Tao Shen
Watch Wider and Think Deeper: Collaborative Cross-modal Chain-of-Thought for Complex Visual Reasoning
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal reasoning requires the seamless integration of visual and linguistic cues, yet existing Chain-of-Thought methods suffer from two critical limitations in cross-modal scenarios: (1) over-reliance on single coarse-grained image regions, and (2) semantic fragmentation between successive reasoning steps. To address these issues, we propose the CoCoT (Collaborative Coross-modal Thought) framework, built upon two key innovations: a) Dynamic Multi-Region Grounding to adaptively detect the most relevant image regions based on the question, and b) Relation-Aware Reasoning to enable multi-region collaboration by iteratively aligning visual cues to form a coherent and logical chain of thought. Through this approach, we construct the CoCoT-70K dataset, comprising 74,691 high-quality samples with multi-region annotations and structured reasoning chains. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoCoT significantly enhances complex visual reasoning, achieving an average accuracy improvement of 15.4% on LLaVA-1.5 and 4.0% on Qwen2-VL across six challenging benchmarks. The data and code are available at: https://github.com/deer-echo/CoCoT.
You Never Know a Person, You Only Know Their Defenses: Detecting Levels of Psychological Defense Mechanisms in Supportive Conversations
Dec 17, 2025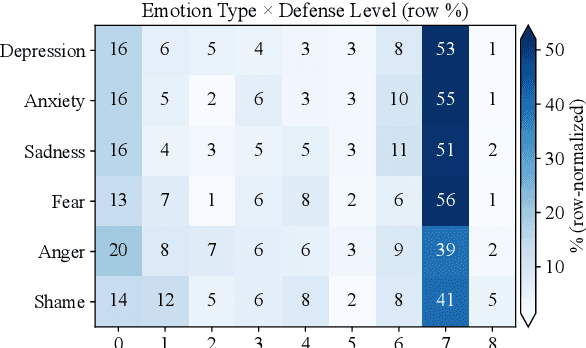
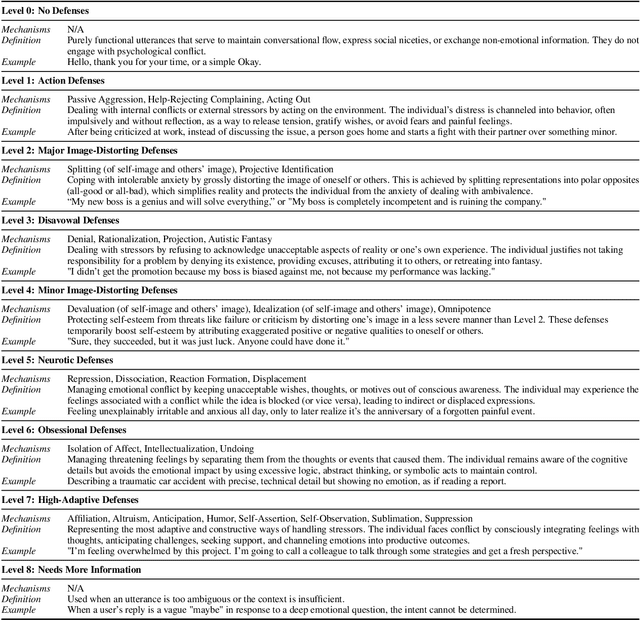
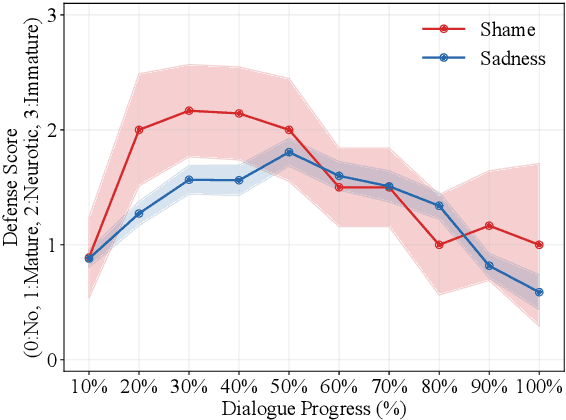
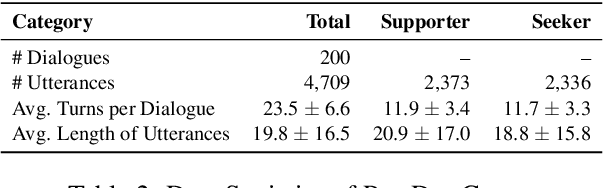
Abstract:Psychological defenses are strategies, often automatic, that people use to manage distress. Rigid or overuse of defenses is negatively linked to mental health and shapes what speakers disclose and how they accept or resist help. However, defenses are complex and difficult to reliably measure, particularly in clinical dialogues. We introduce PsyDefConv, a dialogue corpus with help seeker utterances labeled for defense level, and DMRS Co-Pilot, a four-stage pipeline that provides evidence-based pre-annotations. The corpus contains 200 dialogues and 4709 utterances, including 2336 help seeker turns, with labeling and Cohen's kappa 0.639. In a counterbalanced study, the co-pilot reduced average annotation time by 22.4%. In expert review, it averaged 4.62 for evidence, 4.44 for clinical plausibility, and 4.40 for insight on a seven-point scale. Benchmarks with strong language models in zero-shot and fine-tuning settings demonstrate clear headroom, with the best macro F1-score around 30% and a tendency to overpredict mature defenses. Corpus analyses confirm that mature defenses are most common and reveal emotion-specific deviations. We will release the corpus, annotations, code, and prompts to support research on defensive functioning in language.
MirrorLimb: Implementing hand pose acquisition and robot teleoperation based on RealMirror
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present a PICO-based robot remote operating framework that enables low-cost, real-time acquisition of hand motion and pose data, outperforming mainstream visual tracking and motion capture solutions in terms of cost-effectiveness. The framework is natively compatible with the RealMirror ecosystem, offering ready-to-use functionality for stable and precise robotic trajectory recording within the Isaac simulation environment, thereby facilitating the construction of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) datasets. Additionally, the system supports real-time teleoperation of a variety of end-effector-equipped robots, including dexterous hands and robotic grippers. This work aims to lower the technical barriers in the study of upper-limb robotic manipulation, thereby accelerating advancements in VLA-related research.
RealMirror: A Comprehensive, Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Platform for Embodied AI
Sep 18, 2025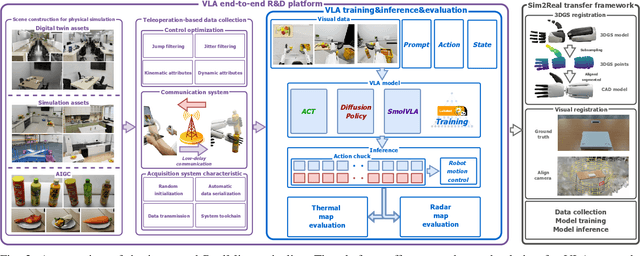
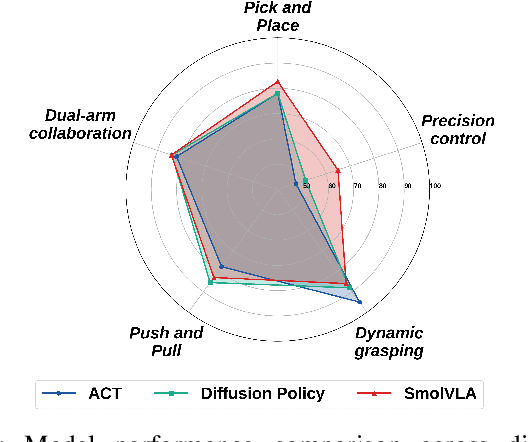
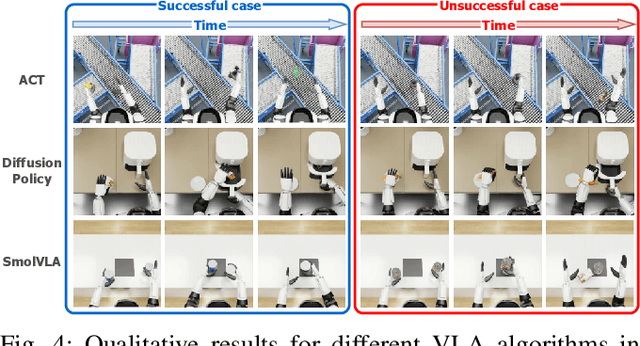

Abstract:The emerging field of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) for humanoid robots faces several fundamental challenges, including the high cost of data acquisition, the lack of a standardized benchmark, and the significant gap between simulation and the real world. To overcome these obstacles, we propose RealMirror, a comprehensive, open-source embodied AI VLA platform. RealMirror builds an efficient, low-cost data collection, model training, and inference system that enables end-to-end VLA research without requiring a real robot. To facilitate model evolution and fair comparison, we also introduce a dedicated VLA benchmark for humanoid robots, featuring multiple scenarios, extensive trajectories, and various VLA models. Furthermore, by integrating generative models and 3D Gaussian Splatting to reconstruct realistic environments and robot models, we successfully demonstrate zero-shot Sim2Real transfer, where models trained exclusively on simulation data can perform tasks on a real robot seamlessly, without any fine-tuning. In conclusion, with the unification of these critical components, RealMirror provides a robust framework that significantly accelerates the development of VLA models for humanoid robots. Project page: https://terminators2025.github.io/RealMirror.github.io
FedEve: On Bridging the Client Drift and Period Drift for Cross-device Federated Learning
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a machine learning paradigm that allows multiple clients to collaboratively train a shared model without exposing their private data. Data heterogeneity is a fundamental challenge in FL, which can result in poor convergence and performance degradation. Client drift has been recognized as one of the factors contributing to this issue resulting from the multiple local updates in FedAvg. However, in cross-device FL, a different form of drift arises due to the partial client participation, but it has not been studied well. This drift, we referred as period drift, occurs as participating clients at each communication round may exhibit distinct data distribution that deviates from that of all clients. It could be more harmful than client drift since the optimization objective shifts with every round. In this paper, we investigate the interaction between period drift and client drift, finding that period drift can have a particularly detrimental effect on cross-device FL as the degree of data heterogeneity increases. To tackle these issues, we propose a predict-observe framework and present an instantiated method, FedEve, where these two types of drift can compensate each other to mitigate their overall impact. We provide theoretical evidence that our approach can reduce the variance of model updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms alternatives on non-iid data in cross-device settings.
Lost in Pronunciation: Detecting Chinese Offensive Language Disguised by Phonetic Cloaking Replacement
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Phonetic Cloaking Replacement (PCR), defined as the deliberate use of homophonic or near-homophonic variants to hide toxic intent, has become a major obstacle to Chinese content moderation. While this problem is well-recognized, existing evaluations predominantly rely on rule-based, synthetic perturbations that ignore the creativity of real users. We organize PCR into a four-way surface-form taxonomy and compile \ours, a dataset of 500 naturally occurring, phonetically cloaked offensive posts gathered from the RedNote platform. Benchmarking state-of-the-art LLMs on this dataset exposes a serious weakness: the best model reaches only an F1-score of 0.672, and zero-shot chain-of-thought prompting pushes performance even lower. Guided by error analysis, we revisit a Pinyin-based prompting strategy that earlier studies judged ineffective and show that it recovers much of the lost accuracy. This study offers the first comprehensive taxonomy of Chinese PCR, a realistic benchmark that reveals current detectors' limits, and a lightweight mitigation technique that advances research on robust toxicity detection.
ThinkQE: Query Expansion via an Evolving Thinking Process
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Effective query expansion for web search benefits from promoting both exploration and result diversity to capture multiple interpretations and facets of a query. While recent LLM-based methods have improved retrieval performance and demonstrate strong domain generalization without additional training, they often generate narrowly focused expansions that overlook these desiderata. We propose ThinkQE, a test-time query expansion framework addressing this limitation through two key components: a thinking-based expansion process that encourages deeper and comprehensive semantic exploration, and a corpus-interaction strategy that iteratively refines expansions using retrieval feedback from the corpus. Experiments on diverse web search benchmarks (DL19, DL20, and BRIGHT) show ThinkQE consistently outperforms prior approaches, including training-intensive dense retrievers and rerankers.
Each Rank Could be an Expert: Single-Ranked Mixture of Experts LoRA for Multi-Task Learning
Jan 25, 2025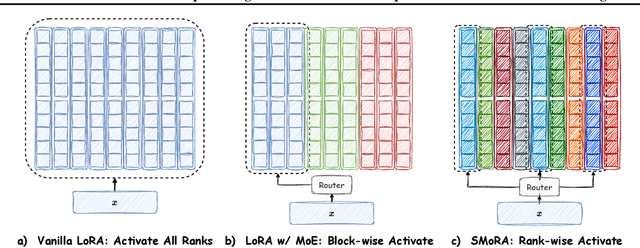
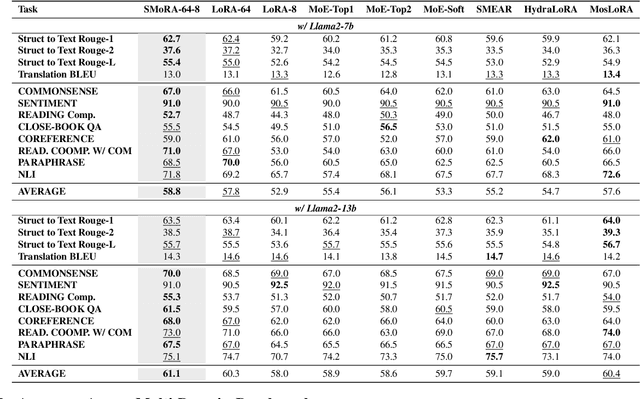
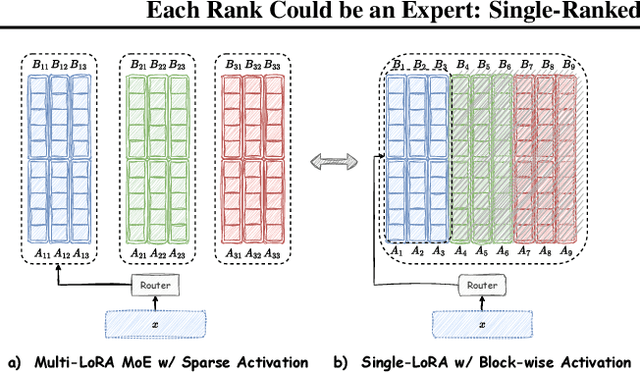
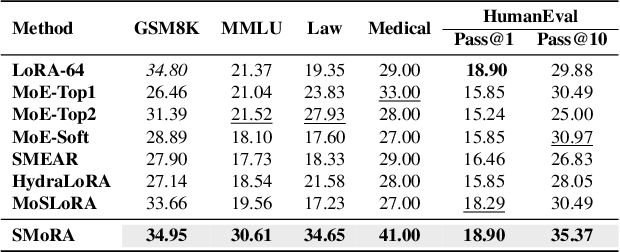
Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is widely used for adapting large language models (LLMs) to specific domains due to its efficiency and modularity. Meanwhile, vanilla LoRA struggles with task conflicts in multi-task scenarios. Recent works adopt Mixture of Experts (MoE) by treating each LoRA module as an expert, thereby mitigating task interference through multiple specialized LoRA modules. While effective, these methods often isolate knowledge within individual tasks, failing to fully exploit the shared knowledge across related tasks. In this paper, we establish a connection between single LoRA and multi-LoRA MoE, integrating them into a unified framework. We demonstrate that the dynamic routing of multiple LoRAs is functionally equivalent to rank partitioning and block-level activation within a single LoRA. We further empirically demonstrate that finer-grained LoRA partitioning, within the same total and activated parameter constraints, leads to better performance gains across heterogeneous tasks. Building on these findings, we propose Single-ranked Mixture of Experts LoRA (\textbf{SMoRA}), which embeds MoE into LoRA by \textit{treating each rank as an independent expert}. With a \textit{dynamic rank-wise activation} mechanism, SMoRA promotes finer-grained knowledge sharing while mitigating task conflicts. Experiments demonstrate that SMoRA activates fewer parameters yet achieves better performance in multi-task scenarios.
Enhancing Lexicon-Based Text Embeddings with Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance on general-purpose text embedding tasks. While dense embeddings have dominated related research, we introduce the first Lexicon-based EmbeddiNgS (LENS) leveraging LLMs that achieve competitive performance on these tasks. Regarding the inherent tokenization redundancy issue and unidirectional attention limitations in traditional causal LLMs, LENS consolidates the vocabulary space through token embedding clustering, and investigates bidirectional attention and various pooling strategies. Specifically, LENS simplifies lexicon matching by assigning each dimension to a specific token cluster, where semantically similar tokens are grouped together, and unlocking the full potential of LLMs through bidirectional attention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LENS outperforms dense embeddings on the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB), delivering compact feature representations that match the sizes of dense counterparts. Notably, combining LENSE with dense embeddings achieves state-of-the-art performance on the retrieval subset of MTEB (i.e. BEIR).
FedCFA: Alleviating Simpson's Paradox in Model Aggregation with Counterfactual Federated Learning
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a promising technology for data privacy and distributed optimization, but it suffers from data imbalance and heterogeneity among clients. Existing FL methods try to solve the problems by aligning client with server model or by correcting client model with control variables. These methods excel on IID and general Non-IID data but perform mediocrely in Simpson's Paradox scenarios. Simpson's Paradox refers to the phenomenon that the trend observed on the global dataset disappears or reverses on a subset, which may lead to the fact that global model obtained through aggregation in FL does not accurately reflect the distribution of global data. Thus, we propose FedCFA, a novel FL framework employing counterfactual learning to generate counterfactual samples by replacing local data critical factors with global average data, aligning local data distributions with the global and mitigating Simpson's Paradox effects. In addition, to improve the quality of counterfactual samples, we introduce factor decorrelation (FDC) loss to reduce the correlation among features and thus improve the independence of extracted factors. We conduct extensive experiments on six datasets and verify that our method outperforms other FL methods in terms of efficiency and global model accuracy under limited communication rounds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge