Guibo Luo
DSFedMed: Dual-Scale Federated Medical Image Segmentation via Mutual Distillation Between Foundation and Lightweight Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Foundation Models (FMs) have demonstrated strong generalization across diverse vision tasks. However, their deployment in federated settings is hindered by high computational demands, substantial communication overhead, and significant inference costs. We propose DSFedMed, a dual-scale federated framework that enables mutual knowledge distillation between a centralized foundation model and lightweight client models for medical image segmentation. To support knowledge distillation, a set of high-quality medical images is generated to replace real public datasets, and a learnability-guided sample selection strategy is proposed to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in dual-scale distillation. This mutual distillation enables the foundation model to transfer general knowledge to lightweight clients, while also incorporating client-specific insights to refine the foundation model. Evaluations on five medical imaging segmentation datasets show that DSFedMed achieves an average 2 percent improvement in Dice score while reducing communication costs and inference time by nearly 90 percent compared to existing federated foundation model baselines. These results demonstrate significant efficiency gains and scalability for resource-limited federated deployments.
Feature-Aware One-Shot Federated Learning via Hierarchical Token Sequences
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:One-shot federated learning (OSFL) reduces the communication cost and privacy risks of iterative federated learning by constructing a global model with a single round of communication. However, most existing methods struggle to achieve robust performance on real-world domains such as medical imaging, or are inefficient when handling non-IID (Independent and Identically Distributed) data. To address these limitations, we introduce FALCON, a framework that enhances the effectiveness of OSFL over non-IID image data. The core idea of FALCON is to leverage the feature-aware hierarchical token sequences generation and knowledge distillation into OSFL. First, each client leverages a pretrained visual encoder with hierarchical scale encoding to compress images into hierarchical token sequences, which capture multi-scale semantics. Second, a multi-scale autoregressive transformer generator is used to model the distribution of these token sequences and generate the synthetic sequences. Third, clients upload the synthetic sequences along with the local classifier trained on the real token sequences to the server. Finally, the server incorporates knowledge distillation into global training to reduce reliance on precise distribution modeling. Experiments on medical and natural image datasets validate the effectiveness of FALCON in diverse non-IID scenarios, outperforming the best OSFL baselines by 9.58% in average accuracy.
Inference Attacks Against Graph Generative Diffusion Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Graph generative diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for generating complex graph structures, effectively capturing intricate dependencies and relationships within graph data. However, the privacy risks associated with these models remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we investigate information leakage in such models through three types of black-box inference attacks. First, we design a graph reconstruction attack, which can reconstruct graphs structurally similar to those training graphs from the generated graphs. Second, we propose a property inference attack to infer the properties of the training graphs, such as the average graph density and the distribution of densities, from the generated graphs. Third, we develop two membership inference attacks to determine whether a given graph is present in the training set. Extensive experiments on three different types of graph generative diffusion models and six real-world graphs demonstrate the effectiveness of these attacks, significantly outperforming the baseline approaches. Finally, we propose two defense mechanisms that mitigate these inference attacks and achieve a better trade-off between defense strength and target model utility than existing methods. Our code is available at https://zenodo.org/records/17946102.
Leash: Adaptive Length Penalty and Reward Shaping for Efficient Large Reasoning Model
Dec 25, 2025



Abstract:Existing approaches typically rely on fixed length penalties, but such penalties are hard to tune and fail to adapt to the evolving reasoning abilities of LLMs, leading to suboptimal trade-offs between accuracy and conciseness. To address this challenge, we propose Leash (adaptive LEngth penAlty and reward SHaping), a reinforcement learning framework for efficient reasoning in LLMs. We formulate length control as a constrained optimization problem and employ a Lagrangian primal-dual method to dynamically adjust the penalty coefficient. When generations exceed the target length, the penalty is intensified; when they are shorter, it is relaxed. This adaptive mechanism guides models toward producing concise reasoning without sacrificing task performance. Experiments on Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B and Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 show that Leash reduces the average reasoning length by 60% across diverse tasks - including in-distribution mathematical reasoning and out-of-distribution domains such as coding and instruction following - while maintaining competitive performance. Our work thus presents a practical and effective paradigm for developing controllable and efficient LLMs that balance reasoning capabilities with computational budgets.
Attention Distance: A Novel Metric for Directed Fuzzing with Large Language Models
Dec 19, 2025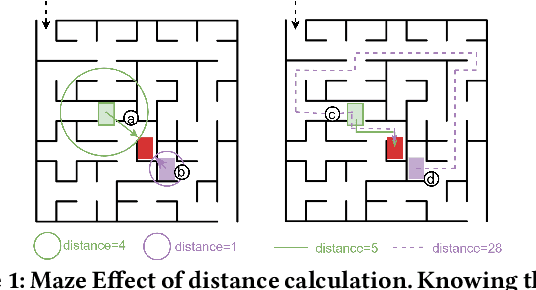
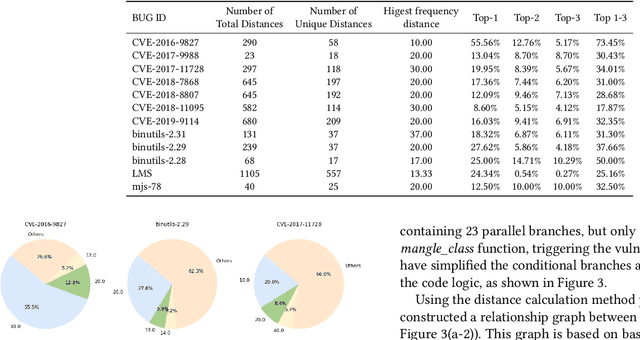
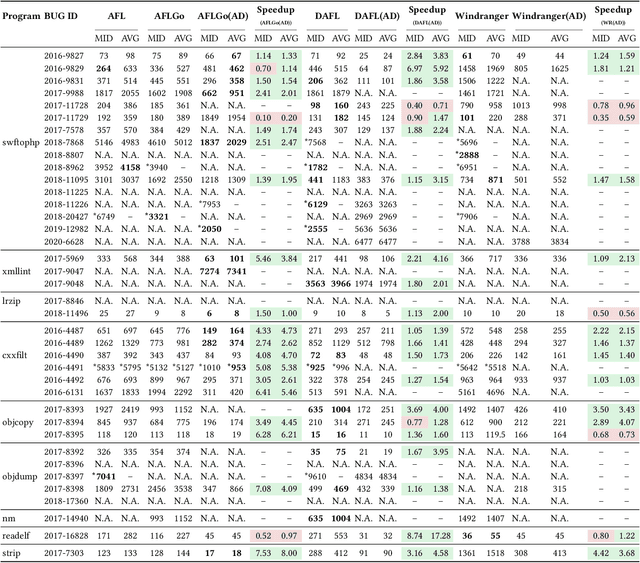
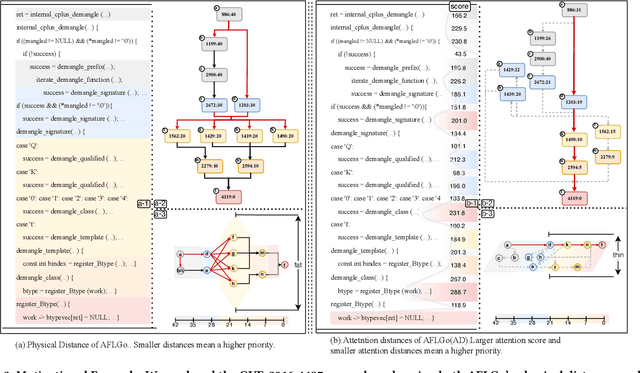
Abstract:In the domain of software security testing, Directed Grey-Box Fuzzing (DGF) has garnered widespread attention for its efficient target localization and excellent detection performance. However, existing approaches measure only the physical distance between seed execution paths and target locations, overlooking logical relationships among code segments. This omission can yield redundant or misleading guidance in complex binaries, weakening DGF's real-world effectiveness. To address this, we introduce \textbf{attention distance}, a novel metric that leverages a large language model's contextual analysis to compute attention scores between code elements and reveal their intrinsic connections. Under the same AFLGo configuration -- without altering any fuzzing components other than the distance metric -- replacing physical distances with attention distances across 38 real vulnerability reproduction experiments delivers a \textbf{3.43$\times$} average increase in testing efficiency over the traditional method. Compared to state-of-the-art directed fuzzers DAFL and WindRanger, our approach achieves \textbf{2.89$\times$} and \textbf{7.13$\times$} improvements, respectively. To further validate the generalizability of attention distance, we integrate it into DAFL and WindRanger, where it also consistently enhances their original performance. All related code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/TheBinKing/Attention\_Distance.git.
LGM-Pose: A Lightweight Global Modeling Network for Real-time Human Pose Estimation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Most of the current top-down multi-person pose estimation lightweight methods are based on multi-branch parallel pure CNN network architecture, which often struggle to capture the global context required for detecting semantically complex keypoints and are hindered by high latency due to their intricate and redundant structures. In this article, an approximate single-branch lightweight global modeling network (LGM-Pose) is proposed to address these challenges. In the network, a lightweight MobileViM Block is designed with a proposed Lightweight Attentional Representation Module (LARM), which integrates information within and between patches using the Non-Parametric Transformation Operation(NPT-Op) to extract global information. Additionally, a novel Shuffle-Integrated Fusion Module (SFusion) is introduced to effectively integrate multi-scale information, mitigating performance degradation often observed in single-branch structures. Experimental evaluations on the COCO and MPII datasets demonstrate that our approach not only reduces the number of parameters compared to existing mainstream lightweight methods but also achieves superior performance and faster processing speeds.
CoT-Vid: Dynamic Chain-of-Thought Routing with Self Verification for Training-Free Video Reasoning
May 17, 2025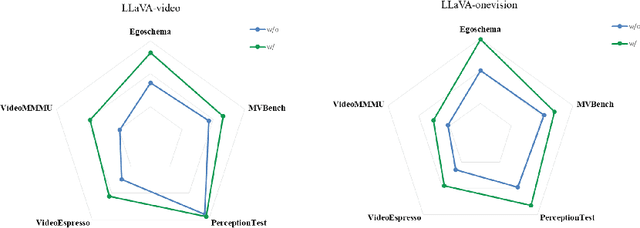
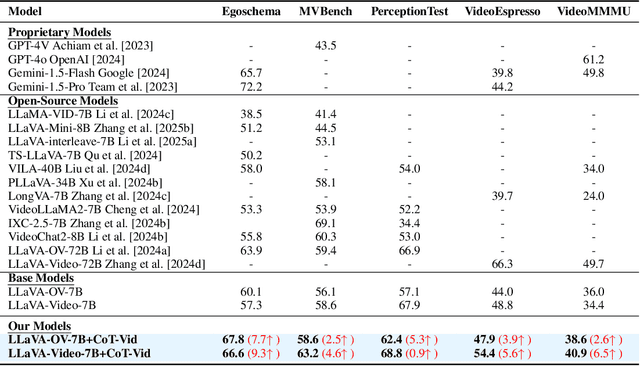
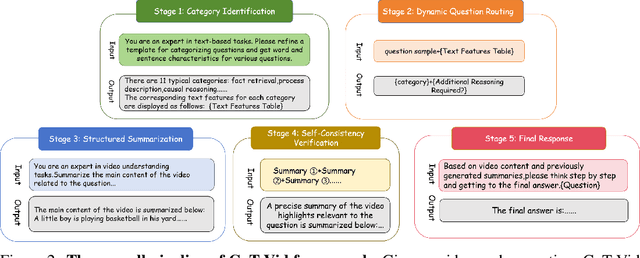
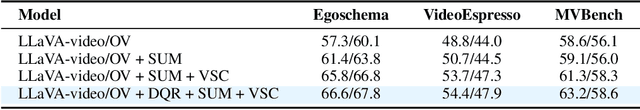
Abstract:System2 reasoning is developing rapidly these days with the emergence of Deep- Thinking Models and chain-of-thought technology, which has become a centralized discussion point in the AI community. However, there is a relative gap in the research on complex video reasoning at present. In this work, we propose CoT-Vid, a novel training-free paradigm for the video domain with a multistage complex reasoning design. Distinguishing from existing video LLMs, which rely heavily on perceptual abilities, it achieved surprising performance gain with explicit reasoning mechanism. The paradigm consists of three main components: dynamic inference path routing, problem decoupling strategy, and video self-consistency verification. In addition, we propose a new standard for categorization of video questions. CoT- Vid showed outstanding results on a wide range of benchmarks, and outperforms its base model by 9.3% on Egochema and 5.6% on VideoEspresso, rivalling or even surpassing larger and proprietary models, such as GPT-4V, GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5-flash. Our codebase will be publicly available soon.
Federated Learning for Medical Image Classification: A Comprehensive Benchmark
Apr 07, 2025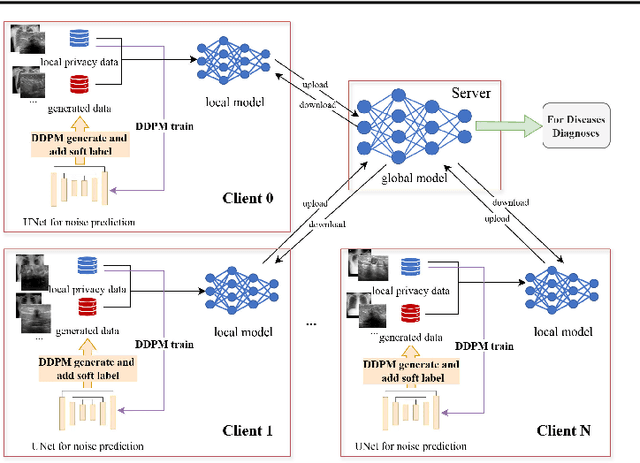
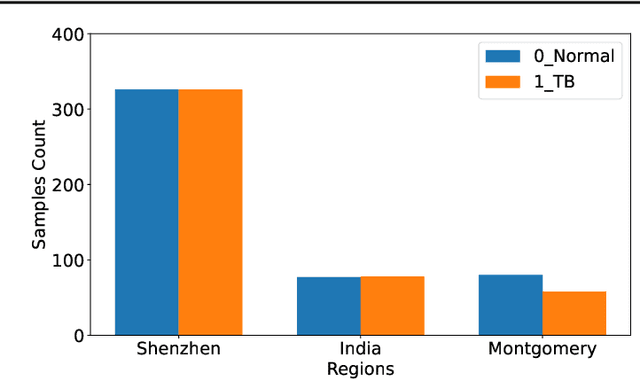
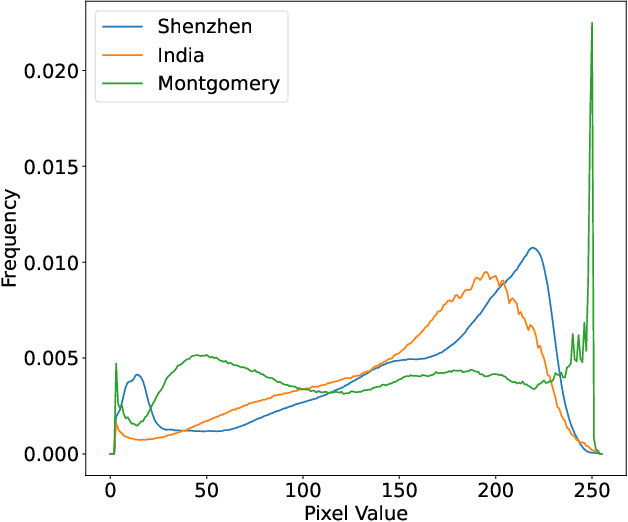
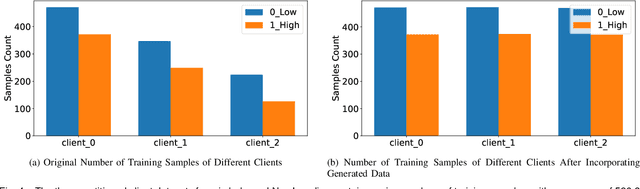
Abstract:The federated learning paradigm is wellsuited for the field of medical image analysis, as it can effectively cope with machine learning on isolated multicenter data while protecting the privacy of participating parties. However, current research on optimization algorithms in federated learning often focuses on limited datasets and scenarios, primarily centered around natural images, with insufficient comparative experiments in medical contexts. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of several state-of-the-art federated learning algorithms in the context of medical imaging. We conduct a fair comparison of classification models trained using various federated learning algorithms across multiple medical imaging datasets. Additionally, we evaluate system performance metrics, such as communication cost and computational efficiency, while considering different federated learning architectures. Our findings show that medical imaging datasets pose substantial challenges for current federated learning optimization algorithms. No single algorithm consistently delivers optimal performance across all medical federated learning scenarios, and many optimization algorithms may underperform when applied to these datasets. Our experiments provide a benchmark and guidance for future research and application of federated learning in medical imaging contexts. Furthermore, we propose an efficient and robust method that combines generative techniques using denoising diffusion probabilistic models with label smoothing to augment datasets, widely enhancing the performance of federated learning on classification tasks across various medical imaging datasets. Our code will be released on GitHub, offering a reliable and comprehensive benchmark for future federated learning studies in medical imaging.
EEGMamba: Bidirectional State Space Models with Mixture of Experts for EEG Classification
Jul 20, 2024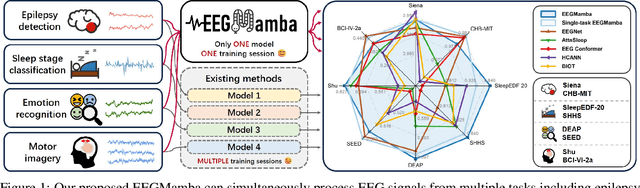
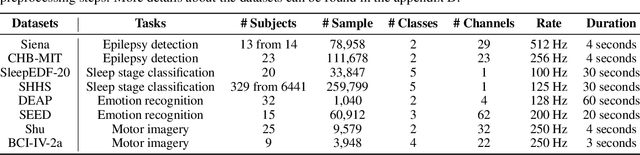
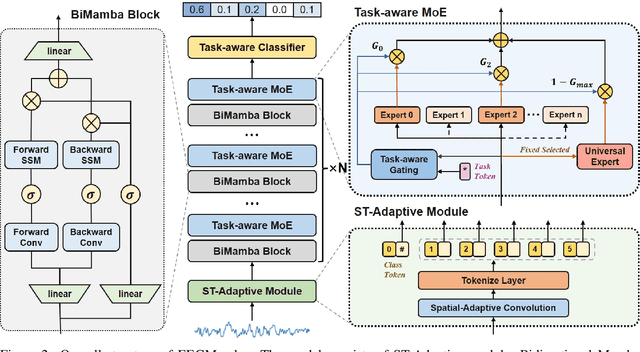
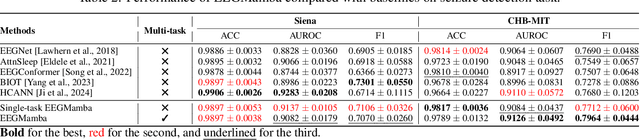
Abstract:In recent years, with the development of deep learning, electroencephalogram (EEG) classification networks have achieved certain progress. Transformer-based models can perform well in capturing long-term dependencies in EEG signals. However, their quadratic computational complexity leads to significant computational overhead. Moreover, most EEG classification models are only suitable for single tasks, showing poor generalization capabilities across different tasks and further unable to handle EEG data from various tasks simultaneously due to variations in signal length and the number of channels. In this paper, we introduce a universal EEG classification network named EEGMamba, which seamlessly integrates the Spatio-Temporal-Adaptive (ST-Adaptive) module, Bidirectional Mamba, and Mixture of Experts (MoE) into a unified framework for multiple tasks. The proposed ST-Adaptive module performs unified feature extraction on EEG signals of different lengths and channel counts through spatio-adaptive convolution and incorporates a class token to achieve temporal-adaptability. Moreover, we design a bidirectional Mamba particularly suitable for EEG signals for further feature extraction, balancing high accuracy and fast inference speed in processing long EEG signals. In order to better process EEG data for different tasks, we introduce Task-aware MoE with a universal expert, achieving the capture of both differences and commonalities between EEG data from different tasks. We test our model on eight publicly available EEG datasets, and experimental results demonstrate its superior performance in four types of tasks: seizure detection, emotion recognition, sleep stage classification, and motor imagery. The code is set to be released soon.
Improving EEG Classification Through Randomly Reassembling Original and Generated Data with Transformer-based Diffusion Models
Jul 20, 2024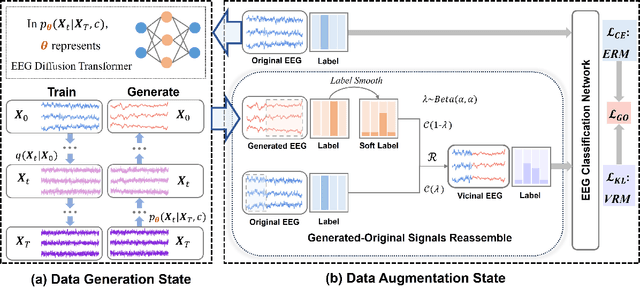
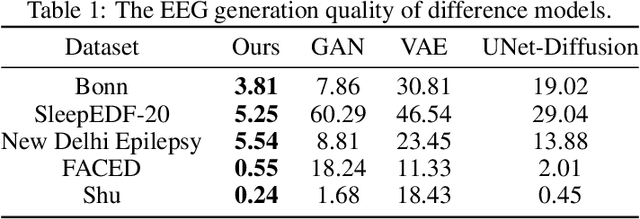
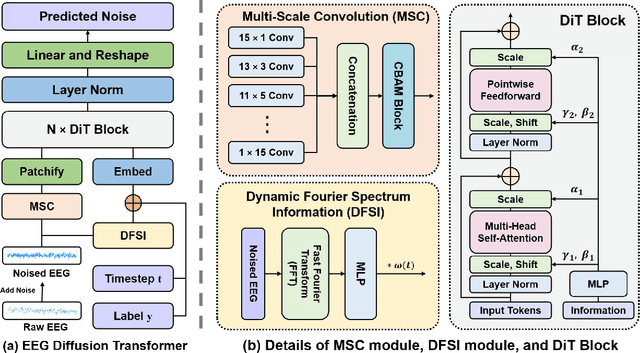
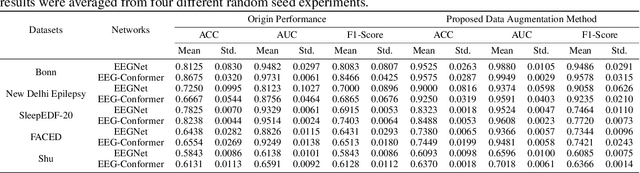
Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) classification has been widely used in various medical and engineering applications, where it is important for understanding brain function, diagnosing diseases, and assessing mental health conditions. However, the scarcity of EEG data severely restricts the performance of EEG classification networks, and generative model-based data augmentation methods emerging as potential solutions to overcome this challenge. There are two problems with existing such methods: (1) The quality of the generated EEG signals is not high. (2) The enhancement of EEG classification networks is not effective. In this paper, we propose a Transformer-based denoising diffusion probabilistic model and a generated data-based data augmentation method to address the above two problems. For the characteristics of EEG signals, we propose a constant-factor scaling method to preprocess the signals, which reduces the loss of information. We incorporated Multi-Scale Convolution and Dynamic Fourier Spectrum Information modules into the model, improving the stability of the training process and the quality of the generated data. The proposed augmentation method randomly reassemble the generated data with original data in the time-domain to obtain vicinal data, which improves the model performance by minimizing the empirical risk and the vicinal risk. We experiment the proposed augmentation method on five EEG datasets for four tasks and observe significant accuracy performance improvements: 14.00% on the Bonn dataset; 25.83% on the New Delhi epilepsy dataset; 4.98% on the SleepEDF-20 dataset; 9.42% on the FACED dataset; 2.5% on the Shu dataset. We intend to make the code of our method publicly accessible shortly
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge