sharpening that strikes a balance between performance and computational efficiency for high-resolution remote sensing images. To finely control the spectral transformation, we devise the PAN-guided look-up table (PGLUT) for channel-wise spectral mapping. To effectively capture fine-grained spatial details and adaptively learn local contexts, we introduce the spatial details look-up table (SDLUT) and adaptive aggregation look-up table (AALUT). Our proposed method contains fewer than 300K parameters and processes a 8K resolution image in under 1 ms using a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU, demonstrating significantly faster performance compared to other methods. Experiments reveal that Pan-LUT efficiently processes large remote sensing images in a lightweight manner, bridging the gap to real-world applications. Furthermore, our model surpasses SOTA methods in full-resolution scenes under real-world conditions, highlighting its effectiveness and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge