Xuesong Wang
Frank
Multi-Scale Wavelet Transformers for Operator Learning of Dynamical Systems
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recent years have seen a surge in data-driven surrogates for dynamical systems that can be orders of magnitude faster than numerical solvers. However, many machine learning-based models such as neural operators exhibit spectral bias, attenuating high-frequency components that often encode small-scale structure. This limitation is particularly damaging in applications such as weather forecasting, where misrepresented high frequencies can induce long-horizon instability. To address this issue, we propose multi-scale wavelet transformers (MSWTs), which learn system dynamics in a tokenized wavelet domain. The wavelet transform explicitly separates low- and high-frequency content across scales. MSWTs leverage a wavelet-preserving downsampling scheme that retains high-frequency features and employ wavelet-based attention to capture dependencies across scales and frequency bands. Experiments on chaotic dynamical systems show substantial error reductions and improved long horizon spectral fidelity. On the ERA5 climate reanalysis, MSWTs further reduce climatological bias, demonstrating their effectiveness in a real-world forecasting setting.
Characteristics Analysis of Autonomous Vehicle Pre-crash Scenarios
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:To date, hundreds of crashes have occurred in open road testing of automated vehicles (AVs), highlighting the need for improving AV reliability and safety. Pre-crash scenario typology classifies crashes based on vehicle dynamics and kinematics features. Building on this, characteristics analysis can identify similar features under comparable crashes, offering a more effective reflection of general crash patterns and providing more targeted recommendations for enhancing AV performance. However, current studies primarily concentrated on crashes among conventional human-driven vehicles, leaving a gap in research dedicated to in-depth AV crash analyses. In this paper, we analyzed the latest California AV collision reports and used the newly revised pre-crash scenario typology to identify pre-crash scenarios. We proposed a set of mapping rules for automatically extracting these AV pre-crash scenarios, successfully identifying 24 types with a 98.1% accuracy rate, and obtaining two key scenarios of AV crashes (i.e., rear-end scenarios and intersection scenarios) through detailed analysis. Association analyses of rear-end scenarios showed that the significant environmental influencing factors were traffic control type, location type, light, etc. For intersection scenarios prone to severe crashes with detailed descriptions, we employed causal analyses to obtain the significant causal factors: habitual violations and expectations of certain behavior. Optimization recommendations were then formulated, addressing both governmental oversight and AV manufacturers' potential improvements. The findings of this paper could guide government authorities to develop related regulations, help manufacturers design AV test scenarios, and identify potential shortcomings in control algorithms specific to various real-world scenarios, thereby optimizing AV systems effectively.
Pre-Trained Large Language Model Based Remaining Useful Life Transfer Prediction of Bearing
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Accurately predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of rotating machinery, such as bearings, is essential for ensuring equipment reliability and minimizing unexpected industrial failures. Traditional data-driven deep learning methods face challenges in practical settings due to inconsistent training and testing data distributions and limited generalization for long-term predictions.
Deep Learning-Based Electricity Price Forecast for Virtual Bidding in Wholesale Electricity Market
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Virtual bidding plays an important role in two-settlement electric power markets, as it can reduce discrepancies between day-ahead and real-time markets. Renewable energy penetration increases volatility in electricity prices, making accurate forecasting critical for virtual bidders, reducing uncertainty and maximizing profits. This study presents a Transformer-based deep learning model to forecast the price spread between real-time and day-ahead electricity prices in the ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas) market. The proposed model leverages various time-series features, including load forecasts, solar and wind generation forecasts, and temporal attributes. The model is trained under realistic constraints and validated using a walk-forward approach by updating the model every week. Based on the price spread prediction results, several trading strategies are proposed and the most effective strategy for maximizing cumulative profit under realistic market conditions is identified through backtesting. The results show that the strategy of trading only at the peak hour with a precision score of over 50% produces nearly consistent profit over the test period. The proposed method underscores the importance of an accurate electricity price forecasting model and introduces a new method of evaluating the price forecast model from a virtual bidder's perspective, providing valuable insights for future research.
MetaFollower: Adaptable Personalized Autonomous Car Following
Jun 23, 2024



Abstract:Car-following (CF) modeling, a fundamental component in microscopic traffic simulation, has attracted increasing interest of researchers in the past decades. In this study, we propose an adaptable personalized car-following framework -MetaFollower, by leveraging the power of meta-learning. Specifically, we first utilize Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) to extract common driving knowledge from various CF events. Afterward, the pre-trained model can be fine-tuned on new drivers with only a few CF trajectories to achieve personalized CF adaptation. We additionally combine Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Intelligent Driver Model (IDM) to reflect temporal heterogeneity with high interpretability. Unlike conventional adaptive cruise control (ACC) systems that rely on predefined settings and constant parameters without considering heterogeneous driving characteristics, MetaFollower can accurately capture and simulate the intricate dynamics of car-following behavior while considering the unique driving styles of individual drivers. We demonstrate the versatility and adaptability of MetaFollower by showcasing its ability to adapt to new drivers with limited training data quickly. To evaluate the performance of MetaFollower, we conduct rigorous experiments comparing it with both data-driven and physics-based models. The results reveal that our proposed framework outperforms baseline models in predicting car-following behavior with higher accuracy and safety. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first car-following model aiming to achieve fast adaptation by considering both driver and temporal heterogeneity based on meta-learning.
Video Frame Interpolation for Polarization via Swin-Transformer
Jun 17, 2024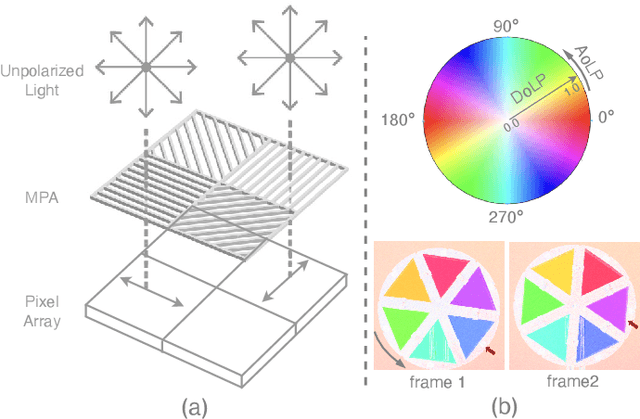
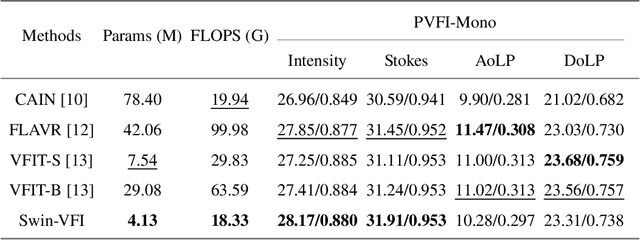
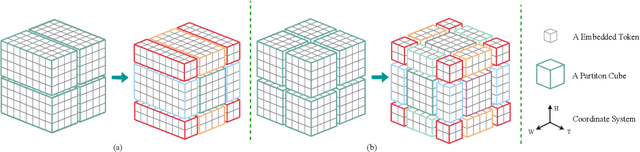
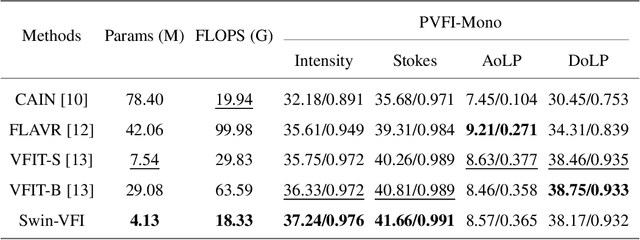
Abstract:Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) has been extensively explored and demonstrated, yet its application to polarization remains largely unexplored. Due to the selective transmission of light by polarized filters, longer exposure times are typically required to ensure sufficient light intensity, which consequently lower the temporal sample rates. Furthermore, because polarization reflected by objects varies with shooting perspective, focusing solely on estimating pixel displacement is insufficient to accurately reconstruct the intermediate polarization. To tackle these challenges, this study proposes a multi-stage and multi-scale network called Swin-VFI based on the Swin-Transformer and introduces a tailored loss function to facilitate the network's understanding of polarization changes. To ensure the practicality of our proposed method, this study evaluates its interpolated frames in Shape from Polarization (SfP) and Human Shape Reconstruction tasks, comparing them with other state-of-the-art methods such as CAIN, FLAVR, and VFIT. Experimental results demonstrate our approach's superior reconstruction accuracy across all tasks.
Rényi Neural Processes
May 25, 2024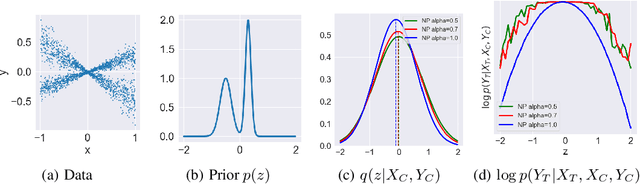
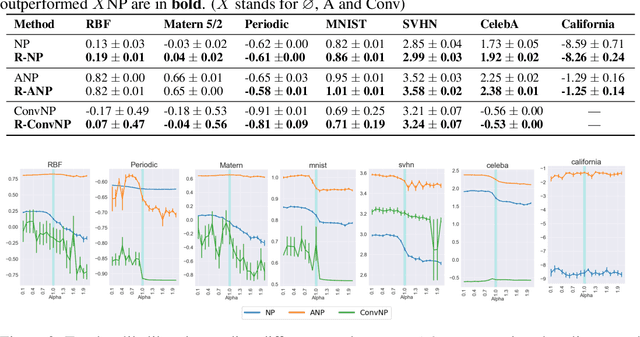
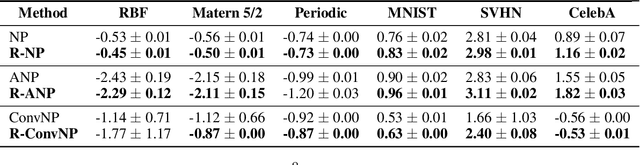
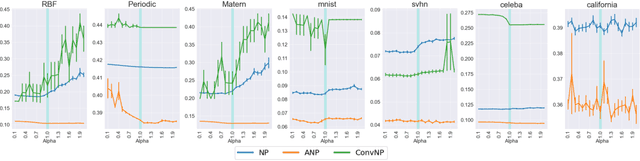
Abstract:Neural Processes (NPs) are variational frameworks that aim to represent stochastic processes with deep neural networks. Despite their obvious benefits in uncertainty estimation for complex distributions via data-driven priors, NPs enforce network parameter sharing between the conditional prior and posterior distributions, thereby risking introducing a misspecified prior. We hereby propose R\'enyi Neural Processes (RNP) to relax the influence of the misspecified prior and optimize a tighter bound of the marginal likelihood. More specifically, by replacing the standard KL divergence with the R\'enyi divergence between the posterior and the approximated prior, we ameliorate the impact of the misspecified prior via a parameter {\alpha} so that the resulting posterior focuses more on tail samples and reduce density on overconfident regions. Our experiments showed log-likelihood improvements on several existing NP families. We demonstrated the superior performance of our approach on various benchmarks including regression and image inpainting tasks. We also validate the effectiveness of RNPs on real-world tabular regression problems.
Deep Learning-Based Weather-Related Power Outage Prediction with Socio-Economic and Power Infrastructure Data
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a deep learning-based approach for hourly power outage probability prediction within census tracts encompassing a utility company's service territory. Two distinct deep learning models, conditional Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) and unconditional MLP, were developed to forecast power outage probabilities, leveraging a rich array of input features gathered from publicly available sources including weather data, weather station locations, power infrastructure maps, socio-economic and demographic statistics, and power outage records. Given a one-hour-ahead weather forecast, the models predict the power outage probability for each census tract, taking into account both the weather prediction and the location's characteristics. The deep learning models employed different loss functions to optimize prediction performance. Our experimental results underscore the significance of socio-economic factors in enhancing the accuracy of power outage predictions at the census tract level.
LC-LLM: Explainable Lane-Change Intention and Trajectory Predictions with Large Language Models
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:To ensure safe driving in dynamic environments, autonomous vehicles should possess the capability to accurately predict the lane change intentions of surrounding vehicles in advance and forecast their future trajectories. Existing motion prediction approaches have ample room for improvement, particularly in terms of long-term prediction accuracy and interpretability. In this paper, we address these challenges by proposing LC-LLM, an explainable lane change prediction model that leverages the strong reasoning capabilities and self-explanation abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Essentially, we reformulate the lane change prediction task as a language modeling problem, processing heterogeneous driving scenario information in natural language as prompts for input into the LLM and employing a supervised fine-tuning technique to tailor the LLM specifically for our lane change prediction task. This allows us to utilize the LLM's powerful common sense reasoning abilities to understand complex interactive information, thereby improving the accuracy of long-term predictions. Furthermore, we incorporate explanatory requirements into the prompts in the inference stage. Therefore, our LC-LLM model not only can predict lane change intentions and trajectories but also provides explanations for its predictions, enhancing the interpretability. Extensive experiments on the large-scale highD dataset demonstrate the superior performance and interpretability of our LC-LLM in lane change prediction task. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to utilize LLMs for predicting lane change behavior. Our study shows that LLMs can encode comprehensive interaction information for driving behavior understanding.
Active Learning for NLP with Large Language Models
Jan 14, 2024



Abstract:Human annotation of training samples is expensive, laborious, and sometimes challenging, especially for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. To reduce the labeling cost and enhance the sample efficiency, Active Learning (AL) technique can be used to label as few samples as possible to reach a reasonable or similar results. To reduce even more costs and with the significant advances of Large Language Models (LLMs), LLMs can be a good candidate to annotate samples. This work investigates the accuracy and cost of using LLMs (GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) to label samples on 3 different datasets. A consistency-based strategy is proposed to select samples that are potentially incorrectly labeled so that human annotations can be used for those samples in AL settings, and we call it mixed annotation strategy. Then we test performance of AL under two different settings: (1) using human annotations only; (2) using the proposed mixed annotation strategy. The accuracy of AL models under 3 AL query strategies are reported on 3 text classification datasets, i.e., AG's News, TREC-6, and Rotten Tomatoes. On AG's News and Rotten Tomatoes, the models trained with the mixed annotation strategy achieves similar or better results compared to that with human annotations. The method reveals great potentials of LLMs as annotators in terms of accuracy and cost efficiency in active learning settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge