Yuqi Liu
CAPTS: Channel-Aware, Preference-Aligned Trigger Selection for Multi-Channel Item-to-Item Retrieval
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Large-scale industrial recommender systems commonly adopt multi-channel retrieval for candidate generation, combining direct user-to-item (U2I) retrieval with two-hop user-to-item-to-item (U2I2I) pipelines. In U2I2I, the system selects a small set of historical interactions as triggers to seed downstream item-to-item (I2I) retrieval across multiple channels. In production, triggers are often selected using rule-based policies or learned scorers and tuned in a channel-by-channel manner. However, these practices face two persistent challenges: biased value attribution that values triggers by on-trigger feedback rather than their downstream utility as retrieval seeds, and uncoordinated multi-channel routing where channels select triggers independently under a shared quota, increasing cross-channel overlap. To address these challenges, we propose Channel-Aware, Preference-Aligned Trigger Selection (CAPTS), a unified and flexible framework that treats multi-channel trigger selection as a learnable routing problem. CAPTS introduces a Value Attribution Module (VAM) that provides look-ahead supervision by crediting each trigger with the subsequent engagement generated by items retrieved from it on each I2I channel, and a Channel-Adaptive Trigger Routing (CATR) module that coordinates trigger-to-channel assignment to maximize the overall value of multi-channel retrieval. Extensive offline experiments and large-scale online A/B tests on Kwai, Kuaishou's international short-video platform, show that CAPTS consistently improves multi-channel recall offline and delivers a +0.351% lift in average time spent per device online.
RePlan: Reasoning-guided Region Planning for Complex Instruction-based Image Editing
Dec 18, 2025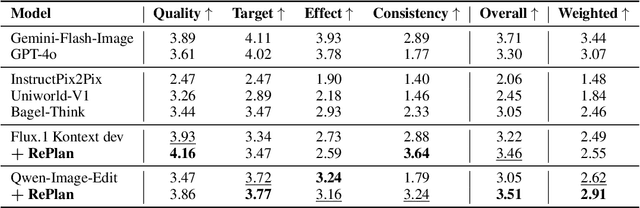
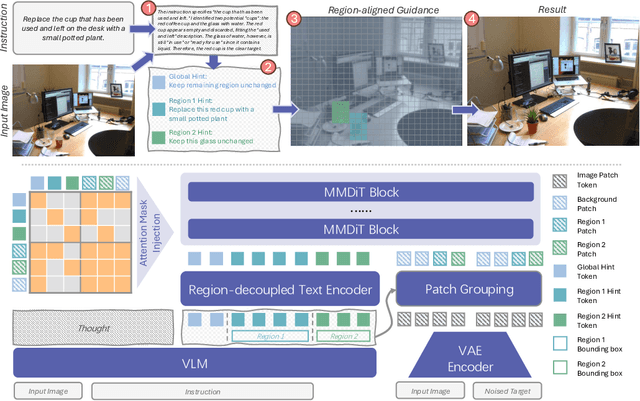

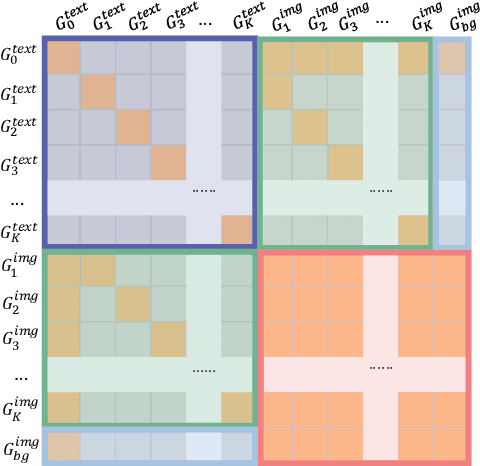
Abstract:Instruction-based image editing enables natural-language control over visual modifications, yet existing models falter under Instruction-Visual Complexity (IV-Complexity), where intricate instructions meet cluttered or ambiguous scenes. We introduce RePlan (Region-aligned Planning), a plan-then-execute framework that couples a vision-language planner with a diffusion editor. The planner decomposes instructions via step-by-step reasoning and explicitly grounds them to target regions; the editor then applies changes using a training-free attention-region injection mechanism, enabling precise, parallel multi-region edits without iterative inpainting. To strengthen planning, we apply GRPO-based reinforcement learning using 1K instruction-only examples, yielding substantial gains in reasoning fidelity and format reliability. We further present IV-Edit, a benchmark focused on fine-grained grounding and knowledge-intensive edits. Across IV-Complex settings, RePlan consistently outperforms strong baselines trained on far larger datasets, improving regional precision and overall fidelity. Our project page: https://replan-iv-edit.github.io
ChartEditor: A Reinforcement Learning Framework for Robust Chart Editing
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Chart editing reduces manual effort in visualization design. Typical benchmarks limited in data diversity and assume access to complete chart code, which is seldom in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we present ChartEditVista, a comprehensive benchmark consisting of 7,964 samples spanning 31 chart categories. It encompasses diverse editing instructions and covers nearly all editable chart elements. The inputs in ChartEditVista include only the original chart image and natural language editing instructions, without the original chart codes. ChartEditVista is generated through a fully automated pipeline that produces, edits, and verifies charts, ensuring high-quality chart editing data. Besides, we introduce two novel fine-grained, rule-based evaluation metrics: the layout metric, which evaluates the position, size and color of graphical components; and the text metric, which jointly assesses textual content and font styling. Building on top of ChartEditVista, we present ChartEditor, a model trained using a reinforcement learning framework that incorporates a novel rendering reward to simultaneously enforce code executability and visual fidelity. Through extensive experiments and human evaluations, we demonstrate that ChartEditVista provides a robust evaluation, while ChartEditor consistently outperforms models with similar-scale and larger-scale on chart editing tasks.
RTime-QA: A Benchmark for Atomic Temporal Event Understanding in Large Multi-modal Models
May 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding accurate atomic temporal event is essential for video comprehension. However, current video-language benchmarks often fall short to evaluate Large Multi-modal Models' (LMMs) temporal event understanding capabilities, as they can be effectively addressed using image-language models. In this paper, we introduce RTime-QA, a novel benchmark specifically designed to assess the atomic temporal event understanding ability of LMMs. RTime-QA comprises 822 high-quality, carefully-curated video-text questions, each meticulously annotated by human experts. Each question features a video depicting an atomic temporal event, paired with both correct answers and temporal negative descriptions, specifically designed to evaluate temporal understanding. To advance LMMs' temporal event understanding ability, we further introduce RTime-IT, a 14k instruction-tuning dataset that employs a similar annotation process as RTime-QA. Extensive experimental analysis demonstrates that RTime-QA presents a significant challenge for LMMs: the state-of-the-art model Qwen2-VL achieves only 34.6 on strict-ACC metric, substantially lagging behind human performance. Furthermore, our experiments reveal that RTime-IT effectively enhance LMMs' capacity in temporal understanding. By fine-tuning on RTime-IT, our Qwen2-VL achieves 65.9 on RTime-QA.
Enhancing LLMs via High-Knowledge Data Selection
May 20, 2025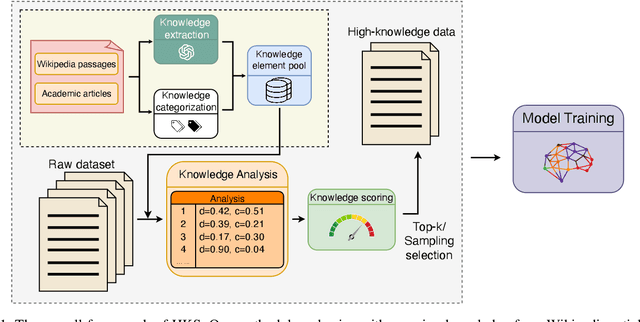
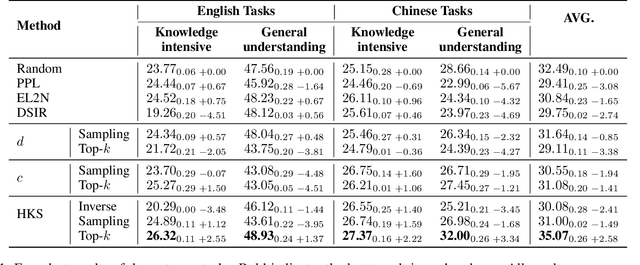
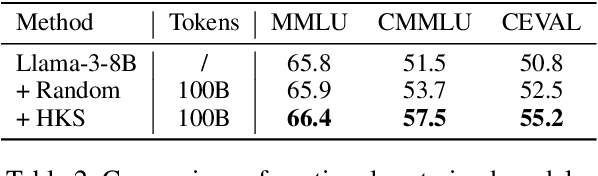
Abstract:The performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) is intrinsically linked to the quality of its training data. Although several studies have proposed methods for high-quality data selection, they do not consider the importance of knowledge richness in text corpora. In this paper, we propose a novel and gradient-free High-Knowledge Scorer (HKS) to select high-quality data from the dimension of knowledge, to alleviate the problem of knowledge scarcity in the pre-trained corpus. We propose a comprehensive multi-domain knowledge element pool and introduce knowledge density and coverage as metrics to assess the knowledge content of the text. Based on this, we propose a comprehensive knowledge scorer to select data with intensive knowledge, which can also be utilized for domain-specific high-knowledge data selection by restricting knowledge elements to the specific domain. We train models on a high-knowledge bilingual dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that our scorer improves the model's performance in knowledge-intensive and general comprehension tasks, and is effective in enhancing both the generic and domain-specific capabilities of the model.
VisionReasoner: Unified Visual Perception and Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models exhibit inherent capabilities to handle diverse visual perception tasks. In this paper, we introduce VisionReasoner, a unified framework capable of reasoning and solving multiple visual perception tasks within a shared model. Specifically, by designing novel multi-object cognitive learning strategies and systematic task reformulation, VisionReasoner enhances its reasoning capabilities to analyze visual inputs, and addresses diverse perception tasks in a unified framework. The model generates a structured reasoning process before delivering the desired outputs responding to user queries. To rigorously assess unified visual perception capabilities, we evaluate VisionReasoner on ten diverse tasks spanning three critical domains: detection, segmentation, and counting. Experimental results show that VisionReasoner achieves superior performance as a unified model, outperforming Qwen2.5VL by relative margins of 29.1% on COCO (detection), 22.1% on ReasonSeg (segmentation), and 15.3% on CountBench (counting).
DataScout: Automatic Data Fact Retrieval for Statement Augmentation with an LLM-Based Agent
Apr 24, 2025
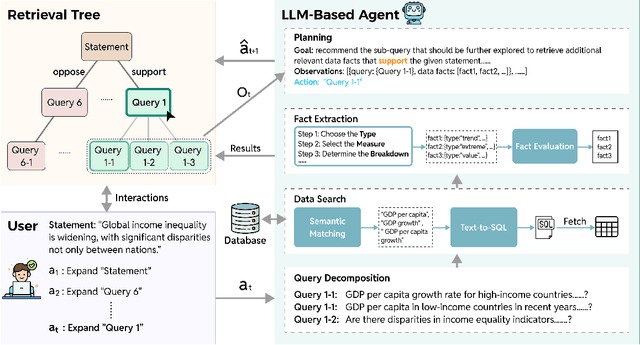
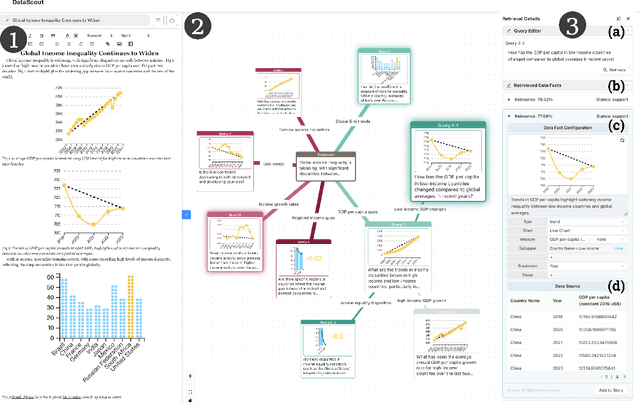
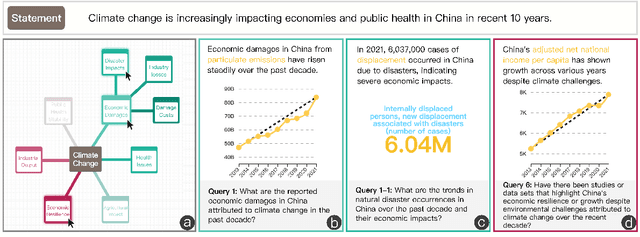
Abstract:A data story typically integrates data facts from multiple perspectives and stances to construct a comprehensive and objective narrative. However, retrieving these facts demands time for data search and challenges the creator's analytical skills. In this work, we introduce DataScout, an interactive system that automatically performs reasoning and stance-based data facts retrieval to augment the user's statement. Particularly, DataScout leverages an LLM-based agent to construct a retrieval tree, enabling collaborative control of its expansion between users and the agent. The interface visualizes the retrieval tree as a mind map that eases users to intuitively steer the retrieval direction and effectively engage in reasoning and analysis. We evaluate the proposed system through case studies and in-depth expert interviews. Our evaluation demonstrates that DataScout can effectively retrieve multifaceted data facts from different stances, helping users verify their statements and enhance the credibility of their stories.
Seg-Zero: Reasoning-Chain Guided Segmentation via Cognitive Reinforcement
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Traditional methods for reasoning segmentation rely on supervised fine-tuning with categorical labels and simple descriptions, limiting its out-of-domain generalization and lacking explicit reasoning processes. To address these limitations, we propose Seg-Zero, a novel framework that demonstrates remarkable generalizability and derives explicit chain-of-thought reasoning through cognitive reinforcement. Seg-Zero introduces a decoupled architecture consisting of a reasoning model and a segmentation model. The reasoning model interprets user intentions, generates explicit reasoning chains, and produces positional prompts, which are subsequently used by the segmentation model to generate precious pixel-level masks. We design a sophisticated reward mechanism that integrates both format and accuracy rewards to effectively guide optimization directions. Trained exclusively via reinforcement learning with GRPO and without explicit reasoning data, Seg-Zero achieves robust zero-shot generalization and exhibits emergent test-time reasoning capabilities. Experiments show that Seg-Zero-7B achieves a zero-shot performance of 57.5 on the ReasonSeg benchmark, surpassing the prior LISA-7B by 18\%. This significant improvement highlights Seg-Zero's ability to generalize across domains while presenting an explicit reasoning process. Code is available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/Seg-Zero.
AdaFlow: Efficient Long Video Editing via Adaptive Attention Slimming And Keyframe Selection
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Despite great progress, text-driven long video editing is still notoriously challenging mainly due to excessive memory overhead. Although recent efforts have simplified this task into a two-step process of keyframe translation and interpolation generation, the token-wise keyframe translation still plagues the upper limit of video length. In this paper, we propose a novel and training-free approach towards efficient and effective long video editing, termed AdaFlow. We first reveal that not all tokens of video frames hold equal importance for keyframe translation, based on which we propose an Adaptive Attention Slimming scheme for AdaFlow to squeeze the $KV$ sequence, thus increasing the number of keyframes for translations by an order of magnitude. In addition, an Adaptive Keyframe Selection scheme is also equipped to select the representative frames for joint editing, further improving generation quality. With these innovative designs, AdaFlow achieves high-quality long video editing of minutes in one inference, i.e., more than 1$k$ frames on one A800 GPU, which is about ten times longer than the compared methods, e.g., TokenFlow. To validate AdaFlow, we also build a new benchmark for long video editing with high-quality annotations, termed LongV-EVAL. Our code is released at: https://github.com/jidantang55/AdaFlow.
SVFR: A Unified Framework for Generalized Video Face Restoration
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Face Restoration (FR) is a crucial area within image and video processing, focusing on reconstructing high-quality portraits from degraded inputs. Despite advancements in image FR, video FR remains relatively under-explored, primarily due to challenges related to temporal consistency, motion artifacts, and the limited availability of high-quality video data. Moreover, traditional face restoration typically prioritizes enhancing resolution and may not give as much consideration to related tasks such as facial colorization and inpainting. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for the Generalized Video Face Restoration (GVFR) task, which integrates video BFR, inpainting, and colorization tasks that we empirically show to benefit each other. We present a unified framework, termed as stable video face restoration (SVFR), which leverages the generative and motion priors of Stable Video Diffusion (SVD) and incorporates task-specific information through a unified face restoration framework. A learnable task embedding is introduced to enhance task identification. Meanwhile, a novel Unified Latent Regularization (ULR) is employed to encourage the shared feature representation learning among different subtasks. To further enhance the restoration quality and temporal stability, we introduce the facial prior learning and the self-referred refinement as auxiliary strategies used for both training and inference. The proposed framework effectively combines the complementary strengths of these tasks, enhancing temporal coherence and achieving superior restoration quality. This work advances the state-of-the-art in video FR and establishes a new paradigm for generalized video face restoration. Code and video demo are available at https://github.com/wangzhiyaoo/SVFR.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge