Zhengwei Tao
BrowseComp-$V^3$: A Visual, Vertical, and Verifiable Benchmark for Multimodal Browsing Agents
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), equipped with increasingly advanced planning and tool-use capabilities, are evolving into autonomous agents capable of performing multimodal web browsing and deep search in open-world environments. However, existing benchmarks for multimodal browsing remain limited in task complexity, evidence accessibility, and evaluation granularity, hindering comprehensive and reproducible assessments of deep search capabilities. To address these limitations, we introduce BrowseComp-$V^3$, a novel benchmark consisting of 300 carefully curated and challenging questions spanning diverse domains. The benchmark emphasizes deep, multi-level, and cross-modal multi-hop reasoning, where critical evidence is interleaved across textual and visual modalities within and across web pages. All supporting evidence is strictly required to be publicly searchable, ensuring fairness and reproducibility. Beyond final-answer accuracy, we incorporate an expert-validated, subgoal-driven process evaluation mechanism that enables fine-grained analysis of intermediate reasoning behaviors and systematic characterization of capability boundaries. In addition, we propose OmniSeeker, a unified multimodal browsing agent framework integrating diverse web search and visual perception tools. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that even state-of-the-art models achieve only 36% accuracy on our benchmark, revealing critical bottlenecks in multimodal information integration and fine-grained perception. Our results highlight a fundamental gap between current model capabilities and robust multimodal deep search in real-world settings.
Exploring Information Seeking Agent Consolidation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Information-seeking agents have emerged as a powerful paradigm for solving knowledge-intensive tasks. Existing information-seeking agents are typically specialized for open web, documents, or local knowledge bases, which constrains scalability and cross-domain generalization. In this work, we investigate how to consolidate heterogeneous information-seeking agents into a single foundation agentic model. We study two complementary consolidation strategies: data-level consolidation, which jointly trains a unified model on a mixture of domain-specific datasets, and parameter-level consolidation, which merges independently trained agent models at the parameter level. Our analysis compares these approaches in terms of performance retention, cross-domain generalization, and interference across information-seeking behaviors. Our results show that data-level consolidation remains a strong and stable baseline, while parameter-level consolidation offers a promising, efficient alternative but suffers from interference and robustness challenges. We further identify key design factors for effective agent consolidation at the parameter level, including fine-grained merging granularity, awareness of task heterogeneity, and principled consensus strategy.
RAGShaper: Eliciting Sophisticated Agentic RAG Skills via Automated Data Synthesis
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) empowers large language models to autonomously plan and retrieve information for complex problem-solving. However, the development of robust agents is hindered by the scarcity of high-quality training data that reflects the noise and complexity of real-world retrieval environments. Conventional manual annotation is unscalable and often fails to capture the dynamic reasoning strategies required to handle retrieval failures. To bridge this gap, we introduce RAGShaper, a novel data synthesis framework designed to automate the construction of RAG tasks and robust agent trajectories. RAGShaper incorporates an InfoCurator to build dense information trees enriched with adversarial distractors spanning Perception and Cognition levels. Furthermore, we propose a constrained navigation strategy that forces a teacher agent to confront these distractors, thereby eliciting trajectories that explicitly demonstrate error correction and noise rejection. Comprehensive experiments confirm that models trained on our synthesized corpus significantly outperform existing baselines, exhibiting superior robustness in noise-intensive and complex retrieval tasks.
DocDancer: Towards Agentic Document-Grounded Information Seeking
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Document Question Answering (DocQA) focuses on answering questions grounded in given documents, yet existing DocQA agents lack effective tool utilization and largely rely on closed-source models. In this work, we introduce DocDancer, an end-to-end trained open-source Doc agent. We formulate DocQA as an information-seeking problem and propose a tool-driven agent framework that explicitly models document exploration and comprehension. To enable end-to-end training of such agents, we introduce an Exploration-then-Synthesis data synthesis pipeline that addresses the scarcity of high-quality training data for DocQA. Training on the synthesized data, the trained models on two long-context document understanding benchmarks, MMLongBench-Doc and DocBench, show their effectiveness. Further analysis provides valuable insights for the agentic tool design and synthetic data.
EvolSQL: Structure-Aware Evolution for Scalable Text-to-SQL Data Synthesis
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Training effective Text-to-SQL models remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality, diverse, and structurally complex datasets. Existing methods either rely on limited human-annotated corpora, or synthesize datasets directly by simply prompting LLMs without explicit control over SQL structures, often resulting in limited structural diversity and complexity. To address this, we introduce EvolSQL, a structure-aware data synthesis framework that evolves SQL queries from seed data into richer and more semantically diverse forms. EvolSQL starts with an exploratory Query-SQL expansion to broaden question diversity and improve schema coverage, and then applies an adaptive directional evolution strategy using six atomic transformation operators derived from the SQL Abstract Syntax Tree to progressively increase query complexity across relational, predicate, aggregation, and nesting dimensions. An execution-grounded SQL refinement module and schema-aware deduplication further ensure the creation of high-quality, structurally diverse mapping pairs. Experimental results show that a 7B model fine-tuned on our data outperforms one trained on the much larger SynSQL dataset using only 1/18 of the data.
Nested Browser-Use Learning for Agentic Information Seeking
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Information-seeking (IS) agents have achieved strong performance across a range of wide and deep search tasks, yet their tool use remains largely restricted to API-level snippet retrieval and URL-based page fetching, limiting access to the richer information available through real browsing. While full browser interaction could unlock deeper capabilities, its fine-grained control and verbose page content returns introduce substantial complexity for ReAct-style function-calling agents. To bridge this gap, we propose Nested Browser-Use Learning (NestBrowse), which introduces a minimal and complete browser-action framework that decouples interaction control from page exploration through a nested structure. This design simplifies agentic reasoning while enabling effective deep-web information acquisition. Empirical results on challenging deep IS benchmarks demonstrate that NestBrowse offers clear benefits in practice. Further in-depth analyses underscore its efficiency and flexibility.
Towards General Agentic Intelligence via Environment Scaling
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Advanced agentic intelligence is a prerequisite for deploying Large Language Models in practical, real-world applications. Diverse real-world APIs demand precise, robust function-calling intelligence, which needs agents to develop these capabilities through interaction in varied environments. The breadth of function-calling competence is closely tied to the diversity of environments in which agents are trained. In this work, we scale up environments as a step towards advancing general agentic intelligence. This gives rise to two central challenges: (i) how to scale environments in a principled manner, and (ii) how to effectively train agentic capabilities from experiences derived through interactions with these environments. To address these, we design a scalable framework that automatically constructs heterogeneous environments that are fully simulated, systematically broadening the space of function-calling scenarios. We further adapt a two-phase agent fine-tuning strategy: first endowing agents with fundamental agentic capabilities, then specializing them for domain-specific contexts. Extensive experiments on agentic benchmarks, tau-bench, tau2-Bench, and ACEBench, demonstrate that our trained model, AgentScaler, significantly enhances the function-calling capability of models.
Scaling Agents via Continual Pre-training
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have evolved into agentic systems capable of autonomous tool use and multi-step reasoning for complex problem-solving. However, post-training approaches building upon general-purpose foundation models consistently underperform in agentic tasks, particularly in open-source implementations. We identify the root cause: the absence of robust agentic foundation models forces models during post-training to simultaneously learn diverse agentic behaviors while aligning them to expert demonstrations, thereby creating fundamental optimization tensions. To this end, we are the first to propose incorporating Agentic Continual Pre-training (Agentic CPT) into the deep research agents training pipeline to build powerful agentic foundational models. Based on this approach, we develop a deep research agent model named AgentFounder. We evaluate our AgentFounder-30B on 10 benchmarks and achieve state-of-the-art performance while retains strong tool-use ability, notably 39.9% on BrowseComp-en, 43.3% on BrowseComp-zh, and 31.5% Pass@1 on HLE.
WebSailor: Navigating Super-human Reasoning for Web Agent
Jul 03, 2025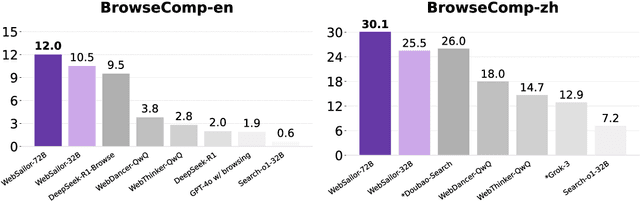
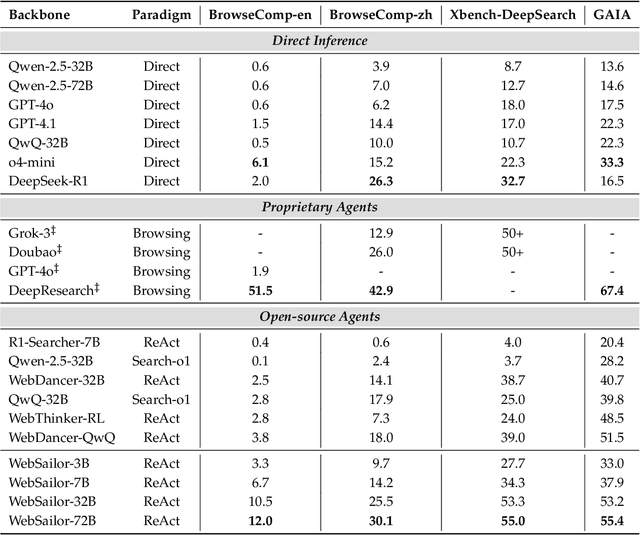
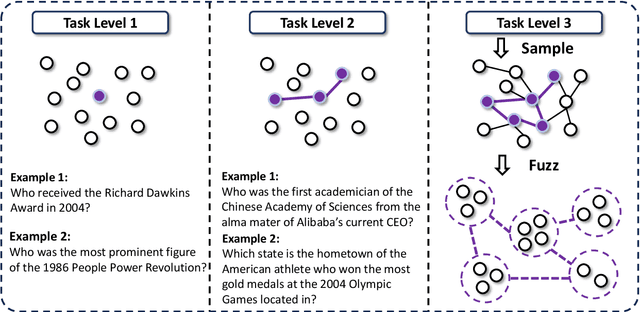

Abstract:Transcending human cognitive limitations represents a critical frontier in LLM training. Proprietary agentic systems like DeepResearch have demonstrated superhuman capabilities on extremely complex information-seeking benchmarks such as BrowseComp, a feat previously unattainable. We posit that their success hinges on a sophisticated reasoning pattern absent in open-source models: the ability to systematically reduce extreme uncertainty when navigating vast information landscapes. Based on this insight, we introduce WebSailor, a complete post-training methodology designed to instill this crucial capability. Our approach involves generating novel, high-uncertainty tasks through structured sampling and information obfuscation, RFT cold start, and an efficient agentic RL training algorithm, Duplicating Sampling Policy Optimization (DUPO). With this integrated pipeline, WebSailor significantly outperforms all opensource agents in complex information-seeking tasks, matching proprietary agents' performance and closing the capability gap.
Rethinking Regularization Methods for Knowledge Graph Completion
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Knowledge graph completion (KGC) has attracted considerable attention in recent years because it is critical to improving the quality of knowledge graphs. Researchers have continuously explored various models. However, most previous efforts have neglected to take advantage of regularization from a deeper perspective and therefore have not been used to their full potential. This paper rethinks the application of regularization methods in KGC. Through extensive empirical studies on various KGC models, we find that carefully designed regularization not only alleviates overfitting and reduces variance but also enables these models to break through the upper bounds of their original performance. Furthermore, we introduce a novel sparse-regularization method that embeds the concept of rank-based selective sparsity into the KGC regularizer. The core idea is to selectively penalize those components with significant features in the embedding vector, thus effectively ignoring many components that contribute little and may only represent noise. Various comparative experiments on multiple datasets and multiple models show that the SPR regularization method is better than other regularization methods and can enable the KGC model to further break through the performance margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge