Xianyu Wu
MuS-Polar3D: A Benchmark Dataset for Computational Polarimetric 3D Imaging under Multi-Scattering Conditions
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Polarization-based underwater 3D imaging exploits polarization cues to suppress background scattering, exhibiting distinct advantages in turbid water. Although data-driven polarization-based underwater 3D reconstruction methods show great potential, existing public datasets lack sufficient diversity in scattering and observation conditions, hindering fair comparisons among different approaches, including single-view and multi-view polarization imaging methods. To address this limitation, we construct MuS-Polar3D, a benchmark dataset comprising polarization images of 42 objects captured under seven quantitatively controlled scattering conditions and five viewpoints, together with high-precision 3D models (+/- 0.05 mm accuracy), normal maps, and foreground masks. The dataset supports multiple vision tasks, including normal estimation, object segmentation, descattering, and 3D reconstruction. Inspired by computational imaging, we further decouple underwater 3D reconstruction under scattering into a two-stage pipeline, namely descattering followed by 3D reconstruction, from an imaging-chain perspective. Extensive evaluations using multiple baseline methods under complex scattering conditions demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed benchmark, achieving a best mean angular error of 15.49 degrees. To the best of our knowledge, MuS-Polar3D is the first publicly available benchmark dataset for quantitative turbidity underwater polarization-based 3D imaging, enabling accurate reconstruction and fair algorithm evaluation under controllable scattering conditions. The dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/WangPuyun/MuS-Polar3D.
Video Frame Interpolation for Polarization via Swin-Transformer
Jun 17, 2024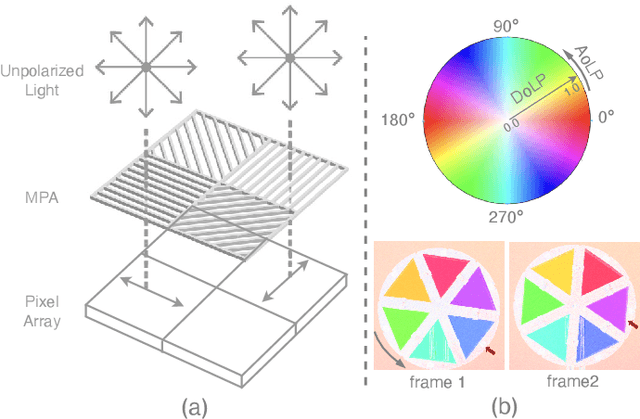
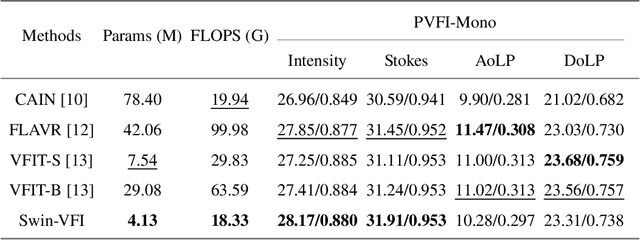
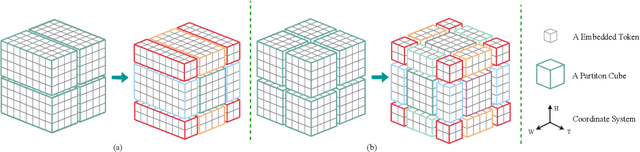
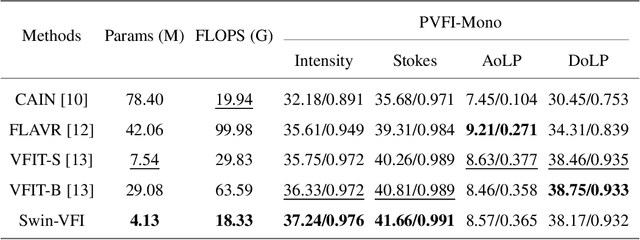
Abstract:Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) has been extensively explored and demonstrated, yet its application to polarization remains largely unexplored. Due to the selective transmission of light by polarized filters, longer exposure times are typically required to ensure sufficient light intensity, which consequently lower the temporal sample rates. Furthermore, because polarization reflected by objects varies with shooting perspective, focusing solely on estimating pixel displacement is insufficient to accurately reconstruct the intermediate polarization. To tackle these challenges, this study proposes a multi-stage and multi-scale network called Swin-VFI based on the Swin-Transformer and introduces a tailored loss function to facilitate the network's understanding of polarization changes. To ensure the practicality of our proposed method, this study evaluates its interpolated frames in Shape from Polarization (SfP) and Human Shape Reconstruction tasks, comparing them with other state-of-the-art methods such as CAIN, FLAVR, and VFIT. Experimental results demonstrate our approach's superior reconstruction accuracy across all tasks.
Infrared Polarization Imaging-based Non-destructive Thermography Inspection
May 06, 2024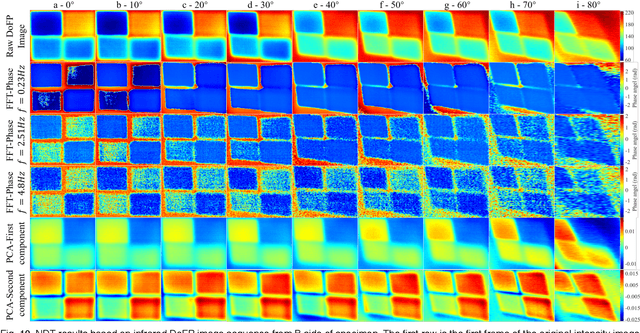
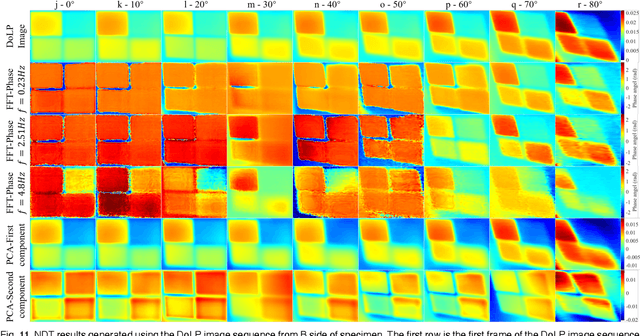
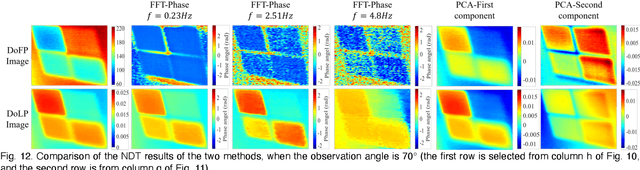
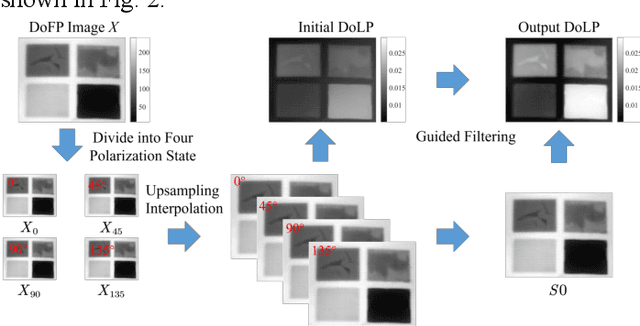
Abstract:Infrared pulse thermography non-destructive testing (NDT) method is developed based on the difference in the infrared radiation intensity emitted by defective and non-defective areas of an object. However, when the radiation intensity of the defective target is similar to that of the non-defective area of the object, the detection results are poor. To address this issue, this study investigated the polarization characteristics of the infrared radiation of different materials. Simulation results showed that the degree of infrared polarization of the object surface changed regularly with changes in thermal environment radiation. An infrared polarization imaging-based NDT method was proposed and demonstrated using specimens with four different simulated defective areas, which were designed and fabricated using four different materials. The experimental results were consistent with the simulation results, thereby proving the effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared with the infrared-radiation-intensity-based NDT method, the proposed method improved the image detail presentation and detection accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge