Tianyuan Qu
N3D-VLM: Native 3D Grounding Enables Accurate Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:While current multimodal models can answer questions based on 2D images, they lack intrinsic 3D object perception, limiting their ability to comprehend spatial relationships and depth cues in 3D scenes. In this work, we propose N3D-VLM, a novel unified framework that seamlessly integrates native 3D object perception with 3D-aware visual reasoning, enabling both precise 3D grounding and interpretable spatial understanding. Unlike conventional end-to-end models that directly predict answers from RGB/RGB-D inputs, our approach equips the model with native 3D object perception capabilities, enabling it to directly localize objects in 3D space based on textual descriptions. Building upon accurate 3D object localization, the model further performs explicit reasoning in 3D, achieving more interpretable and structured spatial understanding. To support robust training for these capabilities, we develop a scalable data construction pipeline that leverages depth estimation to lift large-scale 2D annotations into 3D space, significantly increasing the diversity and coverage for 3D object grounding data, yielding over six times larger than the largest existing single-image 3D detection dataset. Moreover, the pipeline generates spatial question-answering datasets that target chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning in 3D, facilitating joint training for both 3D object localization and 3D spatial reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that our unified framework not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on 3D grounding tasks, but also consistently surpasses existing methods in 3D spatial reasoning in vision-language model.
RePlan: Reasoning-guided Region Planning for Complex Instruction-based Image Editing
Dec 18, 2025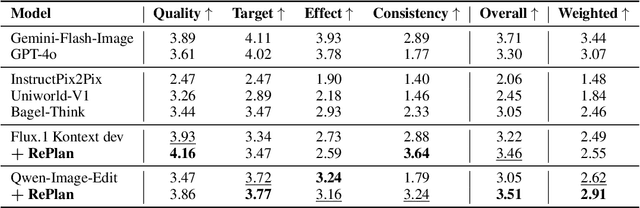
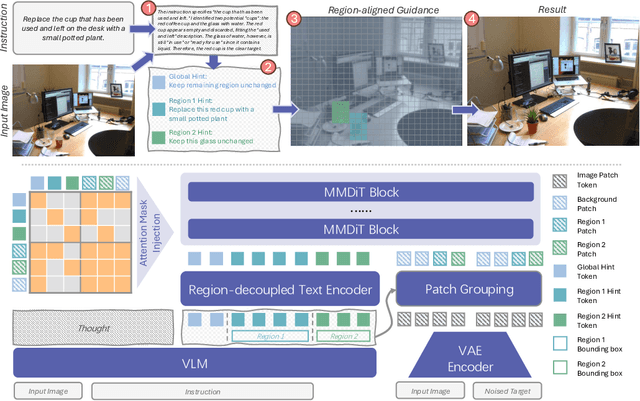

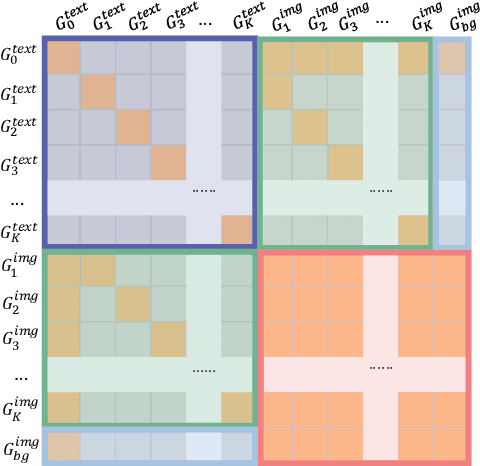
Abstract:Instruction-based image editing enables natural-language control over visual modifications, yet existing models falter under Instruction-Visual Complexity (IV-Complexity), where intricate instructions meet cluttered or ambiguous scenes. We introduce RePlan (Region-aligned Planning), a plan-then-execute framework that couples a vision-language planner with a diffusion editor. The planner decomposes instructions via step-by-step reasoning and explicitly grounds them to target regions; the editor then applies changes using a training-free attention-region injection mechanism, enabling precise, parallel multi-region edits without iterative inpainting. To strengthen planning, we apply GRPO-based reinforcement learning using 1K instruction-only examples, yielding substantial gains in reasoning fidelity and format reliability. We further present IV-Edit, a benchmark focused on fine-grained grounding and knowledge-intensive edits. Across IV-Complex settings, RePlan consistently outperforms strong baselines trained on far larger datasets, improving regional precision and overall fidelity. Our project page: https://replan-iv-edit.github.io
RTime-QA: A Benchmark for Atomic Temporal Event Understanding in Large Multi-modal Models
May 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding accurate atomic temporal event is essential for video comprehension. However, current video-language benchmarks often fall short to evaluate Large Multi-modal Models' (LMMs) temporal event understanding capabilities, as they can be effectively addressed using image-language models. In this paper, we introduce RTime-QA, a novel benchmark specifically designed to assess the atomic temporal event understanding ability of LMMs. RTime-QA comprises 822 high-quality, carefully-curated video-text questions, each meticulously annotated by human experts. Each question features a video depicting an atomic temporal event, paired with both correct answers and temporal negative descriptions, specifically designed to evaluate temporal understanding. To advance LMMs' temporal event understanding ability, we further introduce RTime-IT, a 14k instruction-tuning dataset that employs a similar annotation process as RTime-QA. Extensive experimental analysis demonstrates that RTime-QA presents a significant challenge for LMMs: the state-of-the-art model Qwen2-VL achieves only 34.6 on strict-ACC metric, substantially lagging behind human performance. Furthermore, our experiments reveal that RTime-IT effectively enhance LMMs' capacity in temporal understanding. By fine-tuning on RTime-IT, our Qwen2-VL achieves 65.9 on RTime-QA.
VisionReasoner: Unified Visual Perception and Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models exhibit inherent capabilities to handle diverse visual perception tasks. In this paper, we introduce VisionReasoner, a unified framework capable of reasoning and solving multiple visual perception tasks within a shared model. Specifically, by designing novel multi-object cognitive learning strategies and systematic task reformulation, VisionReasoner enhances its reasoning capabilities to analyze visual inputs, and addresses diverse perception tasks in a unified framework. The model generates a structured reasoning process before delivering the desired outputs responding to user queries. To rigorously assess unified visual perception capabilities, we evaluate VisionReasoner on ten diverse tasks spanning three critical domains: detection, segmentation, and counting. Experimental results show that VisionReasoner achieves superior performance as a unified model, outperforming Qwen2.5VL by relative margins of 29.1% on COCO (detection), 22.1% on ReasonSeg (segmentation), and 15.3% on CountBench (counting).
Does Your Vision-Language Model Get Lost in the Long Video Sampling Dilemma?
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) has significantly advanced video understanding. However, efficiently processing long videos remains a challenge due to the ``Sampling Dilemma'': low-density sampling risks missing critical information, while high-density sampling introduces redundancy. To address this issue, we introduce LSDBench, the first benchmark designed to evaluate LVLMs on long-video tasks by constructing high Necessary Sampling Density (NSD) questions, where NSD represents the minimum sampling density required to accurately answer a given question. LSDBench focuses on dense, short-duration actions to rigorously assess the sampling strategies employed by LVLMs. To tackle the challenges posed by high-NSD questions, we propose a novel Reasoning-Driven Hierarchical Sampling (RHS) framework, which combines global localization of question-relevant cues with local dense sampling for precise inference. Additionally, we develop a lightweight Semantic-Guided Frame Selector to prioritize informative frames, enabling RHS to achieve comparable or superior performance with significantly fewer sampled frames. Together, our LSDBench and RHS framework address the unique challenges of high-NSD long-video tasks, setting a new standard for evaluating and improving LVLMs in this domain.
Lyra: An Efficient and Speech-Centric Framework for Omni-Cognition
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:As Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) evolve, expanding beyond single-domain capabilities is essential to meet the demands for more versatile and efficient AI. However, previous omni-models have insufficiently explored speech, neglecting its integration with multi-modality. We introduce Lyra, an efficient MLLM that enhances multimodal abilities, including advanced long-speech comprehension, sound understanding, cross-modality efficiency, and seamless speech interaction. To achieve efficiency and speech-centric capabilities, Lyra employs three strategies: (1) leveraging existing open-source large models and a proposed multi-modality LoRA to reduce training costs and data requirements; (2) using a latent multi-modality regularizer and extractor to strengthen the relationship between speech and other modalities, thereby enhancing model performance; and (3) constructing a high-quality, extensive dataset that includes 1.5M multi-modal (language, vision, audio) data samples and 12K long speech samples, enabling Lyra to handle complex long speech inputs and achieve more robust omni-cognition. Compared to other omni-methods, Lyra achieves state-of-the-art performance on various vision-language, vision-speech, and speech-language benchmarks, while also using fewer computational resources and less training data.
An Improved Baseline for Reasoning Segmentation with Large Language Model
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:While LISA effectively bridges the gap between segmentation and large language models to enable reasoning segmentation, it poses certain limitations: unable to distinguish different instances of the target region, and constrained by the pre-defined textual response formats. In this work, we introduce LISA++, an update to the existing LISA model, focusing on improving core functionalities while keeping the base architecture intact. The main enhancements in LISA++ include: \textbf{1) Enhanced Segmentation}: The instance segmentation ability has been added, providing a more detailed scene analysis along with the existing multi-region semantic segmentation. \textbf{2) More Natural Conversation}: Improved capability for multi-turn dialogue, with the ability to incorporate segmentation results directly into text responses, i.e., Segmentation in Dialogue (SiD). These improvements are achieved by curating the existing samples of generic segmentation datasets, aimed specifically at enhancing the segmentation and conversational skills without structural change and additional data sources. Comparative analysis with the original LISA model shows significant advancements in these areas, positioning LISA++ as a notable upgrade in visual understanding and interaction. LISA++'s adaptability and improved features highlight the versatility of the mask-as-embedding paradigm proposed by LISA, and the potential as a foundational model for diverse applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge