Chenyang Zhu
Lessons from the Field: An Adaptable Lifecycle Approach to Applied Dialogue Summarization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Summarization of multi-party dialogues is a critical capability in industry, enhancing knowledge transfer and operational effectiveness across many domains. However, automatically generating high-quality summaries is challenging, as the ideal summary must satisfy a set of complex, multi-faceted requirements. While summarization has received immense attention in research, prior work has primarily utilized static datasets and benchmarks, a condition rare in practical scenarios where requirements inevitably evolve. In this work, we present an industry case study on developing an agentic system to summarize multi-party interactions. We share practical insights spanning the full development lifecycle to guide practitioners in building reliable, adaptable summarization systems, as well as to inform future research, covering: 1) robust methods for evaluation despite evolving requirements and task subjectivity, 2) component-wise optimization enabled by the task decomposition inherent in an agentic architecture, 3) the impact of upstream data bottlenecks, and 4) the realities of vendor lock-in due to the poor transferability of LLM prompts.
Improving Consistency in Retrieval-Augmented Systems with Group Similarity Rewards
Oct 05, 2025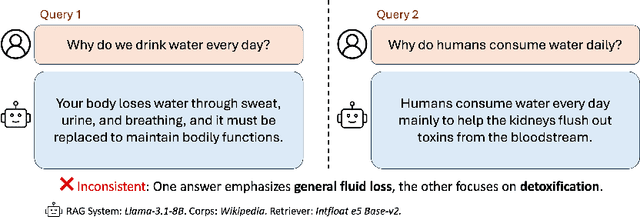
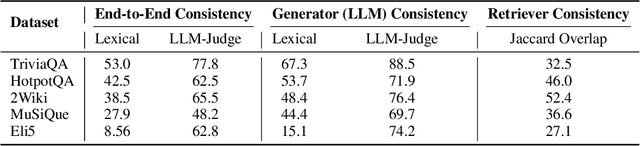
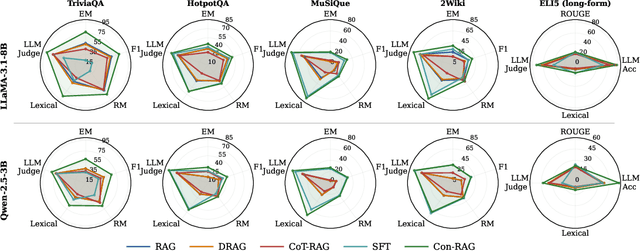
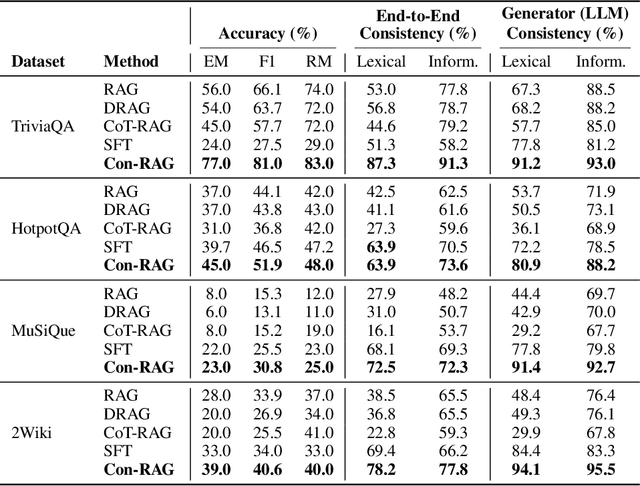
Abstract:RAG systems are increasingly deployed in high-stakes domains where users expect outputs to be consistent across semantically equivalent queries. However, existing systems often exhibit significant inconsistencies due to variability in both the retriever and generator (LLM), undermining trust and reliability. In this work, we focus on information consistency, i.e., the requirement that outputs convey the same core content across semantically equivalent inputs. We introduce a principled evaluation framework that decomposes RAG consistency into retriever-level, generator-level, and end-to-end components, helping identify inconsistency sources. To improve consistency, we propose Paraphrased Set Group Relative Policy Optimization (PS-GRPO), an RL approach that leverages multiple rollouts across paraphrased set to assign group similarity rewards. We leverage PS-GRPO to achieve Information Consistent RAG (Con-RAG), training the generator to produce consistent outputs across paraphrased queries and remain robust to retrieval-induced variability. Because exact reward computation over paraphrase sets is computationally expensive, we also introduce a scalable approximation method that retains effectiveness while enabling efficient, large-scale training. Empirical evaluations across short-form, multi-hop, and long-form QA benchmarks demonstrate that Con-RAG significantly improves both consistency and accuracy over strong baselines, even in the absence of explicit ground-truth supervision. Our work provides practical solutions for evaluating and building reliable RAG systems for safety-critical deployments.
RemixFusion: Residual-based Mixed Representation for Large-scale Online RGB-D Reconstruction
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:The introduction of the neural implicit representation has notably propelled the advancement of online dense reconstruction techniques. Compared to traditional explicit representations, such as TSDF, it improves the mapping completeness and memory efficiency. However, the lack of reconstruction details and the time-consuming learning of neural representations hinder the widespread application of neural-based methods to large-scale online reconstruction. We introduce RemixFusion, a novel residual-based mixed representation for scene reconstruction and camera pose estimation dedicated to high-quality and large-scale online RGB-D reconstruction. In particular, we propose a residual-based map representation comprised of an explicit coarse TSDF grid and an implicit neural module that produces residuals representing fine-grained details to be added to the coarse grid. Such mixed representation allows for detail-rich reconstruction with bounded time and memory budget, contrasting with the overly-smoothed results by the purely implicit representations, thus paving the way for high-quality camera tracking. Furthermore, we extend the residual-based representation to handle multi-frame joint pose optimization via bundle adjustment (BA). In contrast to the existing methods, which optimize poses directly, we opt to optimize pose changes. Combined with a novel technique for adaptive gradient amplification, our method attains better optimization convergence and global optimality. Furthermore, we adopt a local moving volume to factorize the mixed scene representation with a divide-and-conquer design to facilitate efficient online learning in our residual-based framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses all state-of-the-art ones, including those based either on explicit or implicit representations, in terms of the accuracy of both mapping and tracking on large-scale scenes.
Curve-Aware Gaussian Splatting for 3D Parametric Curve Reconstruction
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an end-to-end framework for reconstructing 3D parametric curves directly from multi-view edge maps. Contrasting with existing two-stage methods that follow a sequential ``edge point cloud reconstruction and parametric curve fitting'' pipeline, our one-stage approach optimizes 3D parametric curves directly from 2D edge maps, eliminating error accumulation caused by the inherent optimization gap between disconnected stages. However, parametric curves inherently lack suitability for rendering-based multi-view optimization, necessitating a complementary representation that preserves their geometric properties while enabling differentiable rendering. We propose a novel bi-directional coupling mechanism between parametric curves and edge-oriented Gaussian components. This tight correspondence formulates a curve-aware Gaussian representation, \textbf{CurveGaussian}, that enables differentiable rendering of 3D curves, allowing direct optimization guided by multi-view evidence. Furthermore, we introduce a dynamically adaptive topology optimization framework during training to refine curve structures through linearization, merging, splitting, and pruning operations. Comprehensive evaluations on the ABC dataset and real-world benchmarks demonstrate our one-stage method's superiority over two-stage alternatives, particularly in producing cleaner and more robust reconstructions. Additionally, by directly optimizing parametric curves, our method significantly reduces the parameter count during training, achieving both higher efficiency and superior performance compared to existing approaches.
Angio-Diff: Learning a Self-Supervised Adversarial Diffusion Model for Angiographic Geometry Generation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Vascular diseases pose a significant threat to human health, with X-ray angiography established as the gold standard for diagnosis, allowing for detailed observation of blood vessels. However, angiographic X-rays expose personnel and patients to higher radiation levels than non-angiographic X-rays, which are unwanted. Thus, modality translation from non-angiographic to angiographic X-rays is desirable. Data-driven deep approaches are hindered by the lack of paired large-scale X-ray angiography datasets. While making high-quality vascular angiography synthesis crucial, it remains challenging. We find that current medical image synthesis primarily operates at pixel level and struggles to adapt to the complex geometric structure of blood vessels, resulting in unsatisfactory quality of blood vessel image synthesis, such as disconnections or unnatural curvatures. To overcome this issue, we propose a self-supervised method via diffusion models to transform non-angiographic X-rays into angiographic X-rays, mitigating data shortages for data-driven approaches. Our model comprises a diffusion model that learns the distribution of vascular data from diffusion latent, a generator for vessel synthesis, and a mask-based adversarial module. To enhance geometric accuracy, we propose a parametric vascular model to fit the shape and distribution of blood vessels. The proposed method contributes a pipeline and a synthetic dataset for X-ray angiography. We conducted extensive comparative and ablation experiments to evaluate the Angio-Diff. The results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in synthetic angiography image quality and more accurately synthesizes the geometric structure of blood vessels. The code is available at https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff.
BoxFusion: Reconstruction-Free Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Detection via Real-Time Multi-View Box Fusion
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary 3D object detection has gained significant interest due to its critical applications in autonomous driving and embodied AI. Existing detection methods, whether offline or online, typically rely on dense point cloud reconstruction, which imposes substantial computational overhead and memory constraints, hindering real-time deployment in downstream tasks. To address this, we propose a novel reconstruction-free online framework tailored for memory-efficient and real-time 3D detection. Specifically, given streaming posed RGB-D video input, we leverage Cubify Anything as a pre-trained visual foundation model (VFM) for single-view 3D object detection by bounding boxes, coupled with CLIP to capture open-vocabulary semantics of detected objects. To fuse all detected bounding boxes across different views into a unified one, we employ an association module for correspondences of multi-views and an optimization module to fuse the 3D bounding boxes of the same instance predicted in multi-views. The association module utilizes 3D Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) and a box correspondence matching module, while the optimization module uses an IoU-guided efficient random optimization technique based on particle filtering to enforce multi-view consistency of the 3D bounding boxes while minimizing computational complexity. Extensive experiments on ScanNetV2 and CA-1M datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance among online methods. Benefiting from this novel reconstruction-free paradigm for 3D object detection, our method exhibits great generalization abilities in various scenarios, enabling real-time perception even in environments exceeding 1000 square meters.
AnimeDL-2M: Million-Scale AI-Generated Anime Image Detection and Localization in Diffusion Era
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in image generation, particularly diffusion models, have significantly lowered the barrier for creating sophisticated forgeries, making image manipulation detection and localization (IMDL) increasingly challenging. While prior work in IMDL has focused largely on natural images, the anime domain remains underexplored-despite its growing vulnerability to AI-generated forgeries. Misrepresentations of AI-generated images as hand-drawn artwork, copyright violations, and inappropriate content modifications pose serious threats to the anime community and industry. To address this gap, we propose AnimeDL-2M, the first large-scale benchmark for anime IMDL with comprehensive annotations. It comprises over two million images including real, partially manipulated, and fully AI-generated samples. Experiments indicate that models trained on existing IMDL datasets of natural images perform poorly when applied to anime images, highlighting a clear domain gap between anime and natural images. To better handle IMDL tasks in anime domain, we further propose AniXplore, a novel model tailored to the visual characteristics of anime imagery. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that AniXplore achieves superior performance compared to existing methods. Dataset and code can be found in https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/.
Deliberate Planning of 3D Bin Packing on Packing Configuration Trees
Apr 06, 2025Abstract:Online 3D Bin Packing Problem (3D-BPP) has widespread applications in industrial automation. Existing methods usually solve the problem with limited resolution of spatial discretization, and/or cannot deal with complex practical constraints well. We propose to enhance the practical applicability of online 3D-BPP via learning on a novel hierarchical representation, packing configuration tree (PCT). PCT is a full-fledged description of the state and action space of bin packing which can support packing policy learning based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL). The size of the packing action space is proportional to the number of leaf nodes, making the DRL model easy to train and well-performing even with continuous solution space. We further discover the potential of PCT as tree-based planners in deliberately solving packing problems of industrial significance, including large-scale packing and different variations of BPP setting. A recursive packing method is proposed to decompose large-scale packing into smaller sub-trees while a spatial ensemble mechanism integrates local solutions into global. For different BPP variations with additional decision variables, such as lookahead, buffering, and offline packing, we propose a unified planning framework enabling out-of-the-box problem solving. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our method outperforms existing online BPP baselines and is versatile in incorporating various practical constraints. The planning process excels across large-scale problems and diverse problem variations. We develop a real-world packing robot for industrial warehousing, with careful designs accounting for constrained placement and transportation stability. Our packing robot operates reliably and efficiently on unprotected pallets at 10 seconds per box. It achieves averagely 19 boxes per pallet with 57.4% space utilization for relatively large-size boxes.
VasTSD: Learning 3D Vascular Tree-state Space Diffusion Model for Angiography Synthesis
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Angiography imaging is a medical imaging technique that enhances the visibility of blood vessels within the body by using contrast agents. Angiographic images can effectively assist in the diagnosis of vascular diseases. However, contrast agents may bring extra radiation exposure which is harmful to patients with health risks. To mitigate these concerns, in this paper, we aim to automatically generate angiography from non-angiographic inputs, by leveraging and enhancing the inherent physical properties of vascular structures. Previous methods relying on 2D slice-based angiography synthesis struggle with maintaining continuity in 3D vascular structures and exhibit limited effectiveness across different imaging modalities. We propose VasTSD, a 3D vascular tree-state space diffusion model to synthesize angiography from 3D non-angiographic volumes, with a novel state space serialization approach that dynamically constructs vascular tree topologies, integrating these with a diffusion-based generative model to ensure the generation of anatomically continuous vasculature in 3D volumes. A pre-trained vision embedder is employed to construct vascular state space representations, enabling consistent modeling of vascular structures across multiple modalities. Extensive experiments on various angiographic datasets demonstrate the superiority of VasTSD over prior works, achieving enhanced continuity of blood vessels in synthesized angiographic synthesis for multiple modalities and anatomical regions.
OnlineAnySeg: Online Zero-Shot 3D Segmentation by Visual Foundation Model Guided 2D Mask Merging
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Online 3D open-vocabulary segmentation of a progressively reconstructed scene is both a critical and challenging task for embodied applications. With the success of visual foundation models (VFMs) in the image domain, leveraging 2D priors to address 3D online segmentation has become a prominent research focus. Since segmentation results provided by 2D priors often require spatial consistency to be lifted into final 3D segmentation, an efficient method for identifying spatial overlap among 2D masks is essential - yet existing methods rarely achieve this in real time, mainly limiting its use to offline approaches. To address this, we propose an efficient method that lifts 2D masks generated by VFMs into a unified 3D instance using a hashing technique. By employing voxel hashing for efficient 3D scene querying, our approach reduces the time complexity of costly spatial overlap queries from $O(n^2)$ to $O(n)$. Accurate spatial associations further enable 3D merging of 2D masks through simple similarity-based filtering in a zero-shot manner, making our approach more robust to incomplete and noisy data. Evaluated on the ScanNet and SceneNN benchmarks, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in online, open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation with leading efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge