Jiayuan Ma
Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Content Moderation with Large Language Models
Dec 23, 2025
Abstract:Content moderation at scale remains one of the most pressing challenges in today's digital ecosystem, where billions of user- and AI-generated artifacts must be continuously evaluated for policy violations. Although recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong potential for policy-grounded moderation, the practical challenges of training these systems to achieve expert-level accuracy in real-world settings remain largely unexplored, particularly in regimes characterized by label sparsity, evolving policy definitions, and the need for nuanced reasoning beyond shallow pattern matching. In this work, we present a comprehensive empirical investigation of scaling reinforcement learning (RL) for content classification, systematically evaluating multiple RL training recipes and reward-shaping strategies-including verifiable rewards and LLM-as-judge frameworks-to transform general-purpose language models into specialized, policy-aligned classifiers across three real-world content moderation tasks. Our findings provide actionable insights for industrial-scale moderation systems, demonstrating that RL exhibits sigmoid-like scaling behavior in which performance improves smoothly with increased training data, rollouts, and optimization steps before gradually saturating. Moreover, we show that RL substantially improves performance on tasks requiring complex policy-grounded reasoning while achieving up to 100x higher data efficiency than supervised fine-tuning, making it particularly effective in domains where expert annotations are scarce or costly.
Lost in Pronunciation: Detecting Chinese Offensive Language Disguised by Phonetic Cloaking Replacement
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Phonetic Cloaking Replacement (PCR), defined as the deliberate use of homophonic or near-homophonic variants to hide toxic intent, has become a major obstacle to Chinese content moderation. While this problem is well-recognized, existing evaluations predominantly rely on rule-based, synthetic perturbations that ignore the creativity of real users. We organize PCR into a four-way surface-form taxonomy and compile \ours, a dataset of 500 naturally occurring, phonetically cloaked offensive posts gathered from the RedNote platform. Benchmarking state-of-the-art LLMs on this dataset exposes a serious weakness: the best model reaches only an F1-score of 0.672, and zero-shot chain-of-thought prompting pushes performance even lower. Guided by error analysis, we revisit a Pinyin-based prompting strategy that earlier studies judged ineffective and show that it recovers much of the lost accuracy. This study offers the first comprehensive taxonomy of Chinese PCR, a realistic benchmark that reveals current detectors' limits, and a lightweight mitigation technique that advances research on robust toxicity detection.
Detecting Conversational Mental Manipulation with Intent-Aware Prompting
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Mental manipulation severely undermines mental wellness by covertly and negatively distorting decision-making. While there is an increasing interest in mental health care within the natural language processing community, progress in tackling manipulation remains limited due to the complexity of detecting subtle, covert tactics in conversations. In this paper, we propose Intent-Aware Prompting (IAP), a novel approach for detecting mental manipulations using large language models (LLMs), providing a deeper understanding of manipulative tactics by capturing the underlying intents of participants. Experimental results on the MentalManip dataset demonstrate superior effectiveness of IAP against other advanced prompting strategies. Notably, our approach substantially reduces false negatives, helping detect more instances of mental manipulation with minimal misjudgment of positive cases. The code of this paper is available at https://github.com/Anton-Jiayuan-MA/Manip-IAP.
Bandits for Online Calibration: An Application to Content Moderation on Social Media Platforms
Nov 11, 2022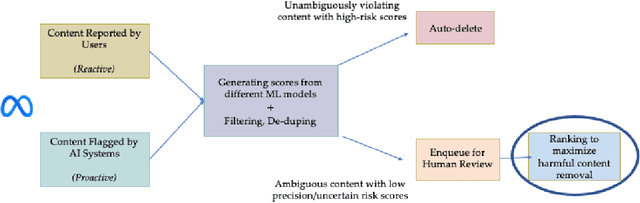
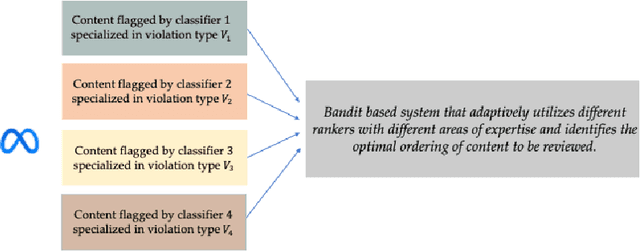
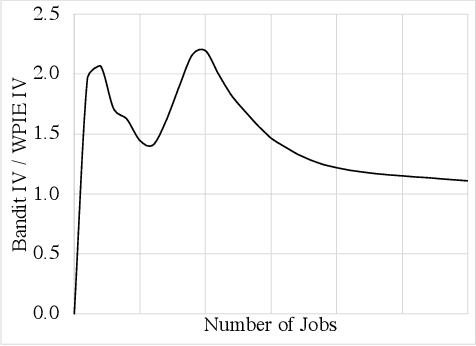
Abstract:We describe the current content moderation strategy employed by Meta to remove policy-violating content from its platforms. Meta relies on both handcrafted and learned risk models to flag potentially violating content for human review. Our approach aggregates these risk models into a single ranking score, calibrating them to prioritize more reliable risk models. A key challenge is that violation trends change over time, affecting which risk models are most reliable. Our system additionally handles production challenges such as changing risk models and novel risk models. We use a contextual bandit to update the calibration in response to such trends. Our approach increases Meta's top-line metric for measuring the effectiveness of its content moderation strategy by 13%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge