Jiaming Zuo
Power Battery Detection
Aug 11, 2025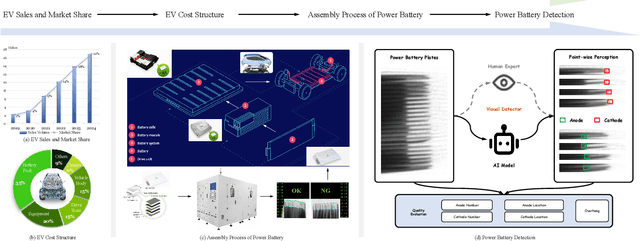
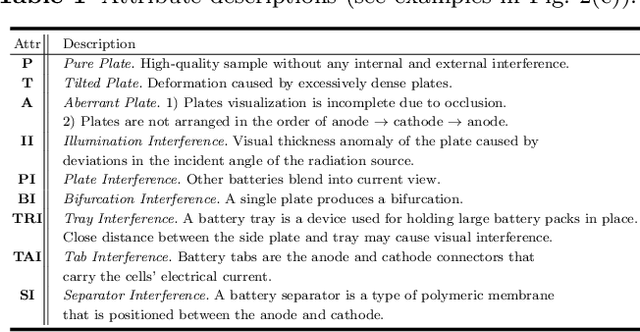
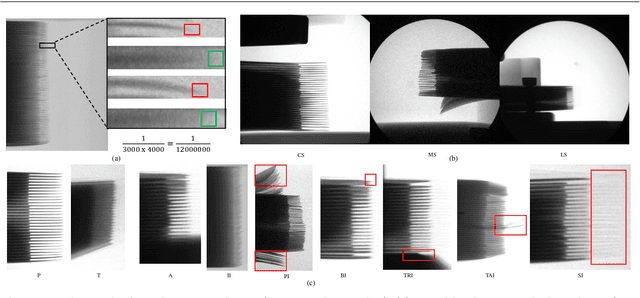

Abstract:Power batteries are essential components in electric vehicles, where internal structural defects can pose serious safety risks. We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task, power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense endpoints of cathode and anode plates from industrial X-ray images for quality inspection. Manual inspection is inefficient and error-prone, while traditional vision algorithms struggle with densely packed plates, low contrast, scale variation, and imaging artifacts. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we present PBD5K, the first large-scale benchmark for this task, consisting of 5,000 X-ray images from nine battery types with fine-grained annotations and eight types of real-world visual interference. To support scalable and consistent labeling, we develop an intelligent annotation pipeline that combines image filtering, model-assisted pre-labeling, cross-verification, and layered quality evaluation. We formulate PBD as a point-level segmentation problem and propose MDCNeXt, a model designed to extract and integrate multi-dimensional structure clues including point, line, and count information from the plate itself. To improve discrimination between plates and suppress visual interference, MDCNeXt incorporates two state space modules. The first is a prompt-filtered module that learns contrastive relationships guided by task-specific prompts. The second is a density-aware reordering module that refines segmentation in regions with high plate density. In addition, we propose a distance-adaptive mask generation strategy to provide robust supervision under varying spatial distributions of anode and cathode positions. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD}{PBD5K}.
Spider: A Unified Framework for Context-dependent Concept Understanding
May 02, 2024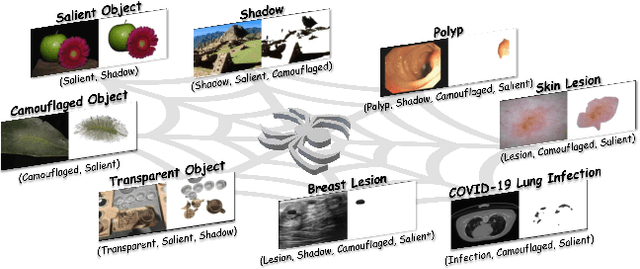
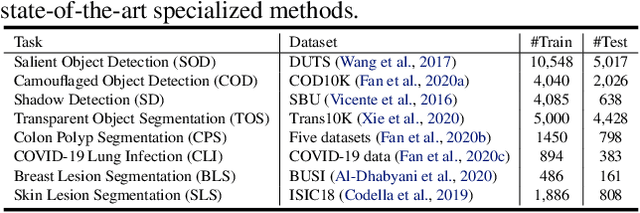
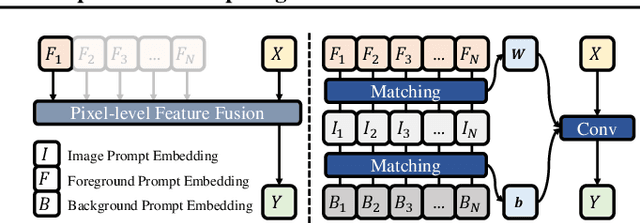
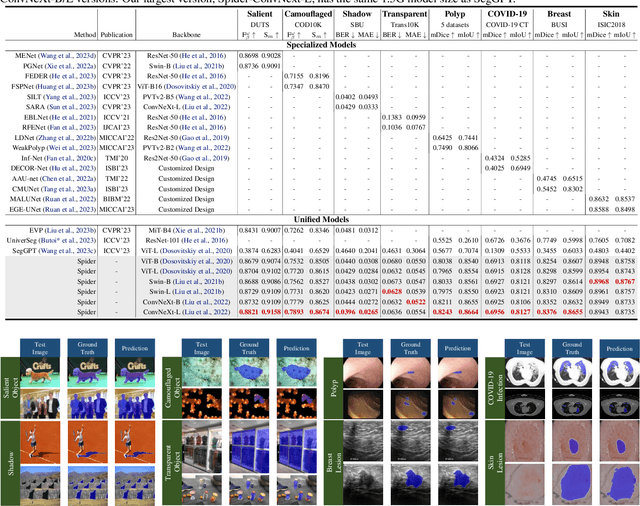
Abstract:Different from the context-independent (CI) concepts such as human, car, and airplane, context-dependent (CD) concepts require higher visual understanding ability, such as camouflaged object and medical lesion. Despite the rapid advance of many CD understanding tasks in respective branches, the isolated evolution leads to their limited cross-domain generalisation and repetitive technique innovation. Since there is a strong coupling relationship between foreground and background context in CD tasks, existing methods require to train separate models in their focused domains. This restricts their real-world CD concept understanding towards artificial general intelligence (AGI). We propose a unified model with a single set of parameters, Spider, which only needs to be trained once. With the help of the proposed concept filter driven by the image-mask group prompt, Spider is able to understand and distinguish diverse strong context-dependent concepts to accurately capture the Prompter's intention. Without bells and whistles, Spider significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art specialized models in 8 different context-dependent segmentation tasks, including 4 natural scenes (salient, camouflaged, and transparent objects and shadow) and 4 medical lesions (COVID-19, polyp, breast, and skin lesion with color colonoscopy, CT, ultrasound, and dermoscopy modalities). Besides, Spider shows obvious advantages in continuous learning. It can easily complete the training of new tasks by fine-tuning parameters less than 1\% and bring a tolerable performance degradation of less than 5\% for all old tasks. The source code will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/Spider-UniCDSeg}{Spider-UniCDSeg}.
Towards Automatic Power Battery Detection: New Challenge, Benchmark Dataset and Baseline
Dec 05, 2023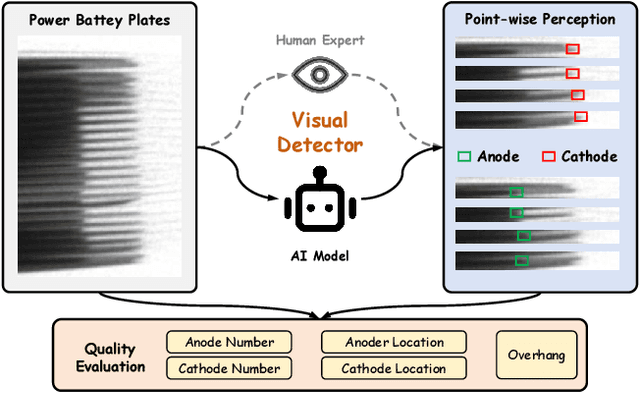
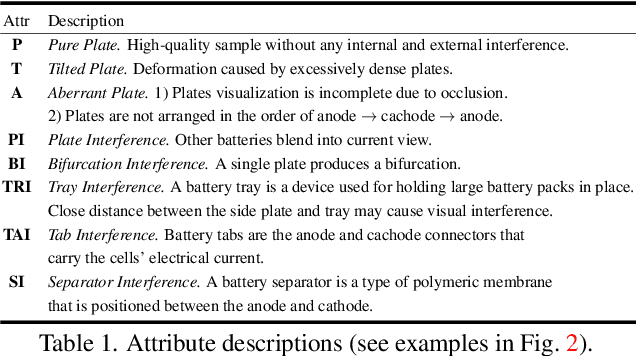
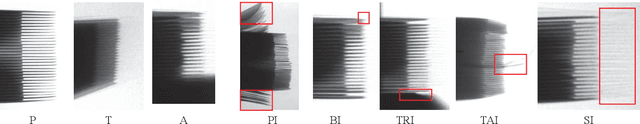
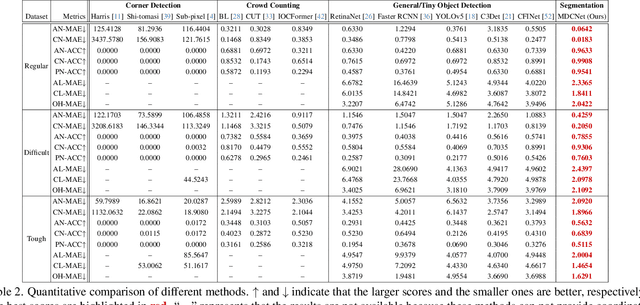
Abstract:We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task named power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense cathode and anode plates endpoints from X-ray images to evaluate the quality of power batteries. Existing manufacturers usually rely on human eye observation to complete PBD, which makes it difficult to balance the accuracy and efficiency of detection. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we first elaborately collect a dataset, called X-ray PBD, which has $1,500$ diverse X-ray images selected from thousands of power batteries of $5$ manufacturers, with $7$ different visual interference. Then, we propose a novel segmentation-based solution for PBD, termed multi-dimensional collaborative network (MDCNet). With the help of line and counting predictors, the representation of the point segmentation branch can be improved at both semantic and detail aspects. Besides, we design an effective distance-adaptive mask generation strategy, which can alleviate the visual challenge caused by the inconsistent distribution density of plates to provide MDCNet with stable supervision. Without any bells and whistles, our segmentation-based MDCNet consistently outperforms various other corner detection, crowd counting and general/tiny object detection-based solutions, making it a strong baseline that can help facilitate future research in PBD. Finally, we share some potential difficulties and works for future researches. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{http://www.gy3000.company/x3000%e5%bc%80%e6%94%be%e5%b9%b3%e5%8f%b0}{X-ray PBD}.
Open-Vocabulary Camouflaged Object Segmentation
Nov 19, 2023



Abstract:Recently, the emergence of the large-scale vision-language model (VLM), such as CLIP, has opened the way towards open-world object perception. Many works has explored the utilization of pre-trained VLM for the challenging open-vocabulary dense prediction task that requires perceive diverse objects with novel classes at inference time. Existing methods construct experiments based on the public datasets of related tasks, which are not tailored for open vocabulary and rarely involves imperceptible objects camouflaged in complex scenes due to data collection bias and annotation costs. To fill in the gaps, we introduce a new task, open-vocabulary camouflaged object segmentation (OVCOS) and construct a large-scale complex scene dataset (\textbf{OVCamo}) which containing 11,483 hand-selected images with fine annotations and corresponding object classes. Further, we build a strong single-stage open-vocabulary \underline{c}amouflaged \underline{o}bject \underline{s}egmentation transform\underline{er} baseline \textbf{OVCoser} attached to the parameter-fixed CLIP with iterative semantic guidance and structure enhancement. By integrating the guidance of class semantic knowledge and the supplement of visual structure cues from the edge and depth information, the proposed method can efficiently capture camouflaged objects. Moreover, this effective framework also surpasses previous state-of-the-arts of open-vocabulary semantic image segmentation by a large margin on our OVCamo dataset. With the proposed dataset and baseline, we hope that this new task with more practical value can further expand the research on open-vocabulary dense prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge