Di Chen
Act2Goal: From World Model To General Goal-conditioned Policy
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Specifying robotic manipulation tasks in a manner that is both expressive and precise remains a central challenge. While visual goals provide a compact and unambiguous task specification, existing goal-conditioned policies often struggle with long-horizon manipulation due to their reliance on single-step action prediction without explicit modeling of task progress. We propose Act2Goal, a general goal-conditioned manipulation policy that integrates a goal-conditioned visual world model with multi-scale temporal control. Given a current observation and a target visual goal, the world model generates a plausible sequence of intermediate visual states that captures long-horizon structure. To translate this visual plan into robust execution, we introduce Multi-Scale Temporal Hashing (MSTH), which decomposes the imagined trajectory into dense proximal frames for fine-grained closed-loop control and sparse distal frames that anchor global task consistency. The policy couples these representations with motor control through end-to-end cross-attention, enabling coherent long-horizon behavior while remaining reactive to local disturbances. Act2Goal achieves strong zero-shot generalization to novel objects, spatial layouts, and environments. We further enable reward-free online adaptation through hindsight goal relabeling with LoRA-based finetuning, allowing rapid autonomous improvement without external supervision. Real-robot experiments demonstrate that Act2Goal improves success rates from 30% to 90% on challenging out-of-distribution tasks within minutes of autonomous interaction, validating that goal-conditioned world models with multi-scale temporal control provide structured guidance necessary for robust long-horizon manipulation. Project page: https://act2goal.github.io/
Real2Edit2Real: Generating Robotic Demonstrations via a 3D Control Interface
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in robot learning has been driven by large-scale datasets and powerful visuomotor policy architectures, yet policy robustness remains limited by the substantial cost of collecting diverse demonstrations, particularly for spatial generalization in manipulation tasks. To reduce repetitive data collection, we present Real2Edit2Real, a framework that generates new demonstrations by bridging 3D editability with 2D visual data through a 3D control interface. Our approach first reconstructs scene geometry from multi-view RGB observations with a metric-scale 3D reconstruction model. Based on the reconstructed geometry, we perform depth-reliable 3D editing on point clouds to generate new manipulation trajectories while geometrically correcting the robot poses to recover physically consistent depth, which serves as a reliable condition for synthesizing new demonstrations. Finally, we propose a multi-conditional video generation model guided by depth as the primary control signal, together with action, edge, and ray maps, to synthesize spatially augmented multi-view manipulation videos. Experiments on four real-world manipulation tasks demonstrate that policies trained on data generated from only 1-5 source demonstrations can match or outperform those trained on 50 real-world demonstrations, improving data efficiency by up to 10-50x. Moreover, experimental results on height and texture editing demonstrate the framework's flexibility and extensibility, indicating its potential to serve as a unified data generation framework.
Self-Interest and Systemic Benefits: Emergence of Collective Rationality in Mixed Autonomy Traffic Through Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are expected to be commercially available in the near future, leading to mixed autonomy traffic consisting of both AVs and human-driven vehicles (HVs). Although numerous studies have shown that AVs can be deployed to benefit the overall traffic system performance by incorporating system-level goals into their decision making, it is not clear whether the benefits still exist when agents act out of self-interest -- a trait common to all driving agents, both human and autonomous. This study aims to understand whether self-interested AVs can bring benefits to all driving agents in mixed autonomy traffic systems. The research is centered on the concept of collective rationality (CR). This concept, originating from game theory and behavioral economics, means that driving agents may cooperate collectively even when pursuing individual interests. Our recent research has proven the existence of CR in an analytical game-theoretical model and empirically in mixed human-driven traffic. In this paper, we demonstrate that CR can be attained among driving agents trained using deep reinforcement learning (DRL) with a simple reward design. We examine the extent to which self-interested traffic agents can achieve CR without directly incorporating system-level objectives. Results show that CR consistently emerges in various scenarios, which indicates the robustness of this property. We also postulate a mechanism to explain the emergence of CR in the microscopic and dynamic environment and verify it based on simulation evidence. This research suggests the possibility of leveraging advanced learning methods (such as federated learning) to achieve collective cooperation among self-interested driving agents in mixed-autonomy systems.
TrajFlow: Multi-modal Motion Prediction via Flow Matching
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Efficient and accurate motion prediction is crucial for ensuring safety and informed decision-making in autonomous driving, particularly under dynamic real-world conditions that necessitate multi-modal forecasts. We introduce TrajFlow, a novel flow matching-based motion prediction framework that addresses the scalability and efficiency challenges of existing generative trajectory prediction methods. Unlike conventional generative approaches that employ i.i.d. sampling and require multiple inference passes to capture diverse outcomes, TrajFlow predicts multiple plausible future trajectories in a single pass, significantly reducing computational overhead while maintaining coherence across predictions. Moreover, we propose a ranking loss based on the Plackett-Luce distribution to improve uncertainty estimation of predicted trajectories. Additionally, we design a self-conditioning training technique that reuses the model's own predictions to construct noisy inputs during a second forward pass, thereby improving generalization and accelerating inference. Extensive experiments on the large-scale Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD) demonstrate that TrajFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance across various key metrics, underscoring its effectiveness for safety-critical autonomous driving applications. The code and other details are available on the project website https://traj-flow.github.io/.
LONGER: Scaling Up Long Sequence Modeling in Industrial Recommenders
May 07, 2025
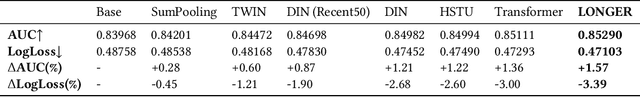
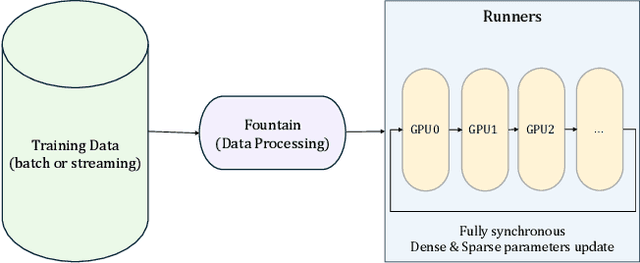
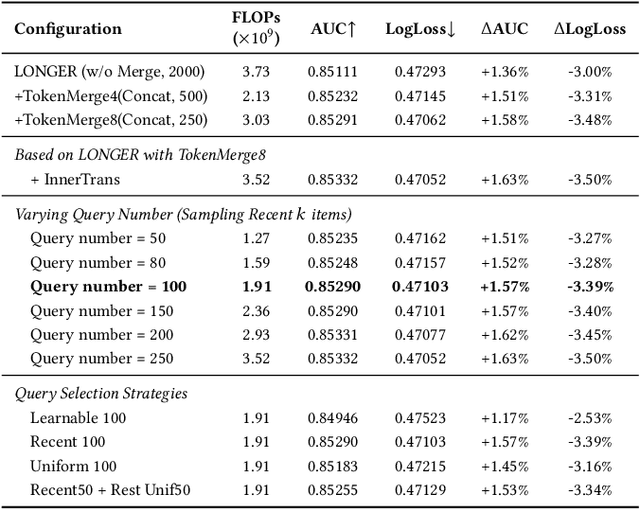
Abstract:Modeling ultra-long user behavior sequences is critical for capturing both long- and short-term preferences in industrial recommender systems. Existing solutions typically rely on two-stage retrieval or indirect modeling paradigms, incuring upstream-downstream inconsistency and computational inefficiency. In this paper, we present LONGER, a Long-sequence Optimized traNsformer for GPU-Efficient Recommenders. LONGER incorporates (i) a global token mechanism for stabilizing attention over long contexts, (ii) a token merge module with lightweight InnerTransformers and hybrid attention strategy to reduce quadratic complexity, and (iii) a series of engineering optimizations, including training with mixed-precision and activation recomputation, KV cache serving, and the fully synchronous model training and serving framework for unified GPU-based dense and sparse parameter updates. LONGER consistently outperforms strong baselines in both offline metrics and online A/B testing in both advertising and e-commerce services at ByteDance, validating its consistent effectiveness and industrial-level scaling laws. Currently, LONGER has been fully deployed at more than 10 influential scenarios at ByteDance, serving billion users.
Effective Reinforcement Learning Control using Conservative Soft Actor-Critic
May 06, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown great potential in complex control tasks, particularly when combined with deep neural networks within the Actor-Critic (AC) framework. However, in practical applications, balancing exploration, learning stability, and sample efficiency remains a significant challenge. Traditional methods such as Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) address these issues by incorporating entropy or relative entropy regularization, but often face problems of instability and low sample efficiency. In this paper, we propose the Conservative Soft Actor-Critic (CSAC) algorithm, which seamlessly integrates entropy and relative entropy regularization within the AC framework. CSAC improves exploration through entropy regularization while avoiding overly aggressive policy updates with the use of relative entropy regularization. Evaluations on benchmark tasks and real-world robotic simulations demonstrate that CSAC offers significant improvements in stability and efficiency over existing methods. These findings suggest that CSAC provides strong robustness and application potential in control tasks under dynamic environments.
Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models
Mar 26, 2025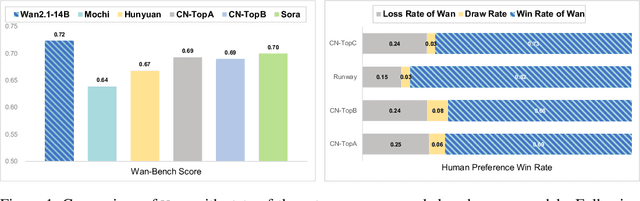



Abstract:This report presents Wan, a comprehensive and open suite of video foundation models designed to push the boundaries of video generation. Built upon the mainstream diffusion transformer paradigm, Wan achieves significant advancements in generative capabilities through a series of innovations, including our novel VAE, scalable pre-training strategies, large-scale data curation, and automated evaluation metrics. These contributions collectively enhance the model's performance and versatility. Specifically, Wan is characterized by four key features: Leading Performance: The 14B model of Wan, trained on a vast dataset comprising billions of images and videos, demonstrates the scaling laws of video generation with respect to both data and model size. It consistently outperforms the existing open-source models as well as state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple internal and external benchmarks, demonstrating a clear and significant performance superiority. Comprehensiveness: Wan offers two capable models, i.e., 1.3B and 14B parameters, for efficiency and effectiveness respectively. It also covers multiple downstream applications, including image-to-video, instruction-guided video editing, and personal video generation, encompassing up to eight tasks. Consumer-Grade Efficiency: The 1.3B model demonstrates exceptional resource efficiency, requiring only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with a wide range of consumer-grade GPUs. Openness: We open-source the entire series of Wan, including source code and all models, with the goal of fostering the growth of the video generation community. This openness seeks to significantly expand the creative possibilities of video production in the industry and provide academia with high-quality video foundation models. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/Wan-Video/Wan2.1.
Adaptive Domain Scaling for Personalized Sequential Modeling in Recommenders
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:Users generally exhibit complex behavioral patterns and diverse intentions in multiple business scenarios of super applications like Douyin, presenting great challenges to current industrial multi-domain recommenders. To mitigate the discrepancies across diverse domains, researches and industrial practices generally emphasize sophisticated network structures to accomodate diverse data distributions, while neglecting the inherent understanding of user behavioral sequence from the multi-domain perspective. In this paper, we present Adaptive Domain Scaling (ADS) model, which comprehensively enhances the personalization capability in target-aware sequence modeling across multiple domains. Specifically, ADS comprises of two major modules, including personalized sequence representation generation (PSRG) and personalized candidate representation generation (PCRG). The modules contribute to the tailored multi-domain learning by dynamically learning both the user behavioral sequence item representation and the candidate target item representation under different domains, facilitating adaptive user intention understanding. Experiments are performed on both a public dataset and two billion-scaled industrial datasets, and the extensive results verify the high effectiveness and compatibility of ADS. Besides, we conduct online experiments on two influential business scenarios including Douyin Advertisement Platform and Douyin E-commerce Service Platform, both of which show substantial business improvements. Currently, ADS has been fully deployed in many recommendation services at ByteDance, serving billions of users.
Dynamic High-Order Control Barrier Functions with Diffuser for Safety-Critical Trajectory Planning at Signal-Free Intersections
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:Planning safe and efficient trajectories through signal-free intersections presents significant challenges for autonomous vehicles (AVs), particularly in dynamic, multi-task environments with unpredictable interactions and an increased possibility of conflicts. This study aims to address these challenges by developing a robust, adaptive framework to ensure safety in such complex scenarios. Existing approaches often struggle to provide reliable safety mechanisms in dynamic and learn multi-task behaviors from demonstrations in signal-free intersections. This study proposes a safety-critical planning method that integrates Dynamic High-Order Control Barrier Functions (DHOCBF) with a diffusion-based model, called Dynamic Safety-Critical Diffuser (DSC-Diffuser), offering a robust solution for adaptive, safe, and multi-task driving in signal-free intersections. Our approach incorporates a goal-oriented, task-guided diffusion model, enabling the model to learn multiple driving tasks simultaneously from real-world data. To further ensure driving safety in dynamic environments, the proposed DHOCBF framework dynamically adjusts to account for the movements of surrounding vehicles, offering enhanced adaptability compared to traditional control barrier functions. Validity evaluations of DHOCBF, conducted through numerical simulations, demonstrate its robustness in adapting to variations in obstacle velocities, sizes, uncertainties, and locations, effectively maintaining driving safety across a wide range of complex and uncertain scenarios. Performance evaluations across various scenes confirm that DSC-Diffuser provides realistic, stable, and generalizable policies, equipping it with the flexibility to adapt to diverse driving tasks.
Divide and Conquer: Hybrid Pre-training for Person Search
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Large-scale pre-training has proven to be an effective method for improving performance across different tasks. Current person search methods use ImageNet pre-trained models for feature extraction, yet it is not an optimal solution due to the gap between the pre-training task and person search task (as a downstream task). Therefore, in this paper, we focus on pre-training for person search, which involves detecting and re-identifying individuals simultaneously. Although labeled data for person search is scarce, datasets for two sub-tasks person detection and re-identification are relatively abundant. To this end, we propose a hybrid pre-training framework specifically designed for person search using sub-task data only. It consists of a hybrid learning paradigm that handles data with different kinds of supervisions, and an intra-task alignment module that alleviates domain discrepancy under limited resources. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that investigates how to support full-task pre-training using sub-task data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our pre-trained model can achieve significant improvements across diverse protocols, such as person search method, fine-tuning data, pre-training data and model backbone. For example, our model improves ResNet50 based NAE by 10.3% relative improvement w.r.t. mAP. Our code and pre-trained models are released for plug-and-play usage to the person search community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge