Youwei Pang
FinMTM: A Multi-Turn Multimodal Benchmark for Financial Reasoning and Agent Evaluation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The financial domain poses substantial challenges for vision-language models (VLMs) due to specialized chart formats and knowledge-intensive reasoning requirements. However, existing financial benchmarks are largely single-turn and rely on a narrow set of question formats, limiting comprehensive evaluation in realistic application scenarios. To address this gap, we propose FinMTM, a multi-turn multimodal benchmark that expands diversity along both data and task dimensions. On the data side, we curate and annotate 11{,}133 bilingual (Chinese and English) financial QA pairs grounded in financial visuals, including candlestick charts, statistical plots, and report figures. On the task side, FinMTM covers single- and multiple-choice questions, multi-turn open-ended dialogues, and agent-based tasks. We further design task-specific evaluation protocols, including a set-overlap scoring rule for multiple-choice questions, a weighted combination of turn-level and session-level scores for multi-turn dialogues, and a composite metric that integrates planning quality with final outcomes for agent tasks. Extensive experimental evaluation of 22 VLMs reveal their limitations in fine-grained visual perception, long-context reasoning, and complex agent workflows.
UniMRSeg: Unified Modality-Relax Segmentation via Hierarchical Self-Supervised Compensation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal image segmentation faces real-world deployment challenges from incomplete/corrupted modalities degrading performance. While existing methods address training-inference modality gaps via specialized per-combination models, they introduce high deployment costs by requiring exhaustive model subsets and model-modality matching. In this work, we propose a unified modality-relax segmentation network (UniMRSeg) through hierarchical self-supervised compensation (HSSC). Our approach hierarchically bridges representation gaps between complete and incomplete modalities across input, feature and output levels. % First, we adopt modality reconstruction with the hybrid shuffled-masking augmentation, encouraging the model to learn the intrinsic modality characteristics and generate meaningful representations for missing modalities through cross-modal fusion. % Next, modality-invariant contrastive learning implicitly compensates the feature space distance among incomplete-complete modality pairs. Furthermore, the proposed lightweight reverse attention adapter explicitly compensates for the weak perceptual semantics in the frozen encoder. Last, UniMRSeg is fine-tuned under the hybrid consistency constraint to ensure stable prediction under all modality combinations without large performance fluctuations. Without bells and whistles, UniMRSeg significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods under diverse missing modality scenarios on MRI-based brain tumor segmentation, RGB-D semantic segmentation, RGB-D/T salient object segmentation. The code will be released at https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/UniMRSeg.
Power Battery Detection
Aug 11, 2025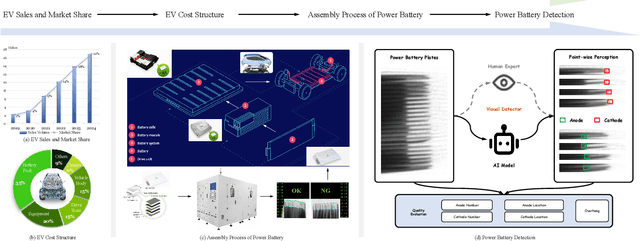
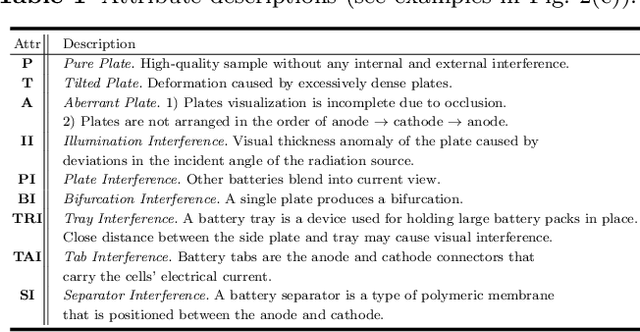
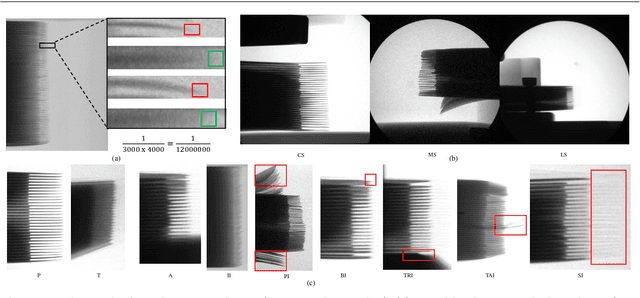

Abstract:Power batteries are essential components in electric vehicles, where internal structural defects can pose serious safety risks. We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task, power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense endpoints of cathode and anode plates from industrial X-ray images for quality inspection. Manual inspection is inefficient and error-prone, while traditional vision algorithms struggle with densely packed plates, low contrast, scale variation, and imaging artifacts. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we present PBD5K, the first large-scale benchmark for this task, consisting of 5,000 X-ray images from nine battery types with fine-grained annotations and eight types of real-world visual interference. To support scalable and consistent labeling, we develop an intelligent annotation pipeline that combines image filtering, model-assisted pre-labeling, cross-verification, and layered quality evaluation. We formulate PBD as a point-level segmentation problem and propose MDCNeXt, a model designed to extract and integrate multi-dimensional structure clues including point, line, and count information from the plate itself. To improve discrimination between plates and suppress visual interference, MDCNeXt incorporates two state space modules. The first is a prompt-filtered module that learns contrastive relationships guided by task-specific prompts. The second is a density-aware reordering module that refines segmentation in regions with high plate density. In addition, we propose a distance-adaptive mask generation strategy to provide robust supervision under varying spatial distributions of anode and cathode positions. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD}{PBD5K}.
Retrospective Memory for Camouflaged Object Detection
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) primarily focuses on learning subtle yet discriminative representations from complex scenes. Existing methods predominantly follow the parametric feedforward architecture based on static visual representation modeling. However, they lack explicit mechanisms for acquiring historical context, limiting their adaptation and effectiveness in handling challenging camouflage scenes. In this paper, we propose a recall-augmented COD architecture, namely RetroMem, which dynamically modulates camouflage pattern perception and inference by integrating relevant historical knowledge into the process. Specifically, RetroMem employs a two-stage training paradigm consisting of a learning stage and a recall stage to construct, update, and utilize memory representations effectively. During the learning stage, we design a dense multi-scale adapter (DMA) to improve the pretrained encoder's capability to capture rich multi-scale visual information with very few trainable parameters, thereby providing foundational inferences. In the recall stage, we propose a dynamic memory mechanism (DMM) and an inference pattern reconstruction (IPR). These components fully leverage the latent relationships between learned knowledge and current sample context to reconstruct the inference of camouflage patterns, thereby significantly improving the model's understanding of camouflage scenes. Extensive experiments on several widely used datasets demonstrate that our RetroMem significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
Uncertainty-Masked Bernoulli Diffusion for Camouflaged Object Detection Refinement
Jun 12, 2025

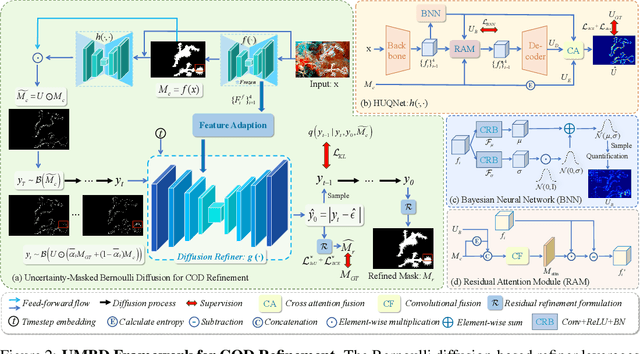

Abstract:Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) presents inherent challenges due to the subtle visual differences between targets and their backgrounds. While existing methods have made notable progress, there remains significant potential for post-processing refinement that has yet to be fully explored. To address this limitation, we propose the Uncertainty-Masked Bernoulli Diffusion (UMBD) model, the first generative refinement framework specifically designed for COD. UMBD introduces an uncertainty-guided masking mechanism that selectively applies Bernoulli diffusion to residual regions with poor segmentation quality, enabling targeted refinement while preserving correctly segmented areas. To support this process, we design the Hybrid Uncertainty Quantification Network (HUQNet), which employs a multi-branch architecture and fuses uncertainty from multiple sources to improve estimation accuracy. This enables adaptive guidance during the generative sampling process. The proposed UMBD framework can be seamlessly integrated with a wide range of existing Encoder-Decoder-based COD models, combining their discriminative capabilities with the generative advantages of diffusion-based refinement. Extensive experiments across multiple COD benchmarks demonstrate consistent performance improvements, achieving average gains of 5.5% in MAE and 3.2% in weighted F-measure with only modest computational overhead. Code will be released.
Segment Concealed Objects with Incomplete Supervision
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Incompletely-Supervised Concealed Object Segmentation (ISCOS) involves segmenting objects that seamlessly blend into their surrounding environments, utilizing incompletely annotated data, such as weak and semi-annotations, for model training. This task remains highly challenging due to (1) the limited supervision provided by the incompletely annotated training data, and (2) the difficulty of distinguishing concealed objects from the background, which arises from the intrinsic similarities in concealed scenarios. In this paper, we introduce the first unified method for ISCOS to address these challenges. To tackle the issue of incomplete supervision, we propose a unified mean-teacher framework, SEE, that leverages the vision foundation model, ``\emph{Segment Anything Model (SAM)}'', to generate pseudo-labels using coarse masks produced by the teacher model as prompts. To mitigate the effect of low-quality segmentation masks, we introduce a series of strategies for pseudo-label generation, storage, and supervision. These strategies aim to produce informative pseudo-labels, store the best pseudo-labels generated, and select the most reliable components to guide the student model, thereby ensuring robust network training. Additionally, to tackle the issue of intrinsic similarity, we design a hybrid-granularity feature grouping module that groups features at different granularities and aggregates these results. By clustering similar features, this module promotes segmentation coherence, facilitating more complete segmentation for both single-object and multiple-object images. We validate the effectiveness of our approach across multiple ISCOS tasks, and experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. Furthermore, SEE can serve as a plug-and-play solution, enhancing the performance of existing models.
* IEEE TPAMI
CGCOD: Class-Guided Camouflaged Object Detection
Dec 25, 2024


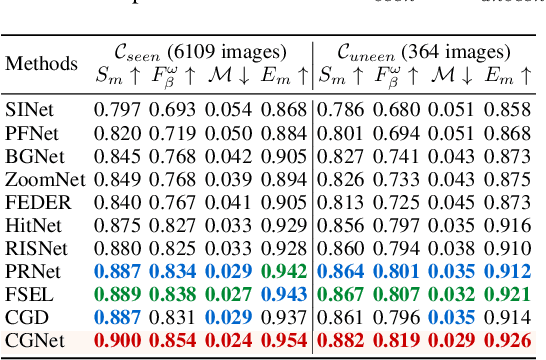
Abstract:Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) is designed to identify objects that blend seamlessly with their surroundings. Due to the complexity of camouflaged objects (such as shape, color, and texture), their semantic cues are often blurred or completely lost, posing a significant challenge for COD. Existing COD methods often rely on visual features, which are not stable enough in changeable camouflage environments. This instability leads to false positives and false negatives, resulting in incomplete or inaccurate segmentation results. In this paper, to solve this problem, we propose a new task, Class-Guided Camouflaged Object Detection (CG-COD), which extends the traditional COD task by introducing object class knowledge, significantly improving the robustness and segmentation accuracy of the model in complex environments. Toward this end, we construct a dataset, CamoClass, containing the camouflaged objects in the real scenes and their corresponding class annotation. Based on this, we propose a multi-stage framework CGNet which consists of a plug-and-play class prompt generator and a class-guided detector. Under the guidance of textual information, CGNet enables efficient segmentation. It is worth emphasizing that for the first time, we extend the object class annotations on existing COD benchmark datasets, and introduce a flexible framework to improve the performance of the existing COD model under text guidance.
Inspiring the Next Generation of Segment Anything Models: Comprehensively Evaluate SAM and SAM 2 with Diverse Prompts Towards Context-Dependent Concepts under Different Scenes
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:As a foundational model, SAM has significantly influenced multiple fields within computer vision, and its upgraded version, SAM 2, enhances capabilities in video segmentation, poised to make a substantial impact once again. While SAMs (SAM and SAM 2) have demonstrated excellent performance in segmenting context-independent concepts like people, cars, and roads, they overlook more challenging context-dependent (CD) concepts, such as visual saliency, camouflage, product defects, and medical lesions. CD concepts rely heavily on global and local contextual information, making them susceptible to shifts in different contexts, which requires strong discriminative capabilities from the model. The lack of comprehensive evaluation of SAMs limits understanding of their performance boundaries, which may hinder the design of future models. In this paper, we conduct a thorough quantitative evaluation of SAMs on 11 CD concepts across 2D and 3D images and videos in various visual modalities within natural, medical, and industrial scenes. We develop a unified evaluation framework for SAM and SAM 2 that supports manual, automatic, and intermediate self-prompting, aided by our specific prompt generation and interaction strategies. We further explore the potential of SAM 2 for in-context learning and introduce prompt robustness testing to simulate real-world imperfect prompts. Finally, we analyze the benefits and limitations of SAMs in understanding CD concepts and discuss their future development in segmentation tasks. This work aims to provide valuable insights to guide future research in both context-independent and context-dependent concepts segmentation, potentially informing the development of the next version - SAM 3.
Beyond Mask: Rethinking Guidance Types in Few-shot Segmentation
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Existing few-shot segmentation (FSS) methods mainly focus on prototype feature generation and the query-support matching mechanism. As a crucial prompt for generating prototype features, the pair of image-mask types in the support set has become the default setting. However, various types such as image, text, box, and mask all can provide valuable information regarding the objects in context, class, localization, and shape appearance. Existing work focuses on specific combinations of guidance, leading FSS into different research branches. Rethinking guidance types in FSS is expected to explore the efficient joint representation of the coupling between the support set and query set, giving rise to research trends in the weakly or strongly annotated guidance to meet the customized requirements of practical users. In this work, we provide the generalized FSS with seven guidance paradigms and develop a universal vision-language framework (UniFSS) to integrate prompts from text, mask, box, and image. Leveraging the advantages of large-scale pre-training vision-language models in textual and visual embeddings, UniFSS proposes high-level spatial correction and embedding interactive units to overcome the semantic ambiguity drawbacks typically encountered by pure visual matching methods when facing intra-class appearance diversities. Extensive experiments show that UniFSS significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Notably, the weakly annotated class-aware box paradigm even surpasses the finely annotated mask paradigm.
Spider: A Unified Framework for Context-dependent Concept Understanding
May 02, 2024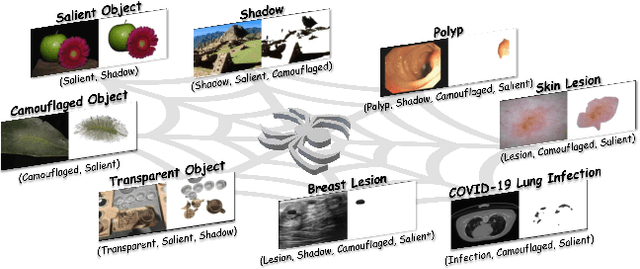
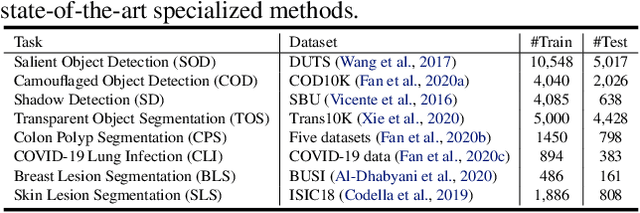
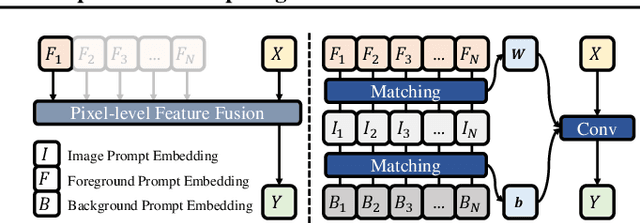
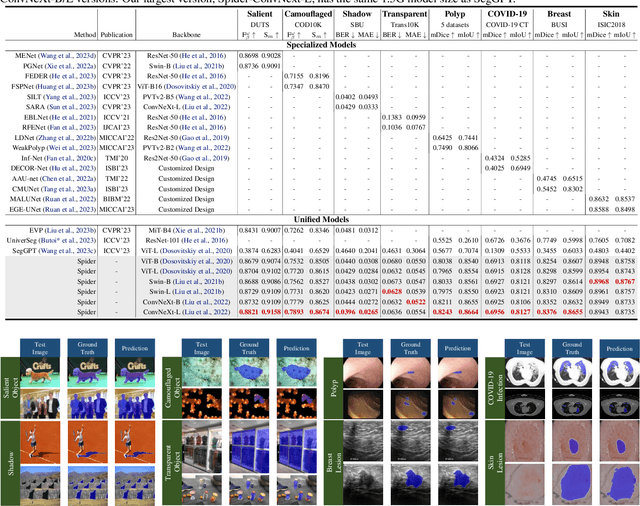
Abstract:Different from the context-independent (CI) concepts such as human, car, and airplane, context-dependent (CD) concepts require higher visual understanding ability, such as camouflaged object and medical lesion. Despite the rapid advance of many CD understanding tasks in respective branches, the isolated evolution leads to their limited cross-domain generalisation and repetitive technique innovation. Since there is a strong coupling relationship between foreground and background context in CD tasks, existing methods require to train separate models in their focused domains. This restricts their real-world CD concept understanding towards artificial general intelligence (AGI). We propose a unified model with a single set of parameters, Spider, which only needs to be trained once. With the help of the proposed concept filter driven by the image-mask group prompt, Spider is able to understand and distinguish diverse strong context-dependent concepts to accurately capture the Prompter's intention. Without bells and whistles, Spider significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art specialized models in 8 different context-dependent segmentation tasks, including 4 natural scenes (salient, camouflaged, and transparent objects and shadow) and 4 medical lesions (COVID-19, polyp, breast, and skin lesion with color colonoscopy, CT, ultrasound, and dermoscopy modalities). Besides, Spider shows obvious advantages in continuous learning. It can easily complete the training of new tasks by fine-tuning parameters less than 1\% and bring a tolerable performance degradation of less than 5\% for all old tasks. The source code will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/Spider-UniCDSeg}{Spider-UniCDSeg}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge