Shuchang Zhou
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025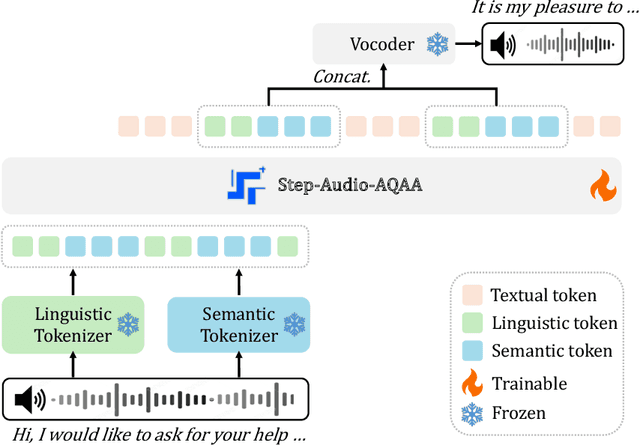
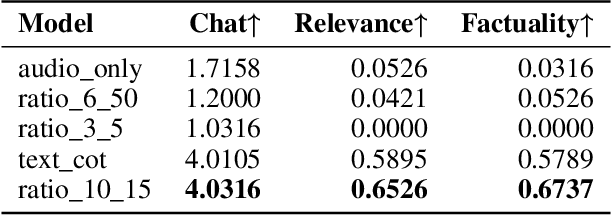
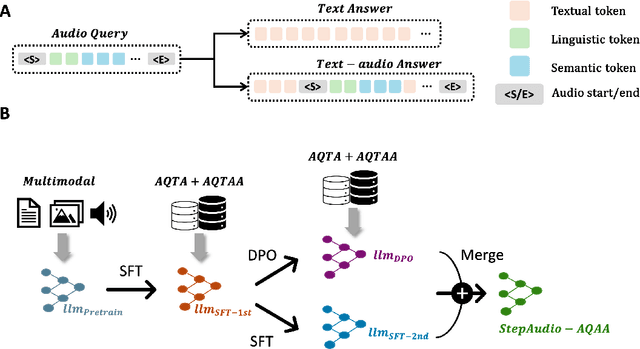
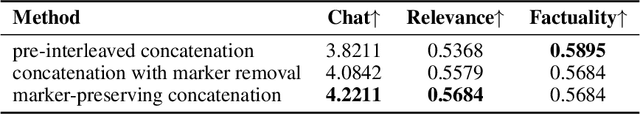
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
DialogueReason: Rule-Based RL Sparks Dialogue Reasoning in LLMs
May 11, 2025Abstract:We propose DialogueReason, a reasoning paradigm that uncovers the lost roles in monologue-style reasoning models, aiming to boost diversity and coherency of the reasoning process. Recent advances in RL-based large reasoning models have led to impressive long CoT capabilities and high performance on math and science benchmarks. However, these reasoning models rely mainly on monologue-style reasoning, which often limits reasoning diversity and coherency, frequently recycling fixed strategies or exhibiting unnecessary shifts in attention. Our work consists of an analysis of monologue reasoning patterns and the development of a dialogue-based reasoning approach. We first introduce the Compound-QA task, which concatenates multiple problems into a single prompt to assess both diversity and coherency of reasoning. Our analysis shows that Compound-QA exposes weaknesses in monologue reasoning, evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative reasoning traces. Building on the analysis, we propose a dialogue-based reasoning, named DialogueReason, structured around agents, environment, and interactions. Using PPO with rule-based rewards, we train open-source LLMs (Qwen-QWQ and Qwen-Base) to adopt dialogue reasoning. We evaluate trained models on MATH, AIME, and GPQA datasets, showing that the dialogue reasoning model outperforms monologue models under more complex compound questions. Additionally, we discuss how dialogue-based reasoning helps enhance interpretability, facilitate more intuitive human interaction, and inspire advances in multi-agent system design.
Step-Video-TI2V Technical Report: A State-of-the-Art Text-Driven Image-to-Video Generation Model
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We present Step-Video-TI2V, a state-of-the-art text-driven image-to-video generation model with 30B parameters, capable of generating videos up to 102 frames based on both text and image inputs. We build Step-Video-TI2V-Eval as a new benchmark for the text-driven image-to-video task and compare Step-Video-TI2V with open-source and commercial TI2V engines using this dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Step-Video-TI2V in the image-to-video generation task. Both Step-Video-TI2V and Step-Video-TI2V-Eval are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Video-TI2V.
InPK: Infusing Prior Knowledge into Prompt for Vision-Language Models
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Prompt tuning has become a popular strategy for adapting Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to zero/few-shot visual recognition tasks. Some prompting techniques introduce prior knowledge due to its richness, but when learnable tokens are randomly initialized and disconnected from prior knowledge, they tend to overfit on seen classes and struggle with domain shifts for unseen ones. To address this issue, we propose the InPK model, which infuses class-specific prior knowledge into the learnable tokens during initialization, thus enabling the model to explicitly focus on class-relevant information. Furthermore, to mitigate the weakening of class information by multi-layer encoders, we continuously reinforce the interaction between learnable tokens and prior knowledge across multiple feature levels. This progressive interaction allows the learnable tokens to better capture the fine-grained differences and universal visual concepts within prior knowledge, enabling the model to extract more discriminative and generalized text features. Even for unseen classes, the learned interaction allows the model to capture their common representations and infer their appropriate positions within the existing semantic structure. Moreover, we introduce a learnable text-to-vision projection layer to accommodate the text adjustments, ensuring better alignment of visual-text semantics. Extensive experiments on 11 recognition datasets show that InPK significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in multiple zero/few-shot image classification tasks.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
CoSER: Coordinating LLM-Based Persona Simulation of Established Roles
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Role-playing language agents (RPLAs) have emerged as promising applications of large language models (LLMs). However, simulating established characters presents a challenging task for RPLAs, due to the lack of authentic character datasets and nuanced evaluation methods using such data. In this paper, we present CoSER, a collection of a high-quality dataset, open models, and an evaluation protocol towards effective RPLAs of established characters. The CoSER dataset covers 17,966 characters from 771 renowned books. It provides authentic dialogues with real-world intricacies, as well as diverse data types such as conversation setups, character experiences and internal thoughts. Drawing from acting methodology, we introduce given-circumstance acting for training and evaluating role-playing LLMs, where LLMs sequentially portray multiple characters in book scenes. Using our dataset, we develop CoSER 8B and CoSER 70B, i.e., advanced open role-playing LLMs built on LLaMA-3.1 models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the value of the CoSER dataset for RPLA training, evaluation and retrieval. Moreover, CoSER 70B exhibits state-of-the-art performance surpassing or matching GPT-4o on our evaluation and three existing benchmarks, i.e., achieving 75.80% and 93.47% accuracy on the InCharacter and LifeChoice benchmarks respectively.
UniScene: Unified Occupancy-centric Driving Scene Generation
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Generating high-fidelity, controllable, and annotated training data is critical for autonomous driving. Existing methods typically generate a single data form directly from a coarse scene layout, which not only fails to output rich data forms required for diverse downstream tasks but also struggles to model the direct layout-to-data distribution. In this paper, we introduce UniScene, the first unified framework for generating three key data forms - semantic occupancy, video, and LiDAR - in driving scenes. UniScene employs a progressive generation process that decomposes the complex task of scene generation into two hierarchical steps: (a) first generating semantic occupancy from a customized scene layout as a meta scene representation rich in both semantic and geometric information, and then (b) conditioned on occupancy, generating video and LiDAR data, respectively, with two novel transfer strategies of Gaussian-based Joint Rendering and Prior-guided Sparse Modeling. This occupancy-centric approach reduces the generation burden, especially for intricate scenes, while providing detailed intermediate representations for the subsequent generation stages. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniScene outperforms previous SOTAs in the occupancy, video, and LiDAR generation, which also indeed benefits downstream driving tasks.
Advancing Auto-Regressive Continuation for Video Frames
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in auto-regressive large language models (LLMs) have shown their potential in generating high-quality text, inspiring researchers to apply them to image and video generation. This paper explores the application of LLMs to video continuation, a task essential for building world models and predicting future frames. In this paper, we tackle challenges including preventing degeneration in long-term frame generation and enhancing the quality of generated images. We design a scheme named ARCON, which involves training our model to alternately generate semantic tokens and RGB tokens, enabling the LLM to explicitly learn and predict the high-level structural information of the video. We find high consistency in the RGB images and semantic maps generated without special design. Moreover, we employ an optical flow-based texture stitching method to enhance the visual quality of the generated videos. Quantitative and qualitative experiments in autonomous driving scenarios demonstrate our model can consistently generate long videos.
ARIC: An Activity Recognition Dataset in Classroom Surveillance Images
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:The application of activity recognition in the ``AI + Education" field is gaining increasing attention. However, current work mainly focuses on the recognition of activities in manually captured videos and a limited number of activity types, with little attention given to recognizing activities in surveillance images from real classrooms. Activity recognition in classroom surveillance images faces multiple challenges, such as class imbalance and high activity similarity. To address this gap, we constructed a novel multimodal dataset focused on classroom surveillance image activity recognition called ARIC (Activity Recognition In Classroom). The ARIC dataset has advantages of multiple perspectives, 32 activity categories, three modalities, and real-world classroom scenarios. In addition to the general activity recognition tasks, we also provide settings for continual learning and few-shot continual learning. We hope that the ARIC dataset can act as a facilitator for future analysis and research for open teaching scenarios. You can download preliminary data from https://ivipclab.github.io/publication_ARIC/ARIC.
Recent Advances in Attack and Defense Approaches of Large Language Models
Sep 05, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized artificial intelligence and machine learning through their advanced text processing and generating capabilities. However, their widespread deployment has raised significant safety and reliability concerns. Established vulnerabilities in deep neural networks, coupled with emerging threat models, may compromise security evaluations and create a false sense of security. Given the extensive research in the field of LLM security, we believe that summarizing the current state of affairs will help the research community better understand the present landscape and inform future developments. This paper reviews current research on LLM vulnerabilities and threats, and evaluates the effectiveness of contemporary defense mechanisms. We analyze recent studies on attack vectors and model weaknesses, providing insights into attack mechanisms and the evolving threat landscape. We also examine current defense strategies, highlighting their strengths and limitations. By contrasting advancements in attack and defense methodologies, we identify research gaps and propose future directions to enhance LLM security. Our goal is to advance the understanding of LLM safety challenges and guide the development of more robust security measures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge