Muhammad Ferjad Naeem
RefAM: Attention Magnets for Zero-Shot Referral Segmentation
Sep 26, 2025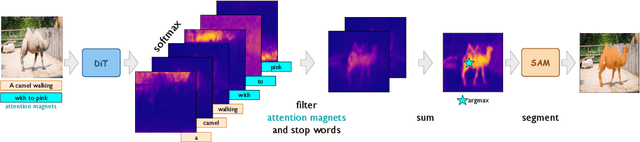
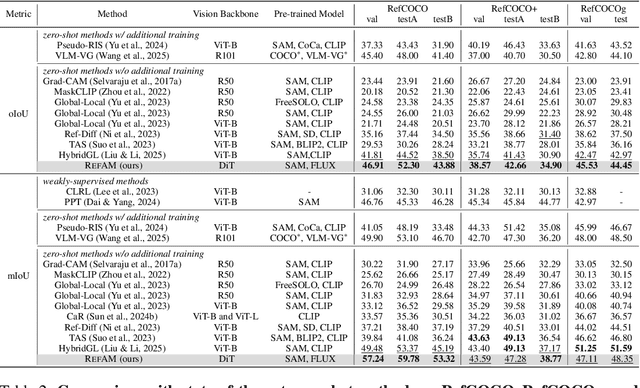

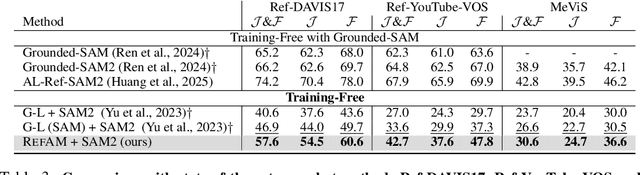
Abstract:Most existing approaches to referring segmentation achieve strong performance only through fine-tuning or by composing multiple pre-trained models, often at the cost of additional training and architectural modifications. Meanwhile, large-scale generative diffusion models encode rich semantic information, making them attractive as general-purpose feature extractors. In this work, we introduce a new method that directly exploits features, attention scores, from diffusion transformers for downstream tasks, requiring neither architectural modifications nor additional training. To systematically evaluate these features, we extend benchmarks with vision-language grounding tasks spanning both images and videos. Our key insight is that stop words act as attention magnets: they accumulate surplus attention and can be filtered to reduce noise. Moreover, we identify global attention sinks (GAS) emerging in deeper layers and show that they can be safely suppressed or redirected onto auxiliary tokens, leading to sharper and more accurate grounding maps. We further propose an attention redistribution strategy, where appended stop words partition background activations into smaller clusters, yielding sharper and more localized heatmaps. Building on these findings, we develop RefAM, a simple training-free grounding framework that combines cross-attention maps, GAS handling, and redistribution. Across zero-shot referring image and video segmentation benchmarks, our approach consistently outperforms prior methods, establishing a new state of the art without fine-tuning or additional components.
SigLIP 2: Multilingual Vision-Language Encoders with Improved Semantic Understanding, Localization, and Dense Features
Feb 20, 2025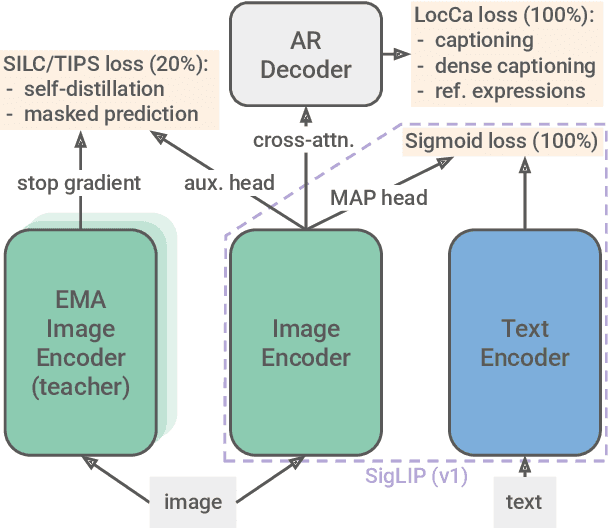
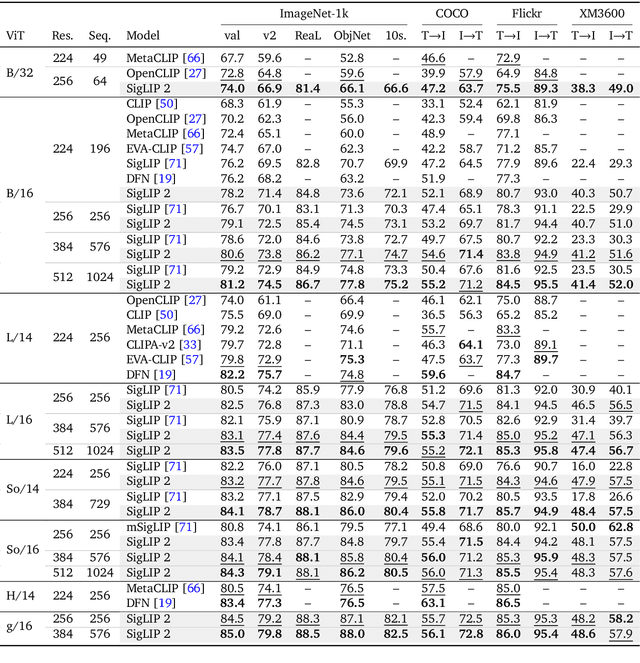
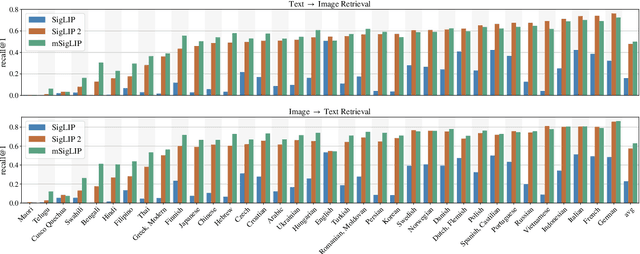
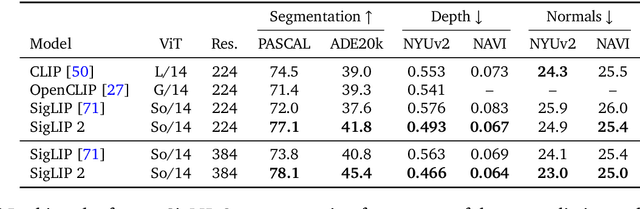
Abstract:We introduce SigLIP 2, a family of new multilingual vision-language encoders that build on the success of the original SigLIP. In this second iteration, we extend the original image-text training objective with several prior, independently developed techniques into a unified recipe -- this includes captioning-based pretraining, self-supervised losses (self-distillation, masked prediction) and online data curation. With these changes, SigLIP 2 models outperform their SigLIP counterparts at all model scales in core capabilities, including zero-shot classification, image-text retrieval, and transfer performance when extracting visual representations for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Furthermore, the new training recipe leads to significant improvements on localization and dense prediction tasks. We also train variants which support multiple resolutions and preserve the input's native aspect ratio. Finally, we train on a more diverse data-mixture that includes de-biasing techniques, leading to much better multilingual understanding and improved fairness. To allow users to trade off inference cost with performance, we release model checkpoints at four sizes: ViT-B (86M), L (303M), So400m (400M), and g (1B).
Active Data Curation Effectively Distills Large-Scale Multimodal Models
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is the de facto standard for compressing large-scale models into smaller ones. Prior works have explored ever more complex KD strategies involving different objective functions, teacher-ensembles, and weight inheritance. In this work we explore an alternative, yet simple approach -- active data curation as effective distillation for contrastive multimodal pretraining. Our simple online batch selection method, ACID, outperforms strong KD baselines across various model-, data- and compute-configurations. Further, we find such an active data curation strategy to in fact be complementary to standard KD, and can be effectively combined to train highly performant inference-efficient models. Our simple and scalable pretraining framework, ACED, achieves state-of-the-art results across 27 zero-shot classification and retrieval tasks with upto 11% less inference FLOPs. We further demonstrate that our ACED models yield strong vision-encoders for training generative multimodal models in the LiT-Decoder setting, outperforming larger vision encoders for image-captioning and visual question-answering tasks.
TokenFormer: Rethinking Transformer Scaling with Tokenized Model Parameters
Oct 30, 2024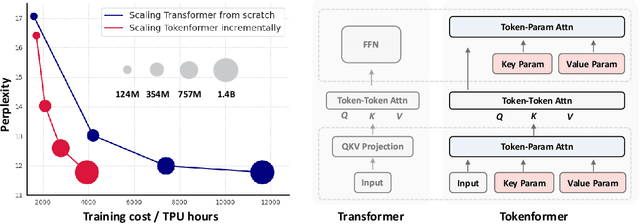
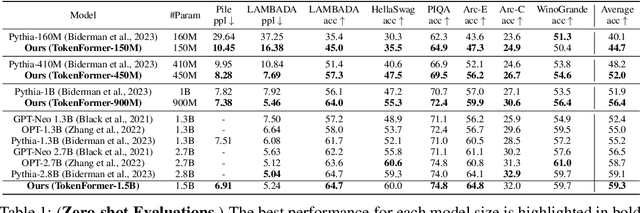
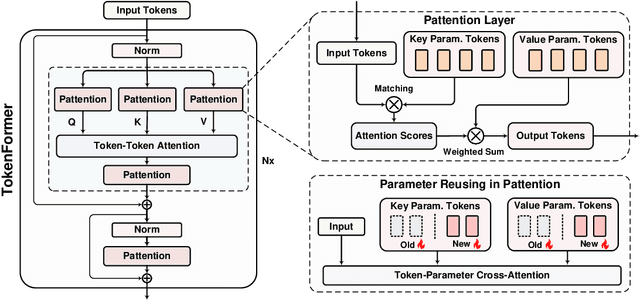
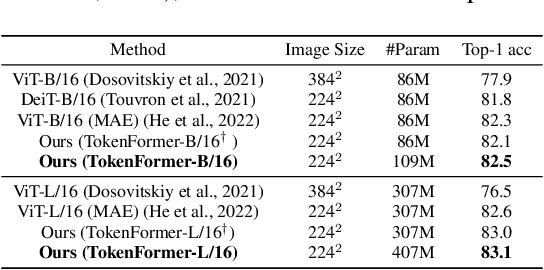
Abstract:Transformers have become the predominant architecture in foundation models due to their excellent performance across various domains. However, the substantial cost of scaling these models remains a significant concern. This problem arises primarily from their dependence on a fixed number of parameters within linear projections. When architectural modifications (e.g., channel dimensions) are introduced, the entire model typically requires retraining from scratch. As model sizes continue growing, this strategy results in increasingly high computational costs and becomes unsustainable. To overcome this problem, we introduce TokenFormer, a natively scalable architecture that leverages the attention mechanism not only for computations among input tokens but also for interactions between tokens and model parameters, thereby enhancing architectural flexibility. By treating model parameters as tokens, we replace all the linear projections in Transformers with our token-parameter attention layer, where input tokens act as queries and model parameters as keys and values. This reformulation allows for progressive and efficient scaling without necessitating retraining from scratch. Our model scales from 124M to 1.4B parameters by incrementally adding new key-value parameter pairs, achieving performance comparable to Transformers trained from scratch while greatly reducing training costs. Code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/Haiyang-W/TokenFormer}.
Toward a Diffusion-Based Generalist for Dense Vision Tasks
Jun 29, 2024



Abstract:Building generalized models that can solve many computer vision tasks simultaneously is an intriguing direction. Recent works have shown image itself can be used as a natural interface for general-purpose visual perception and demonstrated inspiring results. In this paper, we explore diffusion-based vision generalists, where we unify different types of dense prediction tasks as conditional image generation and re-purpose pre-trained diffusion models for it. However, directly applying off-the-shelf latent diffusion models leads to a quantization issue. Thus, we propose to perform diffusion in pixel space and provide a recipe for finetuning pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models for dense vision tasks. In experiments, we evaluate our method on four different types of tasks and show competitive performance to the other vision generalists.
How Good is my Video LMM? Complex Video Reasoning and Robustness Evaluation Suite for Video-LMMs
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to the development of Video Large Multi-modal Models (Video-LMMs) that can handle a wide range of video understanding tasks. These models have the potential to be deployed in real-world applications such as robotics, AI assistants, medical surgery, and autonomous vehicles. The widespread adoption of Video-LMMs in our daily lives underscores the importance of ensuring and evaluating their robust performance in mirroring human-like reasoning and interaction capabilities in complex, real-world contexts. However, existing benchmarks for Video-LMMs primarily focus on general video comprehension abilities and neglect assessing their reasoning capabilities over complex videos in the real-world context, and robustness of these models through the lens of user prompts as text queries. In this paper, we present the Complex Video Reasoning and Robustness Evaluation Suite (CVRR-ES), a novel benchmark that comprehensively assesses the performance of Video-LMMs across 11 diverse real-world video dimensions. We evaluate 9 recent models, including both open-source and closed-source variants, and find that most of the Video-LMMs, especially open-source ones, struggle with robustness and reasoning when dealing with complex videos. Based on our analysis, we develop a training-free Dual-Step Contextual Prompting (DSCP) technique to enhance the performance of existing Video-LMMs. Our findings provide valuable insights for building the next generation of human-centric AI systems with advanced robustness and reasoning capabilities. Our dataset and code are publicly available at: https://mbzuai-oryx.github.io/CVRR-Evaluation-Suite/.
Complex Video Reasoning and Robustness Evaluation Suite for Video-LMMs
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to the development of Video Large Multi-modal Models (Video-LMMs) that can handle a wide range of video understanding tasks. These models have the potential to be deployed in real-world applications such as robotics, AI assistants, medical imaging, and autonomous vehicles. The widespread adoption of Video-LMMs in our daily lives underscores the importance of ensuring and evaluating their robust performance in mirroring human-like reasoning and interaction capabilities in complex, real-world contexts. However, existing benchmarks for Video-LMMs primarily focus on general video comprehension abilities and neglect assessing their reasoning capabilities over complex videos in the real-world context, and robustness of these models through the lens of user prompts as text queries. In this paper, we present the Complex Video Reasoning and Robustness Evaluation Suite (CVRR-ES), a novel benchmark that comprehensively assesses the performance of Video-LMMs across 11 diverse real-world video dimensions. We evaluate 9 recent models, including both open-source and closed-source variants, and find that most of the Video-LMMs, {especially open-source ones,} struggle with robustness and reasoning when dealing with complex videos. Based on our analysis, we develop a training-free Dual-Step Contextual Prompting (DSCP) technique to enhance the performance of existing Video-LMMs. Our findings provide valuable insights for building the next generation of human-centric AI systems with advanced robustness and reasoning capabilities. Our dataset and code are publicly available at: https://mbzuai-oryx.github.io/CVRR-Evaluation-Suite/.
GiT: Towards Generalist Vision Transformer through Universal Language Interface
Mar 14, 2024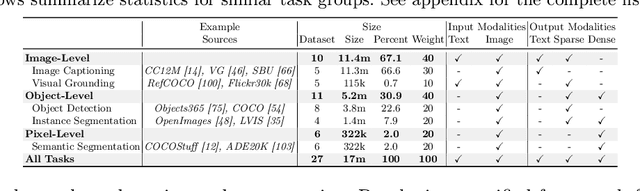
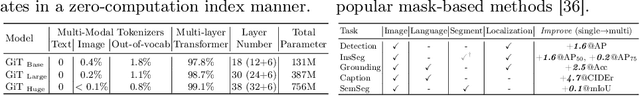
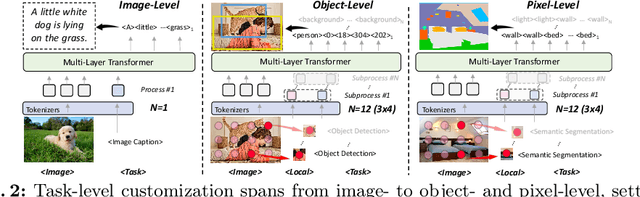
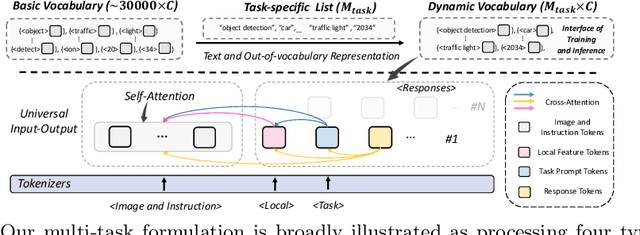
Abstract:This paper proposes a simple, yet effective framework, called GiT, simultaneously applicable for various vision tasks only with a vanilla ViT. Motivated by the universality of the Multi-layer Transformer architecture (e.g, GPT) widely used in large language models (LLMs), we seek to broaden its scope to serve as a powerful vision foundation model (VFM). However, unlike language modeling, visual tasks typically require specific modules, such as bounding box heads for detection and pixel decoders for segmentation, greatly hindering the application of powerful multi-layer transformers in the vision domain. To solve this, we design a universal language interface that empowers the successful auto-regressive decoding to adeptly unify various visual tasks, from image-level understanding (e.g., captioning), over sparse perception (e.g., detection), to dense prediction (e.g., segmentation). Based on the above designs, the entire model is composed solely of a ViT, without any specific additions, offering a remarkable architectural simplification. GiT is a multi-task visual model, jointly trained across five representative benchmarks without task-specific fine-tuning. Interestingly, our GiT builds a new benchmark in generalist performance, and fosters mutual enhancement across tasks, leading to significant improvements compared to isolated training. This reflects a similar impact observed in LLMs. Further enriching training with 27 datasets, GiT achieves strong zero-shot results over various tasks. Due to its simple design, this paradigm holds promise for narrowing the architectural gap between vision and language. Code and models will be available at \url{https://github.com/Haiyang-W/GiT}.
FocusCLIP: Multimodal Subject-Level Guidance for Zero-Shot Transfer in Human-Centric Tasks
Mar 11, 2024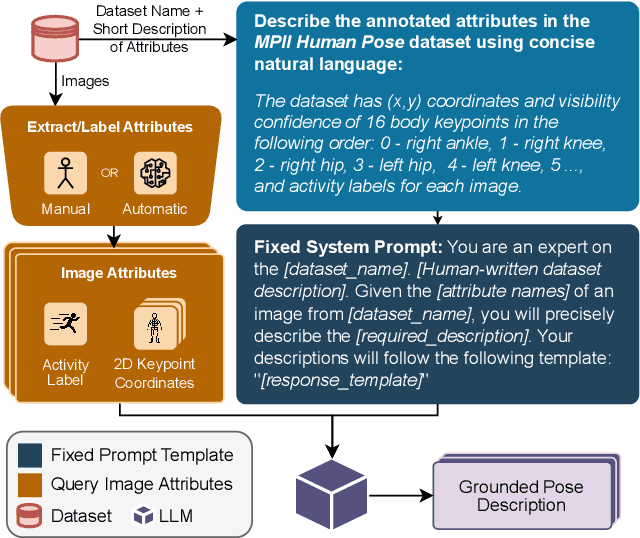
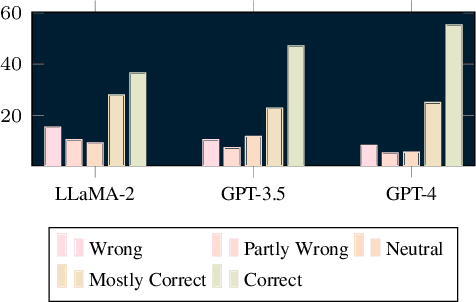

Abstract:We propose FocusCLIP, integrating subject-level guidance--a specialized mechanism for target-specific supervision--into the CLIP framework for improved zero-shot transfer on human-centric tasks. Our novel contributions enhance CLIP on both the vision and text sides. On the vision side, we incorporate ROI heatmaps emulating human visual attention mechanisms to emphasize subject-relevant image regions. On the text side, we introduce human pose descriptions to provide rich contextual information. For human-centric tasks, FocusCLIP is trained with images from the MPII Human Pose dataset. The proposed approach surpassed CLIP by an average of 8.61% across five previously unseen datasets covering three human-centric tasks. FocusCLIP achieved an average accuracy of 33.65% compared to 25.04% by CLIP. We observed a 3.98% improvement in activity recognition, a 14.78% improvement in age classification, and a 7.06% improvement in emotion recognition. Moreover, using our proposed single-shot LLM prompting strategy, we release a high-quality MPII Pose Descriptions dataset to encourage further research in multimodal learning for human-centric tasks. Furthermore, we also demonstrate the effectiveness of our subject-level supervision on non-human-centric tasks. FocusCLIP shows a 2.47% improvement over CLIP in zero-shot bird classification using the CUB dataset. Our findings emphasize the potential of integrating subject-level guidance with general pretraining methods for enhanced downstream performance.
Learning to Prompt with Text Only Supervision for Vision-Language Models
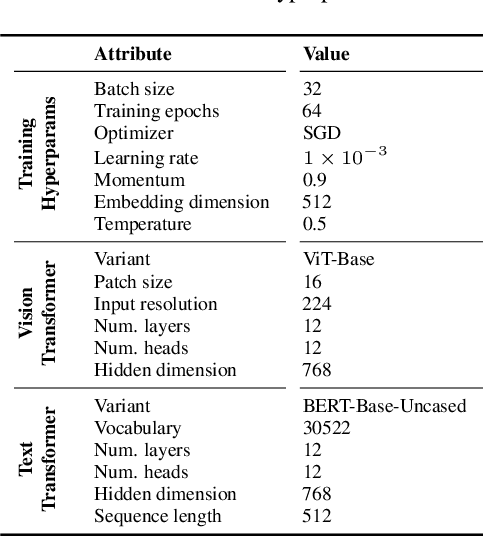
Jan 04, 2024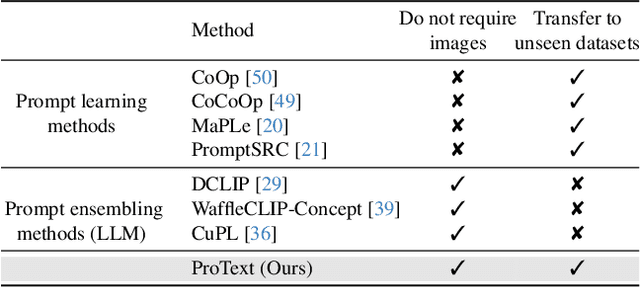
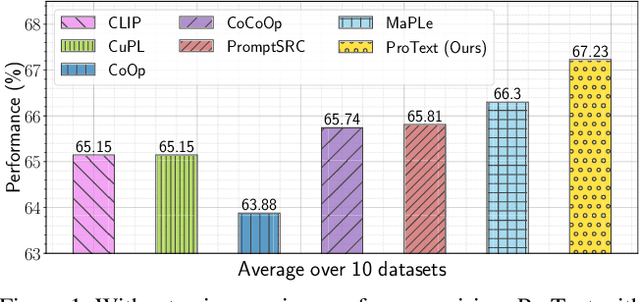
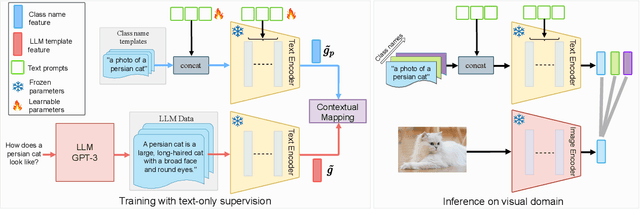
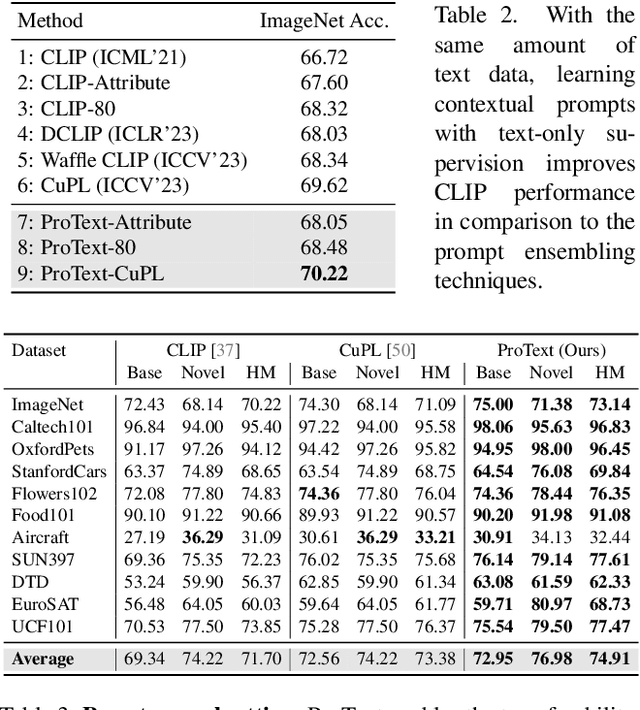
Abstract:Foundational vision-language models such as CLIP are becoming a new paradigm in vision, due to their excellent generalization abilities. However, adapting these models for downstream tasks while maintaining their generalization remains a challenge. In literature, one branch of methods adapts CLIP by learning prompts using visual information. While effective, most of these works require labeled data which is not practical, and often struggle to generalize towards new datasets due to over-fitting on the source data. An alternative approach resorts to training-free methods by generating class descriptions from large language models (LLMs) and perform prompt ensembling. However, these methods often generate class specific prompts that cannot be transferred to other classes, which incur higher costs by generating LLM descriptions for each class separately. In this work, we propose to combine the strengths of these both streams of methods by learning prompts using only text data derived from LLMs. As supervised training of prompts is not trivial due to absence of images, we develop a training approach that allows prompts to extract rich contextual knowledge from LLM data. Moreover, with LLM contextual data mapped within the learned prompts, it enables zero-shot transfer of prompts to new classes and datasets potentially cutting the LLM prompt engineering cost. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that learns generalized prompts using text only data. We perform extensive evaluations on 4 benchmarks where our method improves over prior ensembling works while being competitive to those utilizing labeled images. Our code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/muzairkhattak/ProText.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge