Shaoshuai Shi
LIVE: Long-horizon Interactive Video World Modeling
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive video world models predict future visual observations conditioned on actions. While effective over short horizons, these models often struggle with long-horizon generation, as small prediction errors accumulate over time. Prior methods alleviate this by introducing pre-trained teacher models and sequence-level distribution matching, which incur additional computational cost and fail to prevent error propagation beyond the training horizon. In this work, we propose LIVE, a Long-horizon Interactive Video world modEl that enforces bounded error accumulation via a novel cycle-consistency objective, thereby eliminating the need for teacher-based distillation. Specifically, LIVE first performs a forward rollout from ground-truth frames and then applies a reverse generation process to reconstruct the initial state. The diffusion loss is subsequently computed on the reconstructed terminal state, providing an explicit constraint on long-horizon error propagation. Moreover, we provide an unified view that encompasses different approaches and introduce progressive training curriculum to stabilize training. Experiments demonstrate that LIVE achieves state-of-the-art performance on long-horizon benchmarks, generating stable, high-quality videos far beyond training rollout lengths.
ColaVLA: Leveraging Cognitive Latent Reasoning for Hierarchical Parallel Trajectory Planning in Autonomous Driving
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving requires generating safe and reliable trajectories from complex multimodal inputs. Traditional modular pipelines separate perception, prediction, and planning, while recent end-to-end (E2E) systems learn them jointly. Vision-language models (VLMs) further enrich this paradigm by introducing cross-modal priors and commonsense reasoning, yet current VLM-based planners face three key challenges: (i) a mismatch between discrete text reasoning and continuous control, (ii) high latency from autoregressive chain-of-thought decoding, and (iii) inefficient or non-causal planners that limit real-time deployment. We propose ColaVLA, a unified vision-language-action framework that transfers reasoning from text to a unified latent space and couples it with a hierarchical, parallel trajectory decoder. The Cognitive Latent Reasoner compresses scene understanding into compact, decision-oriented meta-action embeddings through ego-adaptive selection and only two VLM forward passes. The Hierarchical Parallel Planner then generates multi-scale, causality-consistent trajectories in a single forward pass. Together, these components preserve the generalization and interpretability of VLMs while enabling efficient, accurate and safe trajectory generation. Experiments on the nuScenes benchmark show that ColaVLA achieves state-of-the-art performance in both open-loop and closed-loop settings with favorable efficiency and robustness.
GeoPredict: Leveraging Predictive Kinematics and 3D Gaussian Geometry for Precise VLA Manipulation
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models achieve strong generalization in robotic manipulation but remain largely reactive and 2D-centric, making them unreliable in tasks that require precise 3D reasoning. We propose GeoPredict, a geometry-aware VLA framework that augments a continuous-action policy with predictive kinematic and geometric priors. GeoPredict introduces a trajectory-level module that encodes motion history and predicts multi-step 3D keypoint trajectories of robot arms, and a predictive 3D Gaussian geometry module that forecasts workspace geometry with track-guided refinement along future keypoint trajectories. These predictive modules serve exclusively as training-time supervision through depth-based rendering, while inference requires only lightweight additional query tokens without invoking any 3D decoding. Experiments on RoboCasa Human-50, LIBERO, and real-world manipulation tasks show that GeoPredict consistently outperforms strong VLA baselines, especially in geometry-intensive and spatially demanding scenarios.
UniSplat: Unified Spatio-Temporal Fusion via 3D Latent Scaffolds for Dynamic Driving Scene Reconstruction
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Feed-forward 3D reconstruction for autonomous driving has advanced rapidly, yet existing methods struggle with the joint challenges of sparse, non-overlapping camera views and complex scene dynamics. We present UniSplat, a general feed-forward framework that learns robust dynamic scene reconstruction through unified latent spatio-temporal fusion. UniSplat constructs a 3D latent scaffold, a structured representation that captures geometric and semantic scene context by leveraging pretrained foundation models. To effectively integrate information across spatial views and temporal frames, we introduce an efficient fusion mechanism that operates directly within the 3D scaffold, enabling consistent spatio-temporal alignment. To ensure complete and detailed reconstructions, we design a dual-branch decoder that generates dynamic-aware Gaussians from the fused scaffold by combining point-anchored refinement with voxel-based generation, and maintain a persistent memory of static Gaussians to enable streaming scene completion beyond current camera coverage. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that UniSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis, while providing robust and high-quality renderings even for viewpoints outside the original camera coverage.
Foresight in Motion: Reinforcing Trajectory Prediction with Reward Heuristics
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Motion forecasting for on-road traffic agents presents both a significant challenge and a critical necessity for ensuring safety in autonomous driving systems. In contrast to most existing data-driven approaches that directly predict future trajectories, we rethink this task from a planning perspective, advocating a "First Reasoning, Then Forecasting" strategy that explicitly incorporates behavior intentions as spatial guidance for trajectory prediction. To achieve this, we introduce an interpretable, reward-driven intention reasoner grounded in a novel query-centric Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) scheme. Our method first encodes traffic agents and scene elements into a unified vectorized representation, then aggregates contextual features through a query-centric paradigm. This enables the derivation of a reward distribution, a compact yet informative representation of the target agent's behavior within the given scene context via IRL. Guided by this reward heuristic, we perform policy rollouts to reason about multiple plausible intentions, providing valuable priors for subsequent trajectory generation. Finally, we develop a hierarchical DETR-like decoder integrated with bidirectional selective state space models to produce accurate future trajectories along with their associated probabilities. Extensive experiments on the large-scale Argoverse and nuScenes motion forecasting datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances trajectory prediction confidence, achieving highly competitive performance relative to state-of-the-art methods.
Edit360: 2D Image Edits to 3D Assets from Any Angle
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have significantly improved image generation and editing, but extending these capabilities to 3D assets remains challenging, especially for fine-grained edits that require multi-view consistency. Existing methods typically restrict editing to predetermined viewing angles, severely limiting their flexibility and practical applications. We introduce Edit360, a tuning-free framework that extends 2D modifications to multi-view consistent 3D editing. Built upon video diffusion models, Edit360 enables user-specific editing from arbitrary viewpoints while ensuring structural coherence across all views. The framework selects anchor views for 2D modifications and propagates edits across the entire 360-degree range. To achieve this, Edit360 introduces a novel Anchor-View Editing Propagation mechanism, which effectively aligns and merges multi-view information within the latent and attention spaces of diffusion models. The resulting edited multi-view sequences facilitate the reconstruction of high-quality 3D assets, enabling customizable 3D content creation.
TrajFlow: Multi-modal Motion Prediction via Flow Matching
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Efficient and accurate motion prediction is crucial for ensuring safety and informed decision-making in autonomous driving, particularly under dynamic real-world conditions that necessitate multi-modal forecasts. We introduce TrajFlow, a novel flow matching-based motion prediction framework that addresses the scalability and efficiency challenges of existing generative trajectory prediction methods. Unlike conventional generative approaches that employ i.i.d. sampling and require multiple inference passes to capture diverse outcomes, TrajFlow predicts multiple plausible future trajectories in a single pass, significantly reducing computational overhead while maintaining coherence across predictions. Moreover, we propose a ranking loss based on the Plackett-Luce distribution to improve uncertainty estimation of predicted trajectories. Additionally, we design a self-conditioning training technique that reuses the model's own predictions to construct noisy inputs during a second forward pass, thereby improving generalization and accelerating inference. Extensive experiments on the large-scale Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD) demonstrate that TrajFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance across various key metrics, underscoring its effectiveness for safety-critical autonomous driving applications. The code and other details are available on the project website https://traj-flow.github.io/.
DriveX: Omni Scene Modeling for Learning Generalizable World Knowledge in Autonomous Driving
May 25, 2025Abstract:Data-driven learning has advanced autonomous driving, yet task-specific models struggle with out-of-distribution scenarios due to their narrow optimization objectives and reliance on costly annotated data. We present DriveX, a self-supervised world model that learns generalizable scene dynamics and holistic representations (geometric, semantic, and motion) from large-scale driving videos. DriveX introduces Omni Scene Modeling (OSM), a module that unifies multimodal supervision-3D point cloud forecasting, 2D semantic representation, and image generation-to capture comprehensive scene evolution. To simplify learning complex dynamics, we propose a decoupled latent world modeling strategy that separates world representation learning from future state decoding, augmented by dynamic-aware ray sampling to enhance motion modeling. For downstream adaptation, we design Future Spatial Attention (FSA), a unified paradigm that dynamically aggregates spatiotemporal features from DriveX's predictions to enhance task-specific inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate DriveX's effectiveness: it achieves significant improvements in 3D future point cloud prediction over prior work, while attaining state-of-the-art results on diverse tasks including occupancy prediction, flow estimation, and end-to-end driving. These results validate DriveX's capability as a general-purpose world model, paving the way for robust and unified autonomous driving frameworks.
SOLVE: Synergy of Language-Vision and End-to-End Networks for Autonomous Driving
May 22, 2025Abstract:The integration of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) into autonomous driving systems has shown promise in addressing key challenges such as learning complexity, interpretability, and common-sense reasoning. However, existing approaches often struggle with efficient integration and realtime decision-making due to computational demands. In this paper, we introduce SOLVE, an innovative framework that synergizes VLMs with end-to-end (E2E) models to enhance autonomous vehicle planning. Our approach emphasizes knowledge sharing at the feature level through a shared visual encoder, enabling comprehensive interaction between VLM and E2E components. We propose a Trajectory Chain-of-Thought (T-CoT) paradigm, which progressively refines trajectory predictions, reducing uncertainty and improving accuracy. By employing a temporal decoupling strategy, SOLVE achieves efficient cooperation by aligning high-quality VLM outputs with E2E real-time performance. Evaluated on the nuScenes dataset, our method demonstrates significant improvements in trajectory prediction accuracy, paving the way for more robust and reliable autonomous driving systems.
Exposing the Copycat Problem of Imitation-based Planner: A Novel Closed-Loop Simulator, Causal Benchmark and Joint IL-RL Baseline
Apr 20, 2025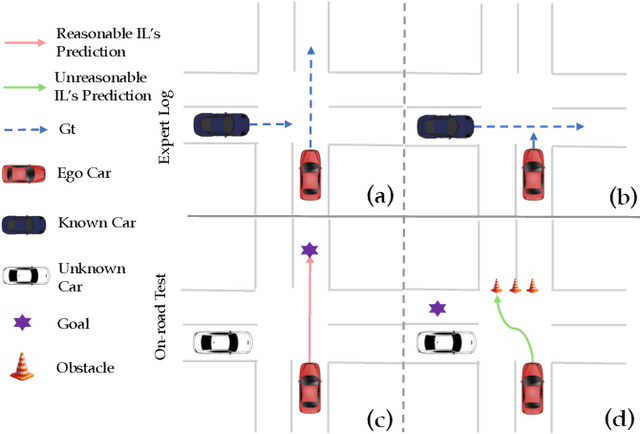
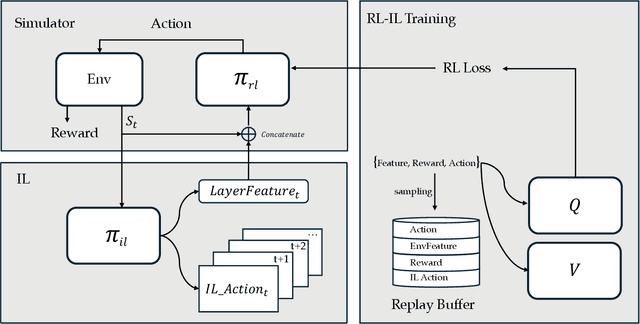
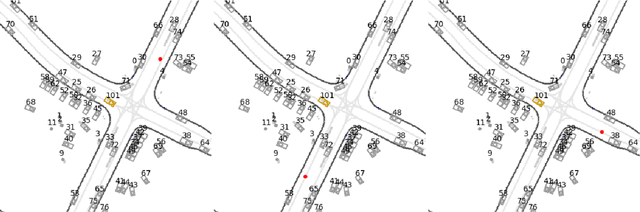
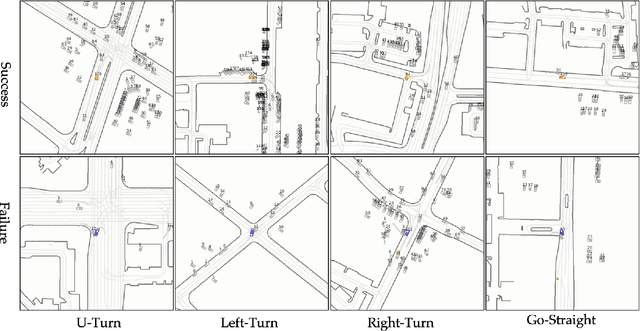
Abstract:Machine learning (ML)-based planners have recently gained significant attention. They offer advantages over traditional optimization-based planning algorithms. These advantages include fewer manually selected parameters and faster development. Within ML-based planning, imitation learning (IL) is a common algorithm. It primarily learns driving policies directly from supervised trajectory data. While IL has demonstrated strong performance on many open-loop benchmarks, it remains challenging to determine if the learned policy truly understands fundamental driving principles, rather than simply extrapolating from the ego-vehicle's initial state. Several studies have identified this limitation and proposed algorithms to address it. However, these methods often use original datasets for evaluation. In these datasets, future trajectories are heavily dependent on initial conditions. Furthermore, IL often overfits to the most common scenarios. It struggles to generalize to rare or unseen situations. To address these challenges, this work proposes: 1) a novel closed-loop simulator supporting both imitation and reinforcement learning, 2) a causal benchmark derived from the Waymo Open Dataset to rigorously assess the impact of the copycat problem, and 3) a novel framework integrating imitation learning and reinforcement learning to overcome the limitations of purely imitative approaches. The code for this work will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge