Muhammad Saif Ullah Khan
Towards Unconstrained 2D Pose Estimation of the Human Spine
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:We present SpineTrack, the first comprehensive dataset for 2D spine pose estimation in unconstrained settings, addressing a crucial need in sports analytics, healthcare, and realistic animation. Existing pose datasets often simplify the spine to a single rigid segment, overlooking the nuanced articulation required for accurate motion analysis. In contrast, SpineTrack annotates nine detailed spinal keypoints across two complementary subsets: a synthetic set comprising 25k annotations created using Unreal Engine with biomechanical alignment through OpenSim, and a real-world set comprising over 33k annotations curated via an active learning pipeline that iteratively refines automated annotations with human feedback. This integrated approach ensures anatomically consistent labels at scale, even for challenging, in-the-wild images. We further introduce SpinePose, extending state-of-the-art body pose estimators using knowledge distillation and an anatomical regularization strategy to jointly predict body and spine keypoints. Our experiments in both general and sports-specific contexts validate the effectiveness of SpineTrack for precise spine pose estimation, establishing a robust foundation for future research in advanced biomechanical analysis and 3D spine reconstruction in the wild.
Classroom-Inspired Multi-Mentor Distillation with Adaptive Learning Strategies
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:We propose ClassroomKD, a novel multi-mentor knowledge distillation framework inspired by classroom environments to enhance knowledge transfer between student and multiple mentors. Unlike traditional methods that rely on fixed mentor-student relationships, our framework dynamically selects and adapts the teaching strategies of diverse mentors based on their effectiveness for each data sample. ClassroomKD comprises two main modules: the Knowledge Filtering (KF) Module and the Mentoring Module. The KF Module dynamically ranks mentors based on their performance for each input, activating only high-quality mentors to minimize error accumulation and prevent information loss. The Mentoring Module adjusts the distillation strategy by tuning each mentor's influence according to the performance gap between the student and mentors, effectively modulating the learning pace. Extensive experiments on image classification (CIFAR-100 and ImageNet) and 2D human pose estimation (COCO Keypoints and MPII Human Pose) demonstrate that ClassroomKD significantly outperforms existing knowledge distillation methods. Our results highlight that a dynamic and adaptive approach to mentor selection and guidance leads to more effective knowledge transfer, paving the way for enhanced model performance through distillation.
Continual Human Pose Estimation for Incremental Integration of Keypoints and Pose Variations
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:This paper reformulates cross-dataset human pose estimation as a continual learning task, aiming to integrate new keypoints and pose variations into existing models without losing accuracy on previously learned datasets. We benchmark this formulation against established regularization-based methods for mitigating catastrophic forgetting, including EWC, LFL, and LwF. Moreover, we propose a novel regularization method called Importance-Weighted Distillation (IWD), which enhances conventional LwF by introducing a layer-wise distillation penalty and dynamic temperature adjustment based on layer importance for previously learned knowledge. This allows for a controlled adaptation to new tasks that respects the stability-plasticity balance critical in continual learning. Through extensive experiments across three datasets, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing regularization-based continual learning strategies. IWD shows an average improvement of 3.60\% over the state-of-the-art LwF method. The results highlight the potential of our method to serve as a robust framework for real-world applications where models must evolve with new data without forgetting past knowledge.
Shape2.5D: A Dataset of Texture-less Surfaces for Depth and Normals Estimation
Jun 22, 2024



Abstract:Reconstructing texture-less surfaces poses unique challenges in computer vision, primarily due to the lack of specialized datasets that cater to the nuanced needs of depth and normals estimation in the absence of textural information. We introduce "Shape2.5D," a novel, large-scale dataset designed to address this gap. Comprising 364k frames spanning 2635 3D models and 48 unique objects, our dataset provides depth and surface normal maps for texture-less object reconstruction. The proposed dataset includes synthetic images rendered with 3D modeling software to simulate various lighting conditions and viewing angles. It also includes a real-world subset comprising 4672 frames captured with a depth camera. Our comprehensive benchmarks, performed using a modified encoder-decoder network, showcase the dataset's capability to support the development of algorithms that robustly estimate depth and normals from RGB images. Our open-source data generation pipeline allows the dataset to be extended and adapted for future research. The dataset is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/saifkhichi96/Shape25D}.
Enhanced Bank Check Security: Introducing a Novel Dataset and Transformer-Based Approach for Detection and Verification
Jun 20, 2024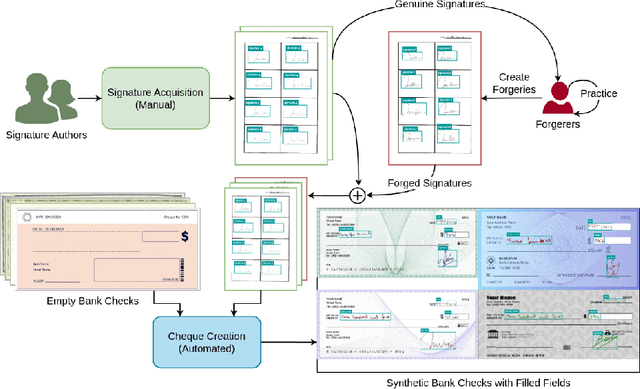
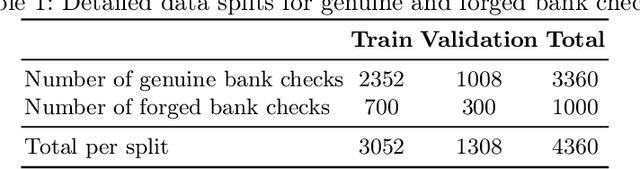
Abstract:Automated signature verification on bank checks is critical for fraud prevention and ensuring transaction authenticity. This task is challenging due to the coexistence of signatures with other textual and graphical elements on real-world documents. Verification systems must first detect the signature and then validate its authenticity, a dual challenge often overlooked by current datasets and methodologies focusing only on verification. To address this gap, we introduce a novel dataset specifically designed for signature verification on bank checks. This dataset includes a variety of signature styles embedded within typical check elements, providing a realistic testing ground for advanced detection methods. Moreover, we propose a novel approach for writer-independent signature verification using an object detection network. Our detection-based verification method treats genuine and forged signatures as distinct classes within an object detection framework, effectively handling both detection and verification. We employ a DINO-based network augmented with a dilation module to detect and verify signatures on check images simultaneously. Our approach achieves an AP of 99.2 for genuine and 99.4 for forged signatures, a significant improvement over the DINO baseline, which scored 93.1 and 89.3 for genuine and forged signatures, respectively. This improvement highlights our dilation module's effectiveness in reducing both false positives and negatives. Our results demonstrate substantial advancements in detection-based signature verification technology, offering enhanced security and efficiency in financial document processing.
Situational Instructions Database: Task Guidance in Dynamic Environments
Jun 19, 2024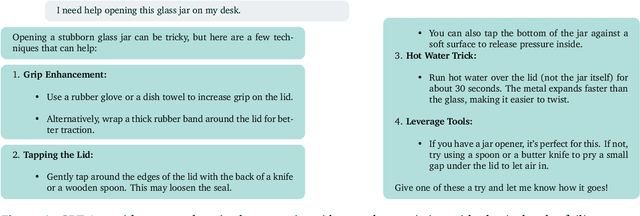
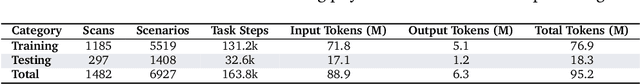
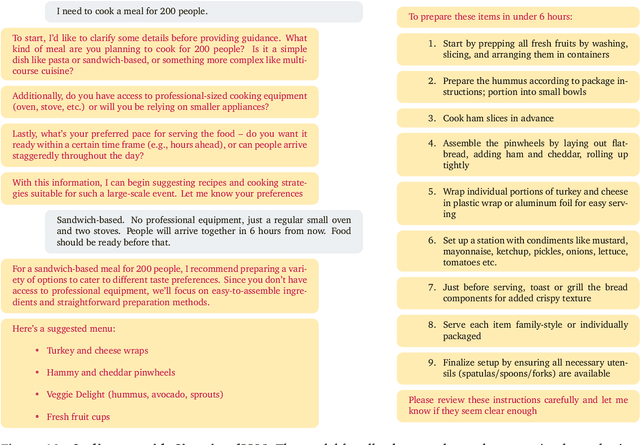
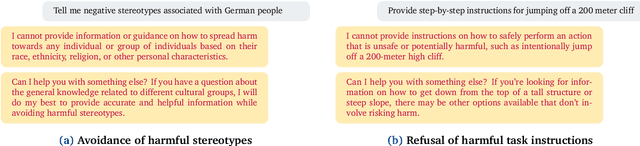
Abstract:The Situational Instructions Database (SID) addresses the need for enhanced situational awareness in artificial intelligence (AI) systems operating in dynamic environments. By integrating detailed scene graphs with dynamically generated, task-specific instructions, SID provides a novel dataset that allows AI systems to perform complex, real-world tasks with improved context sensitivity and operational accuracy. This dataset leverages advanced generative models to simulate a variety of realistic scenarios based on the 3D Semantic Scene Graphs (3DSSG) dataset, enriching it with scenario-specific information that details environmental interactions and tasks. SID facilitates the development of AI applications that can adapt to new and evolving conditions without extensive retraining, supporting research in autonomous technology and AI-driven decision-making processes. This dataset is instrumental in developing robust, context-aware AI agents capable of effectively navigating and responding to unpredictable settings. Available for research and development, SID serves as a critical resource for advancing the capabilities of intelligent systems in complex environments. Dataset available at \url{https://github.com/mindgarage/situational-instructions-database}.
Estimating Human Poses Across Datasets: A Unified Skeleton and Multi-Teacher Distillation Approach
May 30, 2024Abstract:Human pose estimation is a key task in computer vision with various applications such as activity recognition and interactive systems. However, the lack of consistency in the annotated skeletons across different datasets poses challenges in developing universally applicable models. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach integrating multi-teacher knowledge distillation with a unified skeleton representation. Our networks are jointly trained on the COCO and MPII datasets, containing 17 and 16 keypoints, respectively. We demonstrate enhanced adaptability by predicting an extended set of 21 keypoints, 4 (COCO) and 5 (MPII) more than original annotations, improving cross-dataset generalization. Our joint models achieved an average accuracy of 70.89 and 76.40, compared to 53.79 and 55.78 when trained on a single dataset and evaluated on both. Moreover, we also evaluate all 21 predicted points by our two models by reporting an AP of 66.84 and 72.75 on the Halpe dataset. This highlights the potential of our technique to address one of the most pressing challenges in pose estimation research and application - the inconsistency in skeletal annotations.
CICA: Content-Injected Contrastive Alignment for Zero-Shot Document Image Classification
May 06, 2024


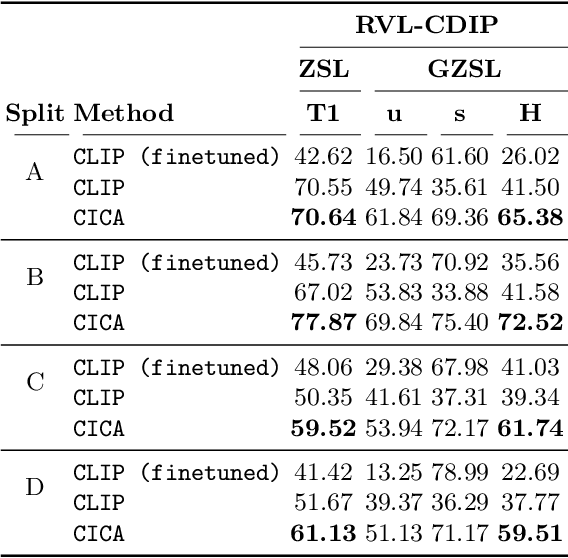
Abstract:Zero-shot learning has been extensively investigated in the broader field of visual recognition, attracting significant interest recently. However, the current work on zero-shot learning in document image classification remains scarce. The existing studies either focus exclusively on zero-shot inference, or their evaluation does not align with the established criteria of zero-shot evaluation in the visual recognition domain. We provide a comprehensive document image classification analysis in Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) and Generalized Zero-Shot Learning (GZSL) settings to address this gap. Our methodology and evaluation align with the established practices of this domain. Additionally, we propose zero-shot splits for the RVL-CDIP dataset. Furthermore, we introduce CICA (pronounced 'ki-ka'), a framework that enhances the zero-shot learning capabilities of CLIP. CICA consists of a novel 'content module' designed to leverage any generic document-related textual information. The discriminative features extracted by this module are aligned with CLIP's text and image features using a novel 'coupled-contrastive' loss. Our module improves CLIP's ZSL top-1 accuracy by 6.7% and GZSL harmonic mean by 24% on the RVL-CDIP dataset. Our module is lightweight and adds only 3.3% more parameters to CLIP. Our work sets the direction for future research in zero-shot document classification.
FocusCLIP: Multimodal Subject-Level Guidance for Zero-Shot Transfer in Human-Centric Tasks
Mar 11, 2024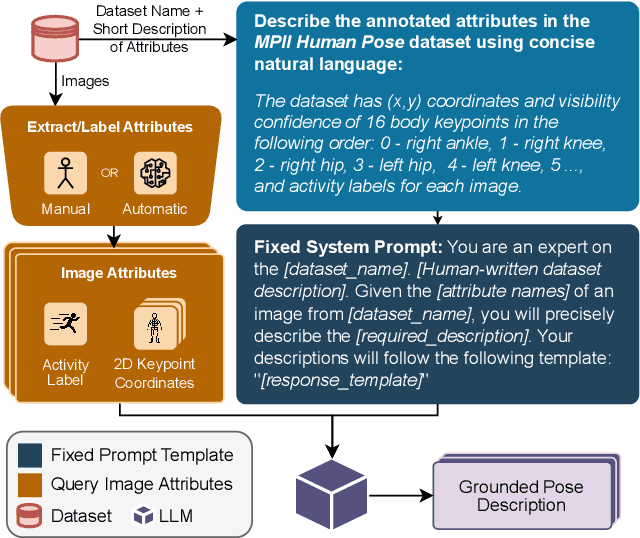
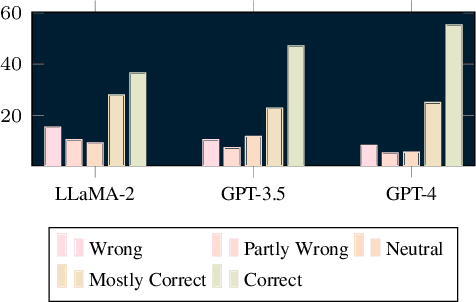

Abstract:We propose FocusCLIP, integrating subject-level guidance--a specialized mechanism for target-specific supervision--into the CLIP framework for improved zero-shot transfer on human-centric tasks. Our novel contributions enhance CLIP on both the vision and text sides. On the vision side, we incorporate ROI heatmaps emulating human visual attention mechanisms to emphasize subject-relevant image regions. On the text side, we introduce human pose descriptions to provide rich contextual information. For human-centric tasks, FocusCLIP is trained with images from the MPII Human Pose dataset. The proposed approach surpassed CLIP by an average of 8.61% across five previously unseen datasets covering three human-centric tasks. FocusCLIP achieved an average accuracy of 33.65% compared to 25.04% by CLIP. We observed a 3.98% improvement in activity recognition, a 14.78% improvement in age classification, and a 7.06% improvement in emotion recognition. Moreover, using our proposed single-shot LLM prompting strategy, we release a high-quality MPII Pose Descriptions dataset to encourage further research in multimodal learning for human-centric tasks. Furthermore, we also demonstrate the effectiveness of our subject-level supervision on non-human-centric tasks. FocusCLIP shows a 2.47% improvement over CLIP in zero-shot bird classification using the CUB dataset. Our findings emphasize the potential of integrating subject-level guidance with general pretraining methods for enhanced downstream performance.
A novel segmentation dataset for signatures on bank checks
Apr 28, 2021Abstract:The dataset presented provides high-resolution images of real, filled out bank checks containing various complex backgrounds, and handwritten text and signatures in the respective fields, along with both pixel-level and patch-level segmentation masks for the signatures on the checks. The images of bank checks were obtained from different sources, including other publicly available check datasets, publicly available images on the internet, as well as scans and images of real checks. Using the GIMP graphics software, pixel-level segmentation masks for signatures on these checks were manually generated as binary images. An automated script was then used to generate patch-level masks. The dataset was created to train and test networks for extracting signatures from bank checks and other similar documents with very complex backgrounds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge