Xiaonan Nie
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
Seedance 1.0: Exploring the Boundaries of Video Generation Models
Jun 10, 2025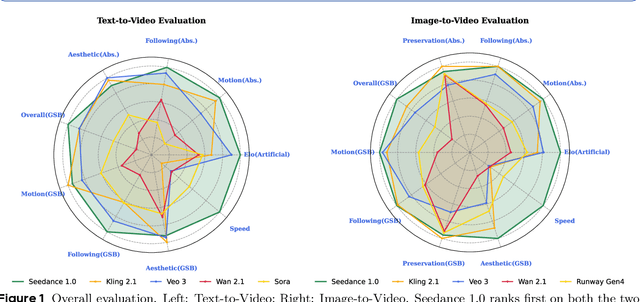
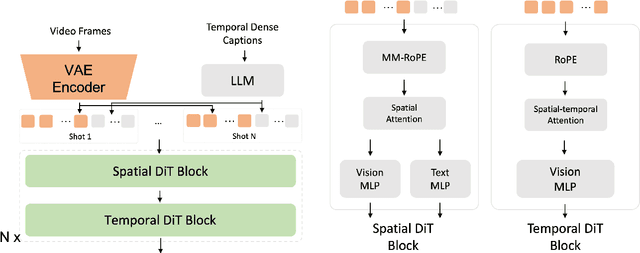
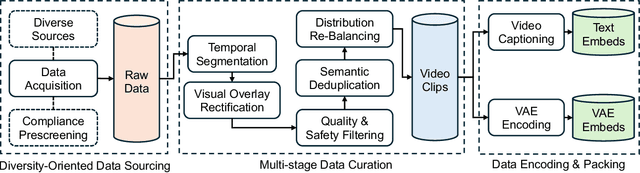
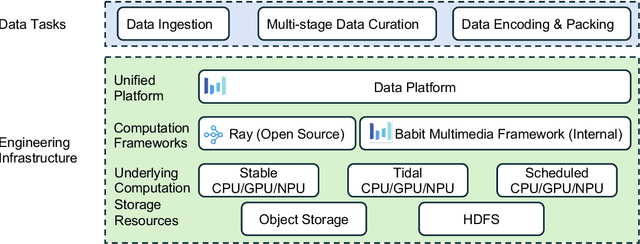
Abstract:Notable breakthroughs in diffusion modeling have propelled rapid improvements in video generation, yet current foundational model still face critical challenges in simultaneously balancing prompt following, motion plausibility, and visual quality. In this report, we introduce Seedance 1.0, a high-performance and inference-efficient video foundation generation model that integrates several core technical improvements: (i) multi-source data curation augmented with precision and meaningful video captioning, enabling comprehensive learning across diverse scenarios; (ii) an efficient architecture design with proposed training paradigm, which allows for natively supporting multi-shot generation and jointly learning of both text-to-video and image-to-video tasks. (iii) carefully-optimized post-training approaches leveraging fine-grained supervised fine-tuning, and video-specific RLHF with multi-dimensional reward mechanisms for comprehensive performance improvements; (iv) excellent model acceleration achieving ~10x inference speedup through multi-stage distillation strategies and system-level optimizations. Seedance 1.0 can generate a 5-second video at 1080p resolution only with 41.4 seconds (NVIDIA-L20). Compared to state-of-the-art video generation models, Seedance 1.0 stands out with high-quality and fast video generation having superior spatiotemporal fluidity with structural stability, precise instruction adherence in complex multi-subject contexts, native multi-shot narrative coherence with consistent subject representation.
Emerging Properties in Unified Multimodal Pretraining
May 20, 2025



Abstract:Unifying multimodal understanding and generation has shown impressive capabilities in cutting-edge proprietary systems. In this work, we introduce BAGEL, an open0source foundational model that natively supports multimodal understanding and generation. BAGEL is a unified, decoder0only model pretrained on trillions of tokens curated from large0scale interleaved text, image, video, and web data. When scaled with such diverse multimodal interleaved data, BAGEL exhibits emerging capabilities in complex multimodal reasoning. As a result, it significantly outperforms open-source unified models in both multimodal generation and understanding across standard benchmarks, while exhibiting advanced multimodal reasoning abilities such as free-form image manipulation, future frame prediction, 3D manipulation, and world navigation. In the hope of facilitating further opportunities for multimodal research, we share the key findings, pretraining details, data creation protocal, and release our code and checkpoints to the community. The project page is at https://bagel-ai.org/
ByteScale: Efficient Scaling of LLM Training with a 2048K Context Length on More Than 12,000 GPUs
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Scaling long-context ability is essential for Large Language Models (LLMs). To amortize the memory consumption across multiple devices in long-context training, inter-data partitioning (a.k.a. Data Parallelism) and intra-data partitioning (a.k.a. Context Parallelism) are commonly used. Current training frameworks predominantly treat the two techniques as orthogonal, and establish static communication groups to organize the devices as a static mesh (e.g., a 2D mesh). However, the sequences for LLM training typically vary in lengths, no matter for texts, multi-modalities or reinforcement learning. The mismatch between data heterogeneity and static mesh causes redundant communication and imbalanced computation, degrading the training efficiency. In this work, we introduce ByteScale, an efficient, flexible, and scalable LLM training framework for large-scale mixed training of long and short sequences. The core of ByteScale is a novel parallelism strategy, namely Hybrid Data Parallelism (HDP), which unifies the inter- and intra-data partitioning with a dynamic mesh design. In particular, we build a communication optimizer, which eliminates the redundant communication for short sequences by data-aware sharding and dynamic communication, and further compresses the communication cost for long sequences by selective offloading. Besides, we also develop a balance scheduler to mitigate the imbalanced computation by parallelism-aware data assignment. We evaluate ByteScale with the model sizes ranging from 7B to 141B, context lengths from 256K to 2048K, on a production cluster with more than 12,000 GPUs. Experiment results show that ByteScale outperforms the state-of-the-art training system by up to 7.89x.
DataSculpt: Crafting Data Landscapes for LLM Post-Training through Multi-objective Partitioning
Sep 02, 2024
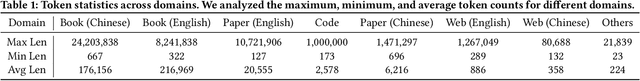
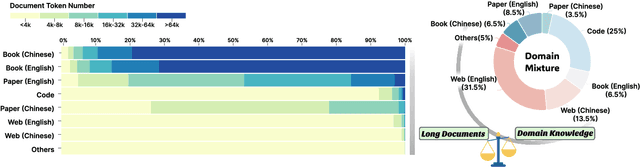
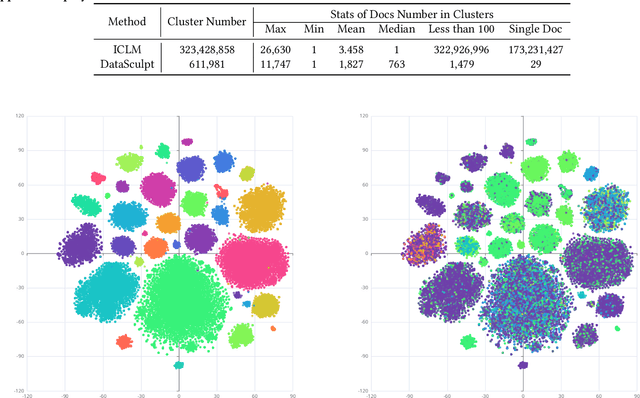
Abstract:The effectiveness of long-context modeling is important for Large Language Models (LLMs) in various applications. Despite their potential, LLMs' efficacy in processing long context does not consistently meet expectations, posing significant challenges for efficient management of prolonged sequences in training. This difficulty is compounded by the scarcity of comprehensive and diverse training datasets suitable for long sequences, which stems from inherent length biases across different data sources, and the logistical complexities associated with massive data management for training in extended contexts. In this work, we introduce DataSculpt, a data construction framework designed to strategically augment the data architecture for extended-context training. Our thorough evaluations demonstrate DataSculpt's remarkable capacity to boost long-context training performance, achieving improvements including an 18.09% increase in retrieval augmentation, 21.23% in summarization, 21.27% in reading comprehension, and a 3.81% rise in code completion, all while preserving the models' overall proficiency with a 4.88% improvement.
BaichuanSEED: Sharing the Potential of ExtensivE Data Collection and Deduplication by Introducing a Competitive Large Language Model Baseline
Aug 27, 2024
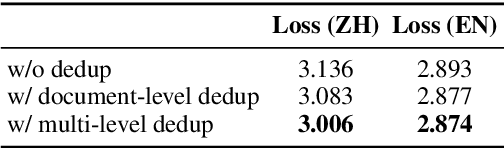

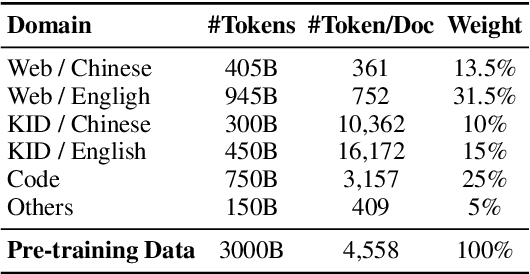
Abstract:The general capabilities of Large Language Models (LLM) highly rely on the composition and selection on extensive pretraining datasets, treated as commercial secrets by several institutions. To mitigate this issue, we open-source the details of a universally applicable data processing pipeline and validate its effectiveness and potential by introducing a competitive LLM baseline. Specifically, the data processing pipeline consists of broad collection to scale up and reweighting to improve quality. We then pretrain a 7B model BaichuanSEED with 3T tokens processed by our pipeline without any deliberate downstream task-related optimization, followed by an easy but effective supervised fine-tuning stage. BaichuanSEED demonstrates consistency and predictability throughout training and achieves comparable performance on comprehensive benchmarks with several commercial advanced large language models, such as Qwen1.5 and Llama3. We also conduct several heuristic experiments to discuss the potential for further optimization of downstream tasks, such as mathematics and coding.
Efficiently Training 7B LLM with 1 Million Sequence Length on 8 GPUs
Jul 16, 2024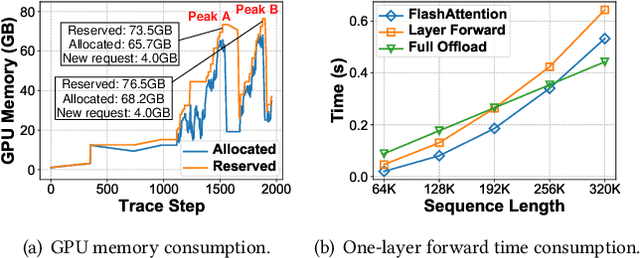
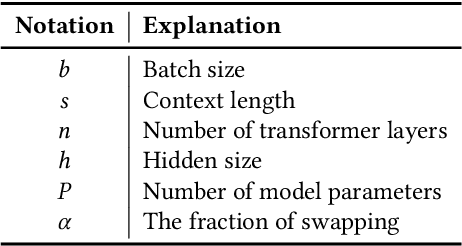
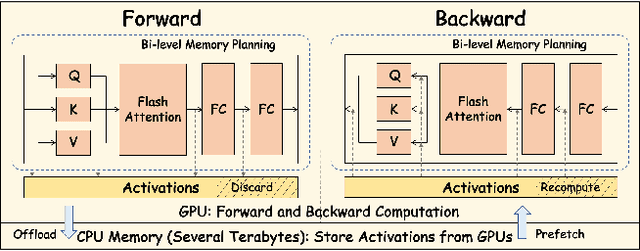
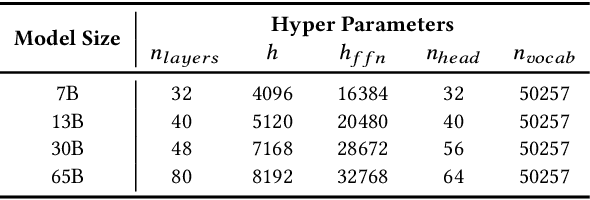
Abstract:Nowadays, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been trained using extended context lengths to foster more creative applications. However, long context training poses great challenges considering the constraint of GPU memory. It not only leads to substantial activation memory consumption during training, but also incurs considerable memory fragmentation. To facilitate long context training, existing frameworks have adopted strategies such as recomputation and various forms of parallelisms. Nevertheless, these techniques rely on redundant computation or extensive communication, resulting in low Model FLOPS Utilization (MFU). In this paper, we propose MEMO, a novel LLM training framework designed for fine-grained activation memory management. Given the quadratic scaling of computation and linear scaling of memory with sequence lengths when using FlashAttention, we offload memory-consuming activations to CPU memory after each layer's forward pass and fetch them during the backward pass. To maximize the swapping of activations without hindering computation, and to avoid exhausting limited CPU memory, we implement a token-wise activation recomputation and swapping mechanism. Furthermore, we tackle the memory fragmentation issue by employing a bi-level Mixed Integer Programming (MIP) approach, optimizing the reuse of memory across transformer layers. Empirical results demonstrate that MEMO achieves an average of 2.42x and 2.26x MFU compared to Megatron-LM and DeepSpeed, respectively. This improvement is attributed to MEMO's ability to minimize memory fragmentation, reduce recomputation and intensive communication, and circumvent the delays associated with the memory reorganization process due to fragmentation. By leveraging fine-grained activation memory management, MEMO facilitates efficient training of 7B LLM with 1 million sequence length on just 8 A800 GPUs, achieving an MFU of 52.30%.
Clover: Regressive Lightweight Speculative Decoding with Sequential Knowledge
May 01, 2024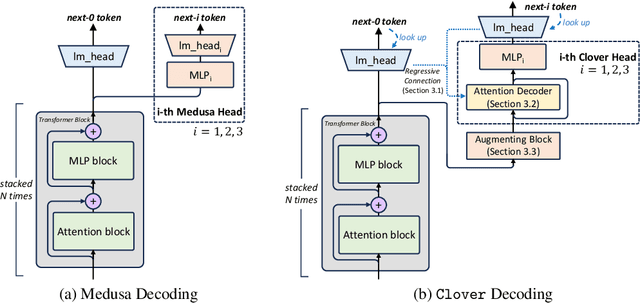
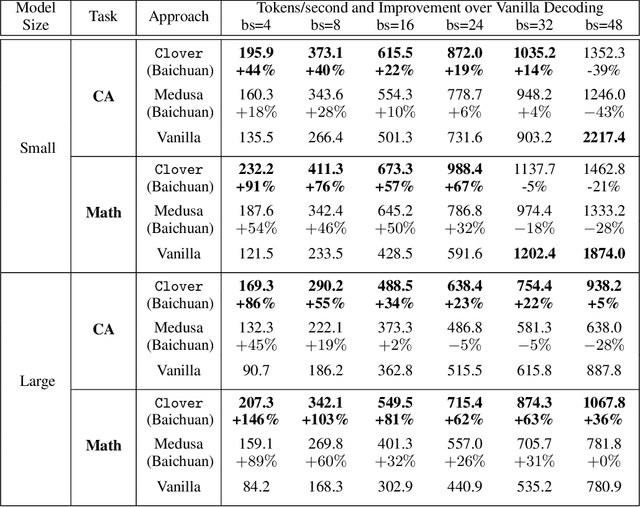
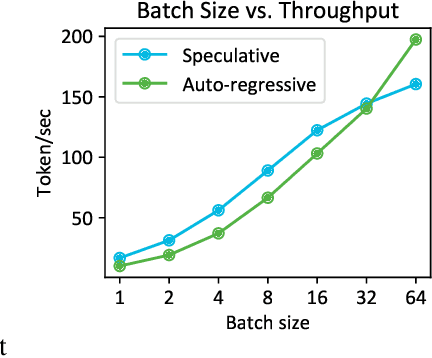
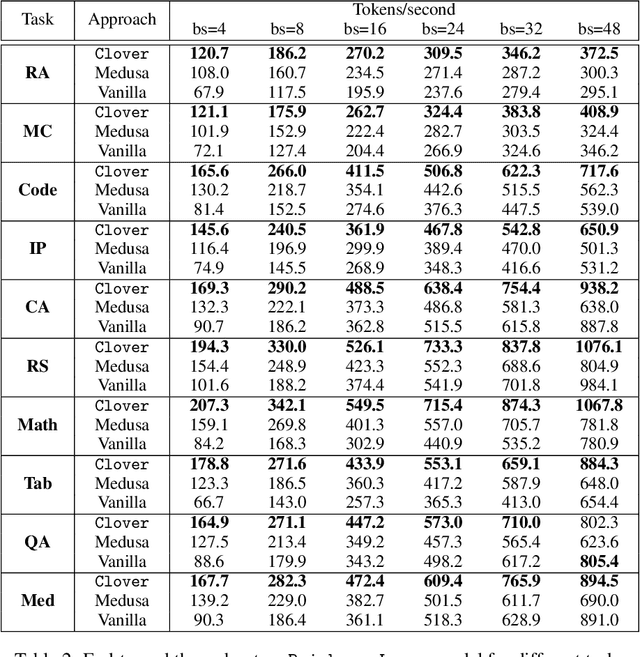
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) suffer from low efficiency as the mismatch between the requirement of auto-regressive decoding and the design of most contemporary GPUs. Specifically, billions to trillions of parameters must be loaded to the GPU cache through its limited memory bandwidth for computation, but only a small batch of tokens is actually computed. Consequently, the GPU spends most of its time on memory transfer instead of computation. Recently, parallel decoding, a type of speculative decoding algorithms, is becoming more popular and has demonstrated impressive efficiency improvement in generation. It introduces extra decoding heads to large models, enabling them to predict multiple subsequent tokens simultaneously and verify these candidate continuations in a single decoding step. However, this approach deviates from the training objective of next token prediction used during pre-training, resulting in a low hit rate for candidate tokens. In this paper, we propose a new speculative decoding algorithm, Clover, which integrates sequential knowledge into the parallel decoding process. This enhancement improves the hit rate of speculators and thus boosts the overall efficiency. Clover transmits the sequential knowledge from pre-speculated tokens via the Regressive Connection, then employs an Attention Decoder to integrate these speculated tokens. Additionally, Clover incorporates an Augmenting Block that modifies the hidden states to better align with the purpose of speculative generation rather than next token prediction. The experiment results demonstrate that Clover outperforms the baseline by up to 91% on Baichuan-Small and 146% on Baichuan-Large, respectively, and exceeds the performance of the previously top-performing method, Medusa, by up to 37% on Baichuan-Small and 57% on Baichuan-Large, respectively.
Improving Automatic Parallel Training via Balanced Memory Workload Optimization
Jul 05, 2023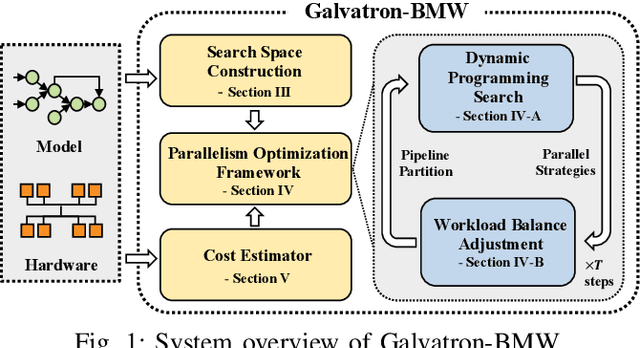
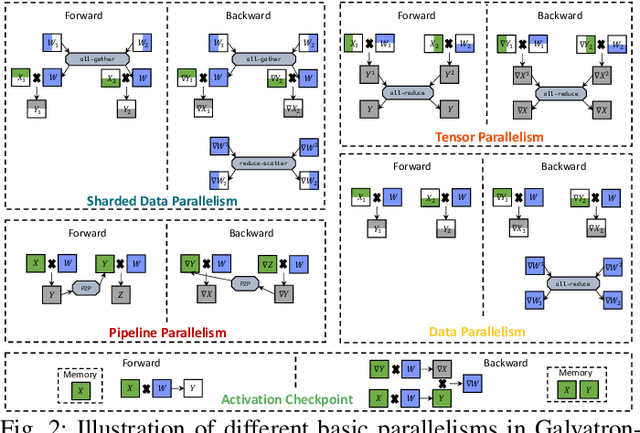
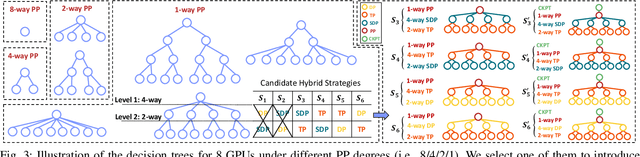
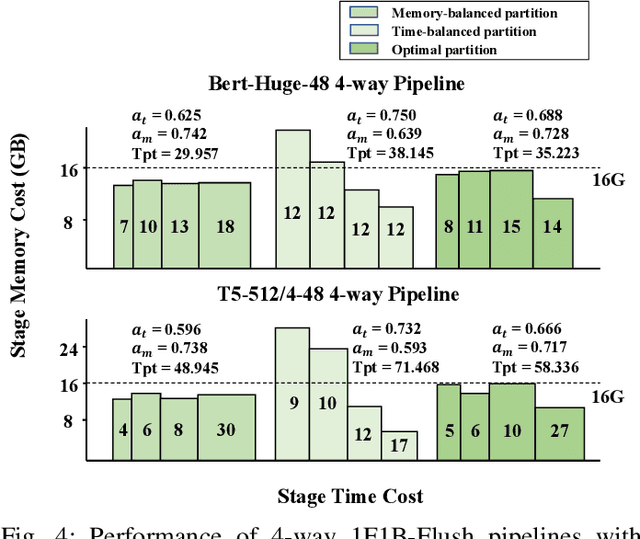
Abstract:Transformer models have emerged as the leading approach for achieving state-of-the-art performance across various application domains, serving as the foundation for advanced large-scale deep learning (DL) models. However, efficiently training these models across multiple GPUs remains a complex challenge due to the abundance of parallelism options. Existing DL systems either require manual efforts to design distributed training plans or limit parallelism combinations to a constrained search space. In this paper, we present Galvatron-BMW, a novel system framework that integrates multiple prevalent parallelism dimensions and automatically identifies the most efficient hybrid parallelism strategy. To effectively navigate this vast search space, we employ a decision tree approach for decomposition and pruning based on intuitive insights. We further utilize a dynamic programming search algorithm to derive the optimal plan. Moreover, to improve resource utilization and enhance system efficiency, we propose a bi-objective optimization workflow that focuses on workload balance. Our evaluations on different Transformer models demonstrate the capabilities of Galvatron-BMW in automating distributed training under varying GPU memory constraints. Across all tested scenarios, Galvatron-BMW consistently achieves superior system throughput, surpassing previous approaches that rely on limited parallelism strategies.
FlexMoE: Scaling Large-scale Sparse Pre-trained Model Training via Dynamic Device Placement
Apr 08, 2023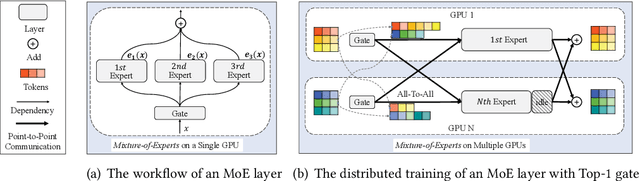

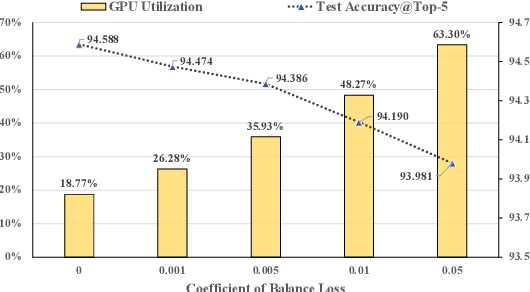
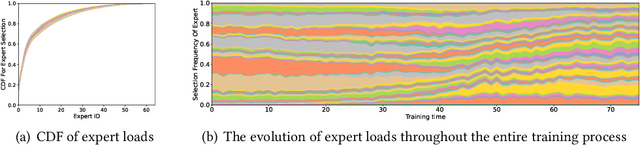
Abstract:With the increasing data volume, there is a trend of using large-scale pre-trained models to store the knowledge into an enormous number of model parameters. The training of these models is composed of lots of dense algebras, requiring a huge amount of hardware resources. Recently, sparsely-gated Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs) are becoming more popular and have demonstrated impressive pretraining scalability in various downstream tasks. However, such a sparse conditional computation may not be effective as expected in practical systems due to the routing imbalance and fluctuation problems. Generally, MoEs are becoming a new data analytics paradigm in the data life cycle and suffering from unique challenges at scales, complexities, and granularities never before possible. In this paper, we propose a novel DNN training framework, FlexMoE, which systematically and transparently address the inefficiency caused by dynamic dataflow. We first present an empirical analysis on the problems and opportunities of training MoE models, which motivates us to overcome the routing imbalance and fluctuation problems by a dynamic expert management and device placement mechanism. Then we introduce a novel scheduling module over the existing DNN runtime to monitor the data flow, make the scheduling plans, and dynamically adjust the model-to-hardware mapping guided by the real-time data traffic. A simple but efficient heuristic algorithm is exploited to dynamically optimize the device placement during training. We have conducted experiments on both NLP models (e.g., BERT and GPT) and vision models (e.g., Swin). And results show FlexMoE can achieve superior performance compared with existing systems on real-world workloads -- FlexMoE outperforms DeepSpeed by 1.70x on average and up to 2.10x, and outperforms FasterMoE by 1.30x on average and up to 1.45x.
* Accepted by SIGMOD 2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge