Xin Lai
Rethinking Recurrent Neural Networks for Time Series Forecasting: A Reinforced Recurrent Encoder with Prediction-Oriented Proximal Policy Optimization
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Time series forecasting plays a crucial role in contemporary engineering information systems for supporting decision-making across various industries, where Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have been widely adopted due to their capability in modeling sequential data. Conventional RNN-based predictors adopt an encoder-only strategy with sliding historical windows as inputs to forecast future values. However, this approach treats all time steps and hidden states equally without considering their distinct contributions to forecasting, leading to suboptimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Reinforced Recurrent Encoder with Prediction-oriented Proximal Policy Optimization, RRE-PPO4Pred, which significantly improves time series modeling capacity and forecasting accuracy of the RNN models. The core innovations of this method are: (1) A novel Reinforced Recurrent Encoder (RRE) framework that enhances RNNs by formulating their internal adaptation as a Markov Decision Process, creating a unified decision environment capable of learning input feature selection, hidden skip connection, and output target selection; (2) An improved Prediction-oriented Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm, termed PPO4Pred, which is equipped with a Transformer-based agent for temporal reasoning and develops a dynamic transition sampling strategy to enhance sampling efficiency; (3) A co-evolutionary optimization paradigm to facilitate the learning of the RNN predictor and the policy agent, providing adaptive and interactive time series modeling. Comprehensive evaluations on five real-world datasets indicate that our method consistently outperforms existing baselines, and attains accuracy better than state-of-the-art Transformer models, thus providing an advanced time series predictor in engineering informatics.
VideoZoomer: Reinforcement-Learned Temporal Focusing for Long Video Reasoning
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in vision-language tasks yet remain limited in long video understanding due to the limited context window. Consequently, prevailing approaches tend to rely on uniform frame sampling or static pre-selection, which might overlook critical evidence and unable to correct its initial selection error during its reasoning process. To overcome these limitations, we propose VideoZoomer, a novel agentic framework that enables MLLMs to dynamically control their visual focus during reasoning. Starting from a coarse low-frame-rate overview, VideoZoomer invokes a temporal zoom tool to obtain high-frame-rate clips at autonomously chosen moments, thereby progressively gathering fine-grained evidence in a multi-turn interactive manner. Accordingly, we adopt a two-stage training strategy: a cold-start supervised fine-tuning phase on a curated dataset of distilled exemplar and reflection trajectories, followed by reinforcement learning to further refine the agentic policy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our 7B model delivers diverse and complex reasoning patterns, yielding strong performance across a broad set of long video understanding and reasoning benchmarks. These emergent capabilities allow it to consistently surpass existing open-source models and even rival proprietary systems on challenging tasks, while achieving superior efficiency under reduced frame budgets.
Making Every Head Count: Sparse Attention Without the Speed-Performance Trade-off
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:The design of Large Language Models (LLMs) has long been hampered by a fundamental conflict within their core attention mechanism: its remarkable expressivity is built upon a computational complexity of $O(H \cdot N^2)$ that grows quadratically with the context size ($N$) and linearly with the number of heads ($H$). This standard implementation harbors significant computational redundancy, as all heads independently compute attention over the same sequence space. Existing sparse methods, meanwhile, often trade information integrity for computational efficiency. To resolve this efficiency-performance trade-off, we propose SPAttention, whose core contribution is the introduction of a new paradigm we term Principled Structural Sparsity. SPAttention does not merely drop connections but instead reorganizes the computational task by partitioning the total attention workload into balanced, non-overlapping distance bands, assigning each head a unique segment. This approach transforms the multi-head attention mechanism from $H$ independent $O(N^2)$ computations into a single, collaborative $O(N^2)$ computation, fundamentally reducing complexity by a factor of $H$. The structured inductive bias compels functional specialization among heads, enabling a more efficient allocation of computational resources from redundant modeling to distinct dependencies across the entire sequence span. Extensive empirical validation on the OLMoE-1B-7B and 0.25B-1.75B model series demonstrates that while delivering an approximately two-fold increase in training throughput, its performance is on par with standard dense attention, even surpassing it on select key metrics, while consistently outperforming representative sparse attention methods including Longformer, Reformer, and BigBird across all evaluation metrics.
Mini-o3: Scaling Up Reasoning Patterns and Interaction Turns for Visual Search
Sep 09, 2025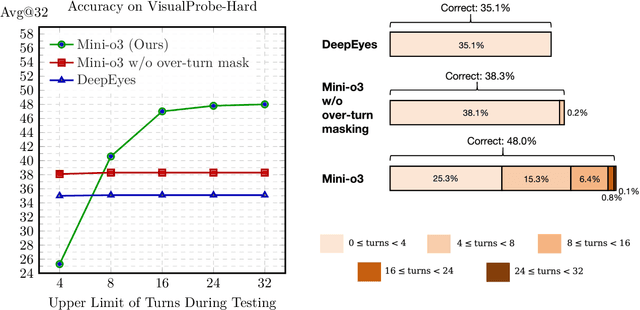
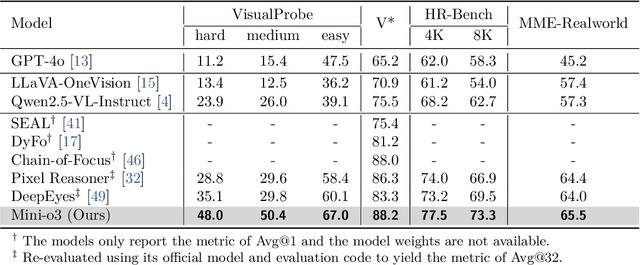
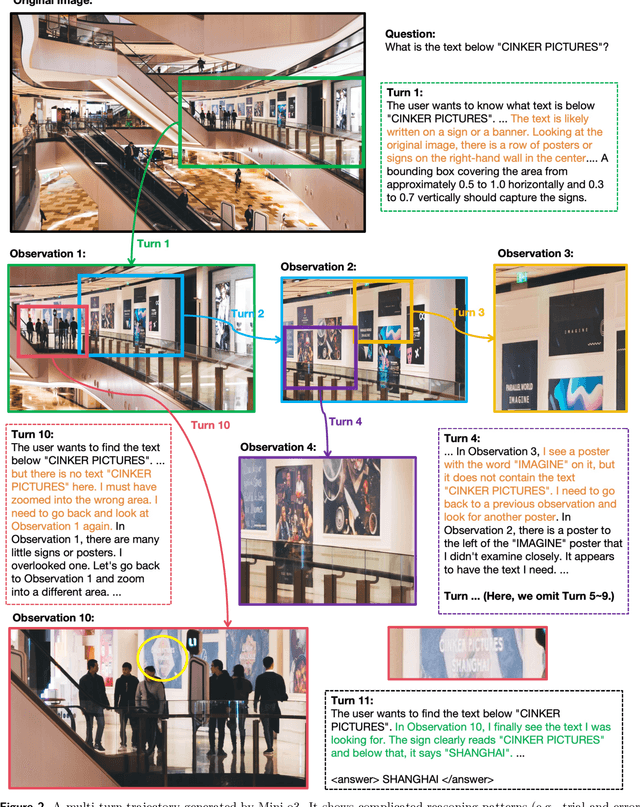
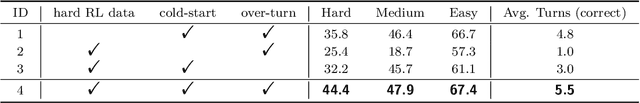
Abstract:Recent advances in large multimodal models have leveraged image-based tools with reinforcement learning to tackle visual problems. However, existing open-source approaches often exhibit monotonous reasoning patterns and allow only a limited number of interaction turns, making them inadequate for difficult tasks that require trial-and-error exploration. In this work, we address this limitation by scaling up tool-based interactions and introduce Mini-o3, a system that executes deep, multi-turn reasoning -- spanning tens of steps -- and achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging visual search tasks. Our recipe for reproducing OpenAI o3-style behaviors comprises three key components. First, we construct the Visual Probe Dataset, a collection of thousands of challenging visual search problems designed for exploratory reasoning. Second, we develop an iterative data collection pipeline to obtain cold-start trajectories that exhibit diverse reasoning patterns, including depth-first search, trial-and-error, and goal maintenance. Third, we propose an over-turn masking strategy that prevents penalization of over-turn responses (those that hit the maximum number of turns) during reinforcement learning, thereby balancing training-time efficiency with test-time scalability. Despite training with an upper bound of only six interaction turns, our model generates trajectories that naturally scale to tens of turns at inference time, with accuracy improving as the number of turns increases. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mini-o3 produces rich reasoning patterns and deep thinking paths, effectively solving challenging visual search problems.
VisionThink: Smart and Efficient Vision Language Model via Reinforcement Learning
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs) have improved performance by increasing the number of visual tokens, which are often significantly longer than text tokens. However, we observe that most real-world scenarios do not require such an extensive number of visual tokens. While the performance drops significantly in a small subset of OCR-related tasks, models still perform accurately in most other general VQA tasks with only 1/4 resolution. Therefore, we propose to dynamically process distinct samples with different resolutions, and present a new paradigm for visual token compression, namely, VisionThink. It starts with a downsampled image and smartly decides whether it is sufficient for problem solving. Otherwise, the model could output a special token to request the higher-resolution image. Compared to existing Efficient VLM methods that compress tokens using fixed pruning ratios or thresholds, VisionThink autonomously decides whether to compress tokens case by case. As a result, it demonstrates strong fine-grained visual understanding capability on OCR-related tasks, and meanwhile saves substantial visual tokens on simpler tasks. We adopt reinforcement learning and propose the LLM-as-Judge strategy to successfully apply RL to general VQA tasks. Moreover, we carefully design a reward function and penalty mechanism to achieve a stable and reasonable image resize call ratio. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority, efficiency, and effectiveness of our method. Our code is available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/VisionThink.
CausalVE: Face Video Privacy Encryption via Causal Video Prediction
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Advanced facial recognition technologies and recommender systems with inadequate privacy technologies and policies for facial interactions increase concerns about bioprivacy violations. With the proliferation of video and live-streaming websites, public-face video distribution and interactions pose greater privacy risks. Existing techniques typically address the risk of sensitive biometric information leakage through various privacy enhancement methods but pose a higher security risk by corrupting the information to be conveyed by the interaction data, or by leaving certain biometric features intact that allow an attacker to infer sensitive biometric information from them. To address these shortcomings, in this paper, we propose a neural network framework, CausalVE. We obtain cover images by adopting a diffusion model to achieve face swapping with face guidance and use the speech sequence features and spatiotemporal sequence features of the secret video for dynamic video inference and prediction to obtain a cover video with the same number of frames as the secret video. In addition, we hide the secret video by using reversible neural networks for video hiding so that the video can also disseminate secret data. Numerous experiments prove that our CausalVE has good security in public video dissemination and outperforms state-of-the-art methods from a qualitative, quantitative, and visual point of view.
LHQ-SVC: Lightweight and High Quality Singing Voice Conversion Modeling
Sep 13, 2024


Abstract:Singing Voice Conversion (SVC) has emerged as a significant subfield of Voice Conversion (VC), enabling the transformation of one singer's voice into another while preserving musical elements such as melody, rhythm, and timbre. Traditional SVC methods have limitations in terms of audio quality, data requirements, and computational complexity. In this paper, we propose LHQ-SVC, a lightweight, CPU-compatible model based on the SVC framework and diffusion model, designed to reduce model size and computational demand without sacrificing performance. We incorporate features to improve inference quality, and optimize for CPU execution by using performance tuning tools and parallel computing frameworks. Our experiments demonstrate that LHQ-SVC maintains competitive performance, with significant improvements in processing speed and efficiency across different devices. The results suggest that LHQ-SVC can meet
Step-DPO: Step-wise Preference Optimization for Long-chain Reasoning of LLMs
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Mathematical reasoning presents a significant challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs) due to the extensive and precise chain of reasoning required for accuracy. Ensuring the correctness of each reasoning step is critical. To address this, we aim to enhance the robustness and factuality of LLMs by learning from human feedback. However, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has shown limited benefits for long-chain mathematical reasoning, as models employing DPO struggle to identify detailed errors in incorrect answers. This limitation stems from a lack of fine-grained process supervision. We propose a simple, effective, and data-efficient method called Step-DPO, which treats individual reasoning steps as units for preference optimization rather than evaluating answers holistically. Additionally, we have developed a data construction pipeline for Step-DPO, enabling the creation of a high-quality dataset containing 10K step-wise preference pairs. We also observe that in DPO, self-generated data is more effective than data generated by humans or GPT-4, due to the latter's out-of-distribution nature. Our findings demonstrate that as few as 10K preference data pairs and fewer than 500 Step-DPO training steps can yield a nearly 3% gain in accuracy on MATH for models with over 70B parameters. Notably, Step-DPO, when applied to Qwen2-72B-Instruct, achieves scores of 70.8% and 94.0% on the test sets of MATH and GSM8K, respectively, surpassing a series of closed-source models, including GPT-4-1106, Claude-3-Opus, and Gemini-1.5-Pro. Our code, data, and models are available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/Step-DPO.
Improved Genetic Algorithm Based on Greedy and Simulated Annealing Ideas for Vascular Robot Ordering Strategy
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:This study presents a comprehensive approach for optimizing the acquisition, utilization, and maintenance of ABLVR vascular robots in healthcare settings. Medical robotics, particularly in vascular treatments, necessitates precise resource allocation and optimization due to the complex nature of robot and operator maintenance. Traditional heuristic methods, though intuitive, often fail to achieve global optimization. To address these challenges, this research introduces a novel strategy, combining mathematical modeling, a hybrid genetic algorithm, and ARIMA time series forecasting. Considering the dynamic healthcare environment, our approach includes a robust resource allocation model for robotic vessels and operators. We incorporate the unique requirements of the adaptive learning process for operators and the maintenance needs of robotic components. The hybrid genetic algorithm, integrating simulated annealing and greedy approaches, efficiently solves the optimization problem. Additionally, ARIMA time series forecasting predicts the demand for vascular robots, further enhancing the adaptability of our strategy. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our approach in terms of optimization, transparency, and convergence speed from other state-of-the-art methods.
An Improved Baseline for Reasoning Segmentation with Large Language Model
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:While LISA effectively bridges the gap between segmentation and large language models to enable reasoning segmentation, it poses certain limitations: unable to distinguish different instances of the target region, and constrained by the pre-defined textual response formats. In this work, we introduce LISA++, an update to the existing LISA model, focusing on improving core functionalities while keeping the base architecture intact. The main enhancements in LISA++ include: \textbf{1) Enhanced Segmentation}: The instance segmentation ability has been added, providing a more detailed scene analysis along with the existing multi-region semantic segmentation. \textbf{2) More Natural Conversation}: Improved capability for multi-turn dialogue, with the ability to incorporate segmentation results directly into text responses, i.e., Segmentation in Dialogue (SiD). These improvements are achieved by curating the existing samples of generic segmentation datasets, aimed specifically at enhancing the segmentation and conversational skills without structural change and additional data sources. Comparative analysis with the original LISA model shows significant advancements in these areas, positioning LISA++ as a notable upgrade in visual understanding and interaction. LISA++'s adaptability and improved features highlight the versatility of the mask-as-embedding paradigm proposed by LISA, and the potential as a foundational model for diverse applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge