Haiyan Zhao
NeuronScope: A Multi-Agent Framework for Explaining Polysemantic Neurons in Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Neuron-level interpretation in large language models (LLMs) is fundamentally challenged by widespread polysemanticity, where individual neurons respond to multiple distinct semantic concepts. Existing single-pass interpretation methods struggle to faithfully capture such multi-concept behavior. In this work, we propose NeuronScope, a multi-agent framework that reformulates neuron interpretation as an iterative, activation-guided process. NeuronScope explicitly deconstructs neuron activations into atomic semantic components, clusters them into distinct semantic modes, and iteratively refines each explanation using neuron activation feedback. Experiments demonstrate that NeuronScope uncovers hidden polysemanticity and produces explanations with significantly higher activation correlation compared to single-pass baselines.
EDGC: Entropy-driven Dynamic Gradient Compression for Efficient LLM Training
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) poses significant challenges regarding computational resources and memory capacity. Although distributed training techniques help mitigate these issues, they still suffer from considerable communication overhead. Existing approaches primarily rely on static gradient compression to enhance communication efficiency; however, these methods neglect the dynamic nature of evolving gradients during training, leading to performance degradation. Accelerating LLM training via compression without sacrificing performance remains a challenge. In this paper, we propose an entropy-driven dynamic gradient compression framework called EDGC. The core concept is to adjust the compression rate during LLM training based on the evolving trends of gradient entropy, taking into account both compression efficiency and error. EDGC consists of three key components.First, it employs a down-sampling method to efficiently estimate gradient entropy, reducing computation overhead. Second, it establishes a theoretical model linking compression rate with gradient entropy, enabling more informed compression decisions. Lastly, a window-based adjustment mechanism dynamically adapts the compression rate across pipeline stages, improving communication efficiency and maintaining model performance. We implemented EDGC on a 32-NVIDIA-V100 cluster and a 64-NVIDIA-H100 cluster to train GPT2-2.5B and GPT2-12.1B, respectively. The results show that EDGC significantly reduces communication latency and training time by up to 46.45% and 16.13% while preserving LLM accuracy.
Rep2Text: Decoding Full Text from a Single LLM Token Representation
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress across diverse tasks, yet their internal mechanisms remain largely opaque. In this work, we address a fundamental question: to what extent can the original input text be recovered from a single last-token representation within an LLM? We propose Rep2Text, a novel framework for decoding full text from last-token representations. Rep2Text employs a trainable adapter that projects a target model's internal representations into the embedding space of a decoding language model, which then autoregressively reconstructs the input text. Experiments on various model combinations (Llama-3.1-8B, Gemma-7B, Mistral-7B-v0.1, Llama-3.2-3B) demonstrate that, on average, over half of the information in 16-token sequences can be recovered from this compressed representation while maintaining strong semantic integrity and coherence. Furthermore, our analysis reveals an information bottleneck effect: longer sequences exhibit decreased token-level recovery while preserving strong semantic integrity. Besides, our framework also demonstrates robust generalization to out-of-distribution medical data.
Denoising Concept Vectors with Sparse Autoencoders for Improved Language Model Steering
May 21, 2025Abstract:Linear Concept Vectors have proven effective for steering large language models (LLMs). While existing approaches like linear probing and difference-in-means derive these vectors from LLM hidden representations, diverse data introduces noises (i.e., irrelevant features) that challenge steering robustness. To address this, we propose Sparse Autoencoder-Denoised Concept Vectors (SDCV), which uses Sparse Autoencoders to filter out noisy features from hidden representations. When applied to linear probing and difference-in-means, our method improves their steering success rates. We validate our noise hypothesis through counterfactual experiments and feature visualizations.
Beyond Input Activations: Identifying Influential Latents by Gradient Sparse Autoencoders
May 12, 2025Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have recently emerged as powerful tools for interpreting and steering the internal representations of large language models (LLMs). However, conventional approaches to analyzing SAEs typically rely solely on input-side activations, without considering the causal influence between each latent feature and the model's output. This work is built on two key hypotheses: (1) activated latents do not contribute equally to the construction of the model's output, and (2) only latents with high causal influence are effective for model steering. To validate these hypotheses, we propose Gradient Sparse Autoencoder (GradSAE), a simple yet effective method that identifies the most influential latents by incorporating output-side gradient information.
PROPHET: An Inferable Future Forecasting Benchmark with Causal Intervened Likelihood Estimation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Predicting future events stands as one of the ultimate aspirations of artificial intelligence. Recent advances in large language model (LLM)-based systems have shown remarkable potential in forecasting future events, thereby garnering significant interest in the research community. Currently, several benchmarks have been established to evaluate the forecasting capabilities by formalizing the event prediction as a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and reasoning task. In these benchmarks, each prediction question is answered with relevant retrieved news articles. However, because there is no consideration on whether the questions can be supported by valid or sufficient supporting rationales, some of the questions in these benchmarks may be inherently noninferable. To address this issue, we introduce a new benchmark, PROPHET, which comprises inferable forecasting questions paired with relevant news for retrieval. To ensure the inferability of the benchmark, we propose Causal Intervened Likelihood (CIL), a statistical measure that assesses inferability through causal inference. In constructing this benchmark, we first collected recent trend forecasting questions and then filtered the data using CIL, resulting in an inferable benchmark for event prediction. Through extensive experiments, we first demonstrate the validity of CIL and in-depth investigations into event prediction with the aid of CIL. Subsequently, we evaluate several representative prediction systems on PROPHET, drawing valuable insights for future directions.
Enhancing LLM Generation with Knowledge Hypergraph for Evidence-Based Medicine
Mar 18, 2025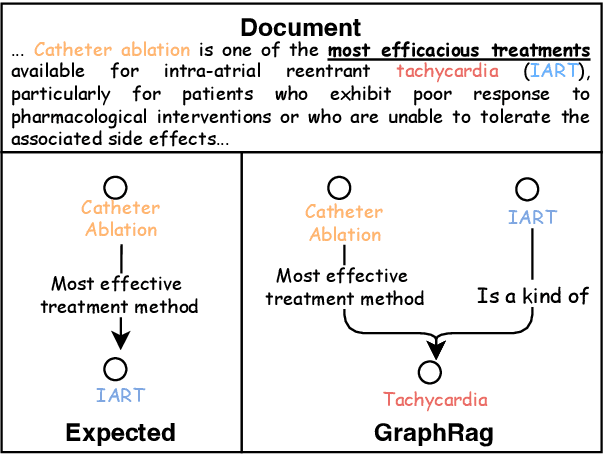
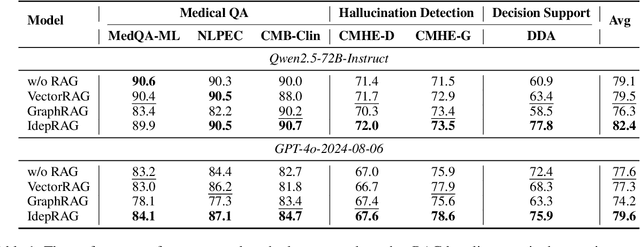
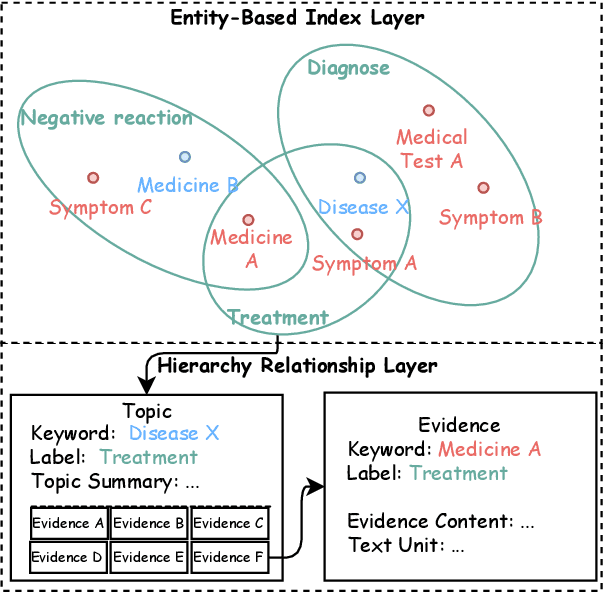
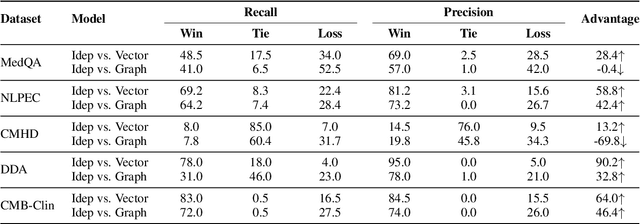
Abstract:Evidence-based medicine (EBM) plays a crucial role in the application of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare, as it provides reliable support for medical decision-making processes. Although it benefits from current retrieval-augmented generation~(RAG) technologies, it still faces two significant challenges: the collection of dispersed evidence and the efficient organization of this evidence to support the complex queries necessary for EBM. To tackle these issues, we propose using LLMs to gather scattered evidence from multiple sources and present a knowledge hypergraph-based evidence management model to integrate these evidence while capturing intricate relationships. Furthermore, to better support complex queries, we have developed an Importance-Driven Evidence Prioritization (IDEP) algorithm that utilizes the LLM to generate multiple evidence features, each with an associated importance score, which are then used to rank the evidence and produce the final retrieval results. Experimental results from six datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing RAG techniques in application domains of interest to EBM, such as medical quizzing, hallucination detection, and decision support. Testsets and the constructed knowledge graph can be accessed at \href{https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WJ9QTokK3MdkjEmwuFQxwH96j_Byawj_/view?usp=drive_link}{https://drive.google.com/rag4ebm}.
RoMA: Scaling up Mamba-based Foundation Models for Remote Sensing
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in self-supervised learning for Vision Transformers (ViTs) have fueled breakthroughs in remote sensing (RS) foundation models. However, the quadratic complexity of self-attention poses a significant barrier to scalability, particularly for large models and high-resolution images. While the linear-complexity Mamba architecture offers a promising alternative, existing RS applications of Mamba remain limited to supervised tasks on small, domain-specific datasets. To address these challenges, we propose RoMA, a framework that enables scalable self-supervised pretraining of Mamba-based RS foundation models using large-scale, diverse, unlabeled data. RoMA enhances scalability for high-resolution images through a tailored auto-regressive learning strategy, incorporating two key innovations: 1) a rotation-aware pretraining mechanism combining adaptive cropping with angular embeddings to handle sparsely distributed objects with arbitrary orientations, and 2) multi-scale token prediction objectives that address the extreme variations in object scales inherent to RS imagery. Systematic empirical studies validate that Mamba adheres to RS data and parameter scaling laws, with performance scaling reliably as model and data size increase. Furthermore, experiments across scene classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation tasks demonstrate that RoMA-pretrained Mamba models consistently outperform ViT-based counterparts in both accuracy and computational efficiency. The source code and pretrained models will be released at https://github.com/MiliLab/RoMA.
A Survey on Sparse Autoencoders: Interpreting the Internal Mechanisms of Large Language Models
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing, yet their internal mechanisms remain largely opaque. Recently, mechanistic interpretability has attracted significant attention from the research community as a means to understand the inner workings of LLMs. Among various mechanistic interpretability approaches, Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a particularly promising method due to their ability to disentangle the complex, superimposed features within LLMs into more interpretable components. This paper presents a comprehensive examination of SAEs as a promising approach to interpreting and understanding LLMs. We provide a systematic overview of SAE principles, architectures, and applications specifically tailored for LLM analysis, covering theoretical foundations, implementation strategies, and recent developments in sparsity mechanisms. We also explore how SAEs can be leveraged to explain the internal workings of LLMs, steer model behaviors in desired directions, and develop more transparent training methodologies for future models. Despite the challenges that remain around SAE implementation and scaling, they continue to provide valuable tools for understanding the internal mechanisms of large language models.
SAIF: A Sparse Autoencoder Framework for Interpreting and Steering Instruction Following of Language Models
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:The ability of large language models (LLMs) to follow instructions is crucial for their practical applications, yet the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. This paper presents a novel framework that leverages sparse autoencoders (SAE) to interpret how instruction following works in these models. We demonstrate how the features we identify can effectively steer model outputs to align with given instructions. Through analysis of SAE latent activations, we identify specific latents responsible for instruction following behavior. Our findings reveal that instruction following capabilities are encoded by a distinct set of instruction-relevant SAE latents. These latents both show semantic proximity to relevant instructions and demonstrate causal effects on model behavior. Our research highlights several crucial factors for achieving effective steering performance: precise feature identification, the role of final layer, and optimal instruction positioning. Additionally, we demonstrate that our methodology scales effectively across SAEs and LLMs of varying sizes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge