Keshi Zhao
VersaTune: An Efficient Data Composition Framework for Training Multi-Capability LLMs
Dec 02, 2024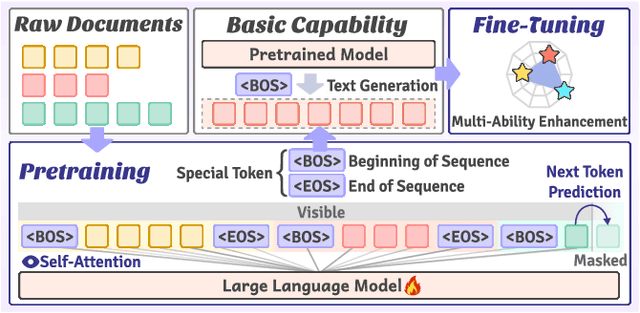



Abstract:Large-scale pretrained models, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs), have exhibited remarkable capabilities in handling multiple tasks across domains due to their emergent properties. These capabilities are further augmented during the Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) phase. Despite their potential, existing work mainly focuses on domain-specific enhancements during fine-tuning, the challenge of which lies in catastrophic forgetting of knowledge across other domains. In this study, we introduce VersaTune, a novel data composition framework designed for enhancing LLMs' overall multi-ability performances during training. We categorize knowledge into distinct domains including law, medicine, finance, science, code, etc. We begin with detecting the distribution of domain-specific knowledge within the base model, followed by the training data composition that aligns with the model's existing knowledge distribution. During the training process, domain weights are dynamically adjusted based on their learnable potential and forgetting degree. Experimental results demonstrate that VersaTune achieves significant improvements in multi-domain performance, with an 35.21% enhancement in comprehensive multi-domain tasks. Additionally, in scenarios where specific domain optimization is required, VersaTune reduces the degradation of performance in other domains by 38.77%, without compromising the target domain's training efficacy.
VersaTune: Harnessing Vertical Domain Insights for Multi-Ability LLM Supervised Fine-Tuning
Nov 24, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in handling multiple tasks across domains due to their emergent properties. These capabilities are further augmented during the Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) phase. Despite their potential, existing work mainly focuses on domain-specific enhancements during fine-tuning, the challenge of which lies in catastrophic forgetting of knowledge across other domains. In this study, we introduce VersaTune, a novel data composition framework designed for enhancing LLMs' overall multi-ability performances during fine-tuning. We categorize knowledge into distinct domains including law, medicine, finance, science, code. We begin with detecting the distribution of domain-specific knowledge within the base model, followed by the composition of training data that aligns with the model's existing knowledge distribution. During the fine-tuning process, weights of different domains are dynamically adjusted based on their learnable potential and forgetting degree. Experimental results demonstrate that VersaTune achieves significant improvements in multi-domain performance, with a 35.21% enhancement in comprehensive multi-domain tasks. Additionally, in scenarios where specific domain optimization is required, VersaTune reduces the degradation of performance in other domains by 38.77%, without compromising the target domain's training efficacy.
VersaTune: Fine-Tuning Multi-Ability LLMs Efficiently
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in handling multiple tasks across domains due to their emergent properties. These capabilities are further augmented during the Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) phase. Despite their potential, existing work mainly focuses on domain-specific enhancements during fine-tuning, the challenge of which lies in catastrophic forgetting of knowledge across other domains. In this study, we introduce VersaTune, a novel data composition framework designed for enhancing LLMs' overall multi-ability performances during fine-tuning. We categorize knowledge into distinct domains including law, medicine, finance, science, code. We begin with detecting the distribution of domain-specific knowledge within the base model, followed by the composition of training data that aligns with the model's existing knowledge distribution. During the fine-tuning process, weights of different domains are dynamically adjusted based on their learnable potential and forgetting degree. Experimental results demonstrate that VersaTune achieves significant improvements in multi-domain performance, with a 35.21% enhancement in comprehensive multi-domain tasks. Additionally, in scenarios where specific domain optimization is required, VersaTune reduces the degradation of performance in other domains by 38.77%, without compromising the target domain's training efficacy.
Data Proportion Detection for Optimized Data Management for Large Language Models
Sep 26, 2024
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance across a wide range of tasks and domains, with data preparation playing a critical role in achieving these results. Pre-training data typically combines information from multiple domains. To maximize performance when integrating data from various domains, determining the optimal data proportion is essential. However, state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs rarely disclose details about their pre-training data, making it difficult for researchers to identify ideal data proportions. In this paper, we introduce a new topic, \textit{data proportion detection}, which enables the automatic estimation of pre-training data proportions by analyzing the generated outputs of LLMs. We provide rigorous theoretical proofs, practical algorithms, and preliminary experimental results for data proportion detection. Based on these findings, we offer valuable insights into the challenges and future directions for effective data proportion detection and data management.
DataSculpt: Crafting Data Landscapes for LLM Post-Training through Multi-objective Partitioning
Sep 02, 2024
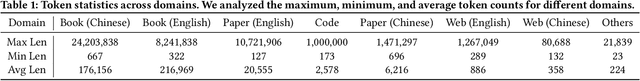
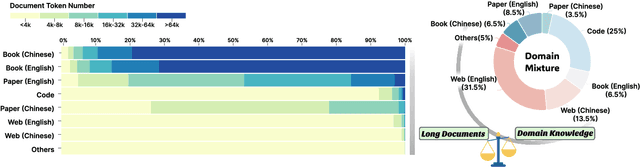
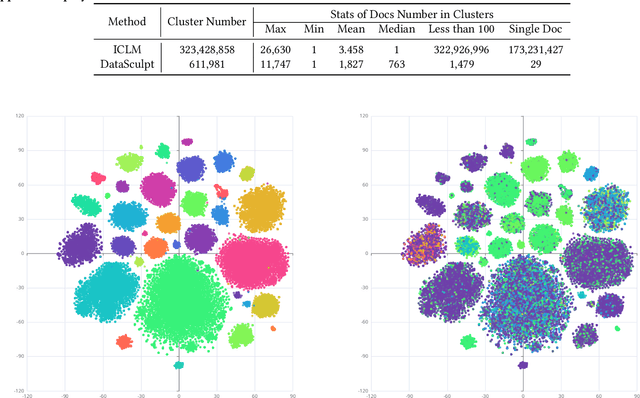
Abstract:The effectiveness of long-context modeling is important for Large Language Models (LLMs) in various applications. Despite their potential, LLMs' efficacy in processing long context does not consistently meet expectations, posing significant challenges for efficient management of prolonged sequences in training. This difficulty is compounded by the scarcity of comprehensive and diverse training datasets suitable for long sequences, which stems from inherent length biases across different data sources, and the logistical complexities associated with massive data management for training in extended contexts. In this work, we introduce DataSculpt, a data construction framework designed to strategically augment the data architecture for extended-context training. Our thorough evaluations demonstrate DataSculpt's remarkable capacity to boost long-context training performance, achieving improvements including an 18.09% increase in retrieval augmentation, 21.23% in summarization, 21.27% in reading comprehension, and a 3.81% rise in code completion, all while preserving the models' overall proficiency with a 4.88% improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge