Shuai Ma
Adaptive Prompt Elicitation for Text-to-Image Generation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Aligning text-to-image generation with user intent remains challenging, for users who provide ambiguous inputs and struggle with model idiosyncrasies. We propose Adaptive Prompt Elicitation (APE), a technique that adaptively asks visual queries to help users refine prompts without extensive writing. Our technical contribution is a formulation of interactive intent inference under an information-theoretic framework. APE represents latent intent as interpretable feature requirements using language model priors, adaptively generates visual queries, and compiles elicited requirements into effective prompts. Evaluation on IDEA-Bench and DesignBench shows that APE achieves stronger alignment with improved efficiency. A user study with challenging user-defined tasks demonstrates 19.8% higher alignment without workload overhead. Our work contributes a principled approach to prompting that, for general users, offers an effective and efficient complement to the prevailing prompt-based interaction paradigm with text-to-image models.
Your Group-Relative Advantage Is Biased
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Verifier Rewards (RLVR) has emerged as a widely used approach for post-training large language models on reasoning tasks, with group-based methods such as GRPO and its variants gaining broad adoption. These methods rely on group-relative advantage estimation to avoid learned critics, yet its theoretical properties remain poorly understood. In this work, we uncover a fundamental issue of group-based RL: the group-relative advantage estimator is inherently biased relative to the true (expected) advantage. We provide the first theoretical analysis showing that it systematically underestimates advantages for hard prompts and overestimates them for easy prompts, leading to imbalanced exploration and exploitation. To address this issue, we propose History-Aware Adaptive Difficulty Weighting (HA-DW), an adaptive reweighting scheme that adjusts advantage estimates based on an evolving difficulty anchor and training dynamics. Both theoretical analysis and experiments on five mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that HA-DW consistently improves performance when integrated into GRPO and its variants. Our results suggest that correcting biased advantage estimation is critical for robust and efficient RLVR training.
EvolSQL: Structure-Aware Evolution for Scalable Text-to-SQL Data Synthesis
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Training effective Text-to-SQL models remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality, diverse, and structurally complex datasets. Existing methods either rely on limited human-annotated corpora, or synthesize datasets directly by simply prompting LLMs without explicit control over SQL structures, often resulting in limited structural diversity and complexity. To address this, we introduce EvolSQL, a structure-aware data synthesis framework that evolves SQL queries from seed data into richer and more semantically diverse forms. EvolSQL starts with an exploratory Query-SQL expansion to broaden question diversity and improve schema coverage, and then applies an adaptive directional evolution strategy using six atomic transformation operators derived from the SQL Abstract Syntax Tree to progressively increase query complexity across relational, predicate, aggregation, and nesting dimensions. An execution-grounded SQL refinement module and schema-aware deduplication further ensure the creation of high-quality, structurally diverse mapping pairs. Experimental results show that a 7B model fine-tuned on our data outperforms one trained on the much larger SynSQL dataset using only 1/18 of the data.
AIR: Post-training Data Selection for Reasoning via Attention Head Influence
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:LLMs achieve remarkable multi-step reasoning capabilities, yet effectively transferring these skills via post-training distillation remains challenging. Existing data selection methods, ranging from manual curation to heuristics based on length, entropy, or overall loss, fail to capture the causal importance of individual reasoning steps, limiting distillation efficiency. To address this, we propose Attention Influence for Reasoning (AIR), a principled, unsupervised and training-free framework that leverages mechanistic insights of the retrieval head to select high-value post-training data. AIR first identifies reasoning-critical attention heads of an off-the-shelf model, then constructs a weakened reference model with disabled head influence, and finally quantifies the resulting loss divergence as the Attention Influence Score. This score enables fine-grained assessment at both the step and sample levels, supporting step-level weighted fine-tuning and global sample selection. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks show that AIR consistently improves reasoning accuracy, surpassing heuristic baselines and effectively isolating the most critical steps and samples. Our work establishes a mechanism-driven, data-efficient approach for reasoning distillation in LLMs.
NOC4SC: A Bandwidth-Efficient Multi-User Semantic Communication Framework for Interference-Resilient Transmission
Dec 10, 2025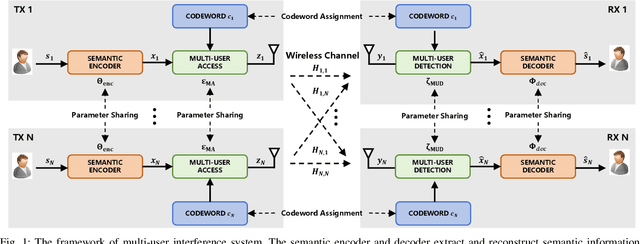
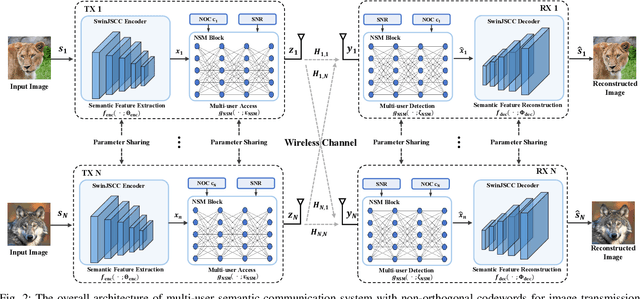
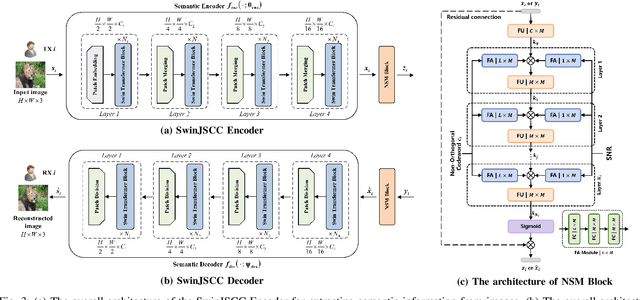
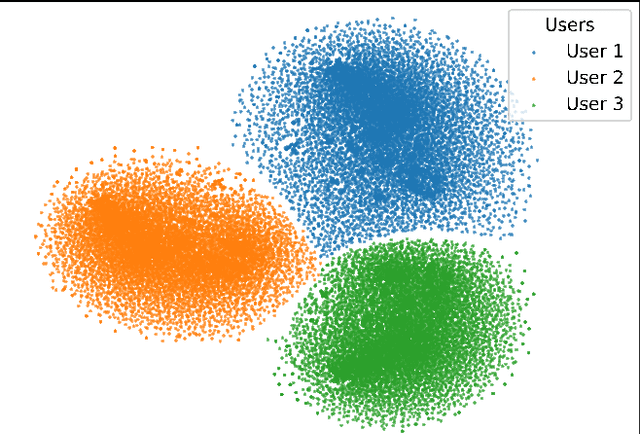
Abstract:With the explosive growth of connected devices and emerging applications, current wireless networks are encountering unprecedented demands for massive user access, where the inter-user interference has become a critical challenge to maintaining high quality of service (QoS) in multi-user communication systems. To tackle this issue, we propose a bandwidth-efficient semantic communication paradigm termed Non-Orthogonal Codewords for Semantic Communication (NOC4SC), which enables simultaneous same-frequency transmission without spectrum spreading. By leveraging the Swin Transformer, the proposed NOC4SC framework enables each user to independently extract semantic features through a unified encoder-decoder architecture with shared network parameters across all users, which ensures that the user's data remains protected from unauthorized decoding. Furthermore, we introduce an adaptive NOC and SNR Modulation (NSM) block, which employs deep learning to dynamically regulate SNR and generate approximately orthogonal semantic features within distinct feature subspaces, thereby effectively mitigating inter-user interference. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed NOC4SC achieves comparable performance to the DeepJSCC-PNOMA and outperforms other multi-user SemCom baseline methods.
SITP: A High-Reliability Semantic Information Transport Protocol Without Retransmission for Semantic Communication
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:With the evolution of 6G networks, modern communication systems are facing unprecedented demands for high reliability and low latency. However, conventional transport protocols are designed for bit-level reliability, failing to meet the semantic robustness requirements. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a novel Semantic Information Transport Protocol (SITP), which achieves TCP-level reliability and UDP level latency by verifying only packet headers while retaining potentially corrupted payloads for semantic decoding. Building upon SITP, a cross-layer analytical model is established to quantify packet-loss probability across the physical, data-link, network, transport, and application layers. The model provides a unified probabilistic formulation linking signal noise rate (SNR) and packet-loss rate, offering theoretical foundation into end-to-end semantic transmission. Furthermore, a cross-image feature interleaving mechanism is developed to mitigate consecutive burst losses by redistributing semantic features across multiple correlated images, thereby enhancing robustness in burst-fade channels. Extensive experiments show that SITP offers lower latency than TCP with comparable reliability at low SNRs, while matching UDP-level latency and delivering superior reconstruction quality. In addition, the proposed cross-image semantic interleaving mechanism further demonstrates its effectiveness in mitigating degradation caused by bursty packet losses.
A Style is Worth One Code: Unlocking Code-to-Style Image Generation with Discrete Style Space
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Innovative visual stylization is a cornerstone of artistic creation, yet generating novel and consistent visual styles remains a significant challenge. Existing generative approaches typically rely on lengthy textual prompts, reference images, or parameter-efficient fine-tuning to guide style-aware image generation, but often struggle with style consistency, limited creativity, and complex style representations. In this paper, we affirm that a style is worth one numerical code by introducing the novel task, code-to-style image generation, which produces images with novel, consistent visual styles conditioned solely on a numerical style code. To date, this field has only been primarily explored by the industry (e.g., Midjourney), with no open-source research from the academic community. To fill this gap, we propose CoTyle, the first open-source method for this task. Specifically, we first train a discrete style codebook from a collection of images to extract style embeddings. These embeddings serve as conditions for a text-to-image diffusion model (T2I-DM) to generate stylistic images. Subsequently, we train an autoregressive style generator on the discrete style embeddings to model their distribution, allowing the synthesis of novel style embeddings. During inference, a numerical style code is mapped to a unique style embedding by the style generator, and this embedding guides the T2I-DM to generate images in the corresponding style. Unlike existing methods, our method offers unparalleled simplicity and diversity, unlocking a vast space of reproducible styles from minimal input. Extensive experiments validate that CoTyle effectively turns a numerical code into a style controller, demonstrating a style is worth one code.
Task-Oriented Semantic Communication with Importance-Aware Rate Control
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:Semantic communication is recognized for its high compression efficiency and robust resistance to noise. However, utilizing a fixed transmission rate in environments with dynamic signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) often results in inefficient use of communication resources. To address this challenge, this letter proposes an importance-aware rate control semantic communication (IRCSC) scheme, which dynamically adjusts transmission rates in response to both channel conditions and semantic importance. The scheme employs a contribution-based importance analyzer to rank semantic importance. Additionaly, a novel metric, the semantic transmission integrity index (STII), is proposed to quantify the amount of correctly transmitted information and to correlate it with inference performance. Simulations indicate that, with low computational complexity, IRCSC guarantees a controllable trade-off between performance and rate, delivering higher compression efficiency and improved task performance in high-SNR scenarios.
Modeling and Performance Analysis for Semantic Communications Based on Empirical Results
Apr 29, 2025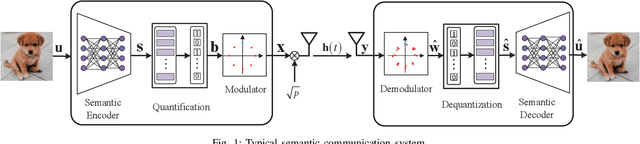
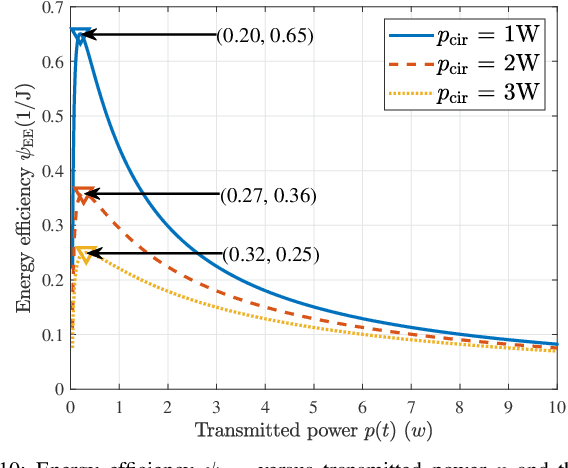
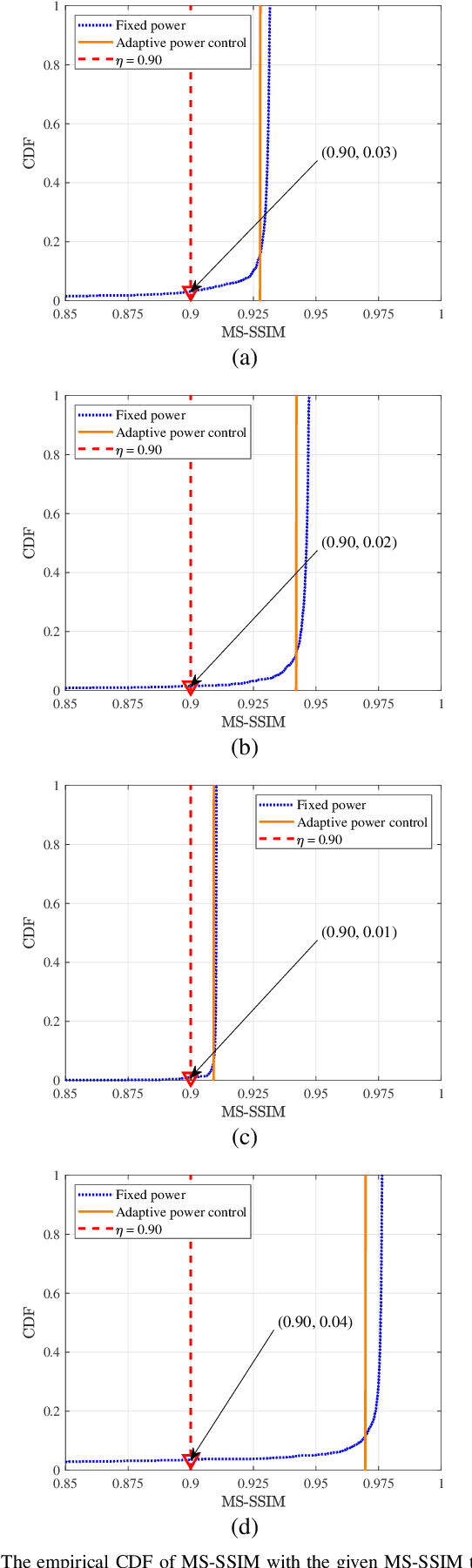
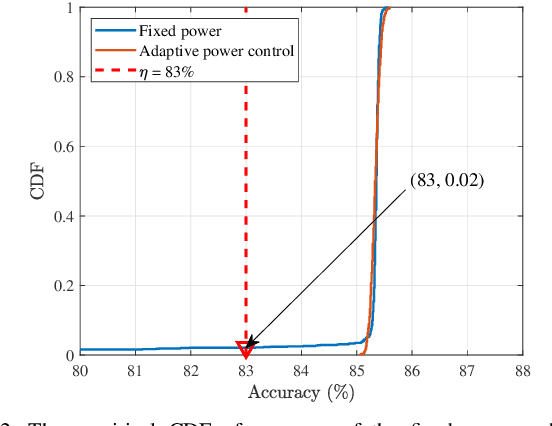
Abstract:Due to the black-box characteristics of deep learning based semantic encoders and decoders, finding a tractable method for the performance analysis of semantic communications is a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose an Alpha-Beta-Gamma (ABG) formula to model the relationship between the end-to-end measurement and SNR, which can be applied for both image reconstruction tasks and inference tasks. Specifically, for image reconstruction tasks, the proposed ABG formula can well fit the commonly used DL networks, such as SCUNet, and Vision Transformer, for semantic encoding with the multi scale-structural similarity index measure (MS-SSIM) measurement. Furthermore, we find that the upper bound of the MS-SSIM depends on the number of quantized output bits of semantic encoders, and we also propose a closed-form expression to fit the relationship between the MS-SSIM and quantized output bits. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first theoretical expression between end-to-end performance metrics and SNR for semantic communications. Based on the proposed ABG formula, we investigate an adaptive power control scheme for semantic communications over random fading channels, which can effectively guarantee quality of service (QoS) for semantic communications, and then design the optimal power allocation scheme to maximize the energy efficiency of the semantic communication system. Furthermore, by exploiting the bisection algorithm, we develop the power allocation scheme to maximize the minimum QoS of multiple users for OFDMA downlink semantic communication Extensive simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed ABG formula and power allocation schemes.
Leveraging Labelled Data Knowledge: A Cooperative Rectification Learning Network for Semi-supervised 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised 3D medical image segmentation aims to achieve accurate segmentation using few labelled data and numerous unlabelled data. The main challenge in the design of semi-supervised learning methods consists in the effective use of the unlabelled data for training. A promising solution consists of ensuring consistent predictions across different views of the data, where the efficacy of this strategy depends on the accuracy of the pseudo-labels generated by the model for this consistency learning strategy. In this paper, we introduce a new methodology to produce high-quality pseudo-labels for a consistency learning strategy to address semi-supervised 3D medical image segmentation. The methodology has three important contributions. The first contribution is the Cooperative Rectification Learning Network (CRLN) that learns multiple prototypes per class to be used as external knowledge priors to adaptively rectify pseudo-labels at the voxel level. The second contribution consists of the Dynamic Interaction Module (DIM) to facilitate pairwise and cross-class interactions between prototypes and multi-resolution image features, enabling the production of accurate voxel-level clues for pseudo-label rectification. The third contribution is the Cooperative Positive Supervision (CPS), which optimises uncertain representations to align with unassertive representations of their class distributions, improving the model's accuracy in classifying uncertain regions. Extensive experiments on three public 3D medical segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our semi-supervised learning method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge