Kunchang Li
LightBagel: A Light-weighted, Double Fusion Framework for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Oct 27, 2025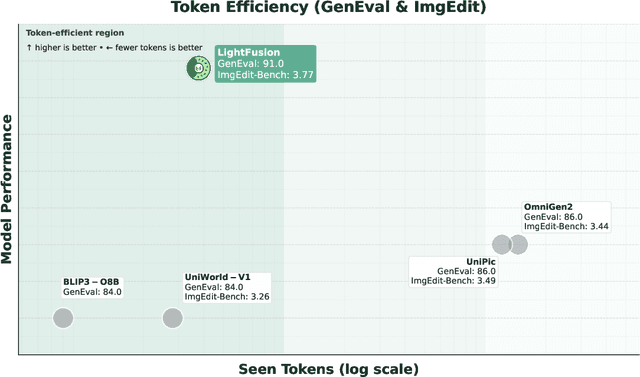
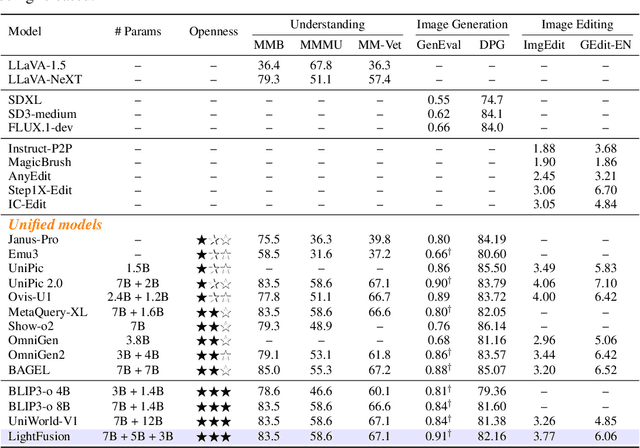
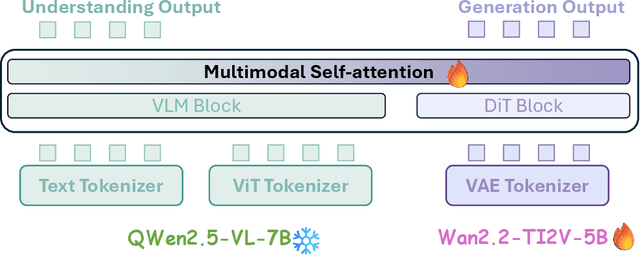
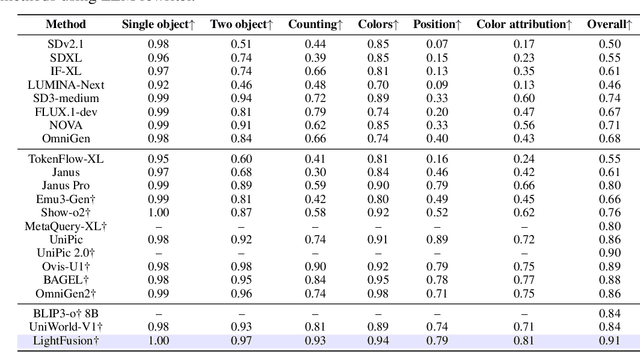
Abstract:Unified multimodal models have recently shown remarkable gains in both capability and versatility, yet most leading systems are still trained from scratch and require substantial computational resources. In this paper, we show that competitive performance can be obtained far more efficiently by strategically fusing publicly available models specialized for either generation or understanding. Our key design is to retain the original blocks while additionally interleaving multimodal self-attention blocks throughout the networks. This double fusion mechanism (1) effectively enables rich multi-modal fusion while largely preserving the original strengths of the base models, and (2) catalyzes synergistic fusion of high-level semantic representations from the understanding encoder with low-level spatial signals from the generation encoder. By training with only ~ 35B tokens, this approach achieves strong results across multiple benchmarks: 0.91 on GenEval for compositional text-to-image generation, 82.16 on DPG-Bench for complex text-to-image generation, 6.06 on GEditBench, and 3.77 on ImgEdit-Bench for image editing. By fully releasing the entire suite of code, model weights, and datasets, we hope to support future research on unified multimodal modeling.
Super Encoding Network: Recursive Association of Multi-Modal Encoders for Video Understanding
Jun 09, 2025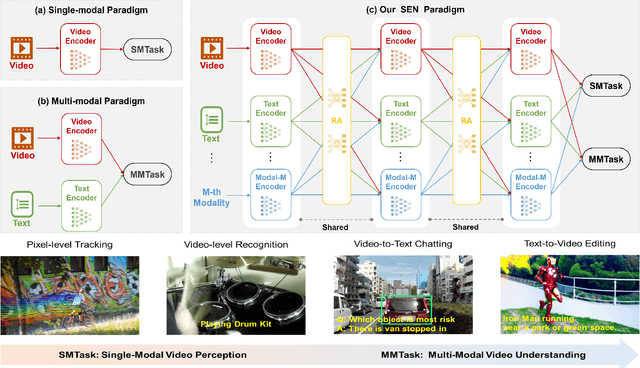
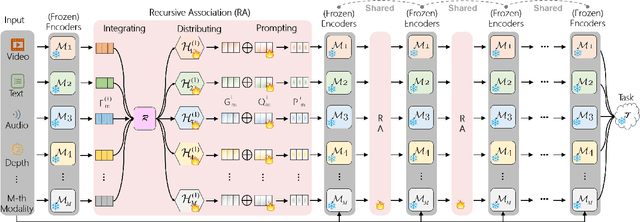
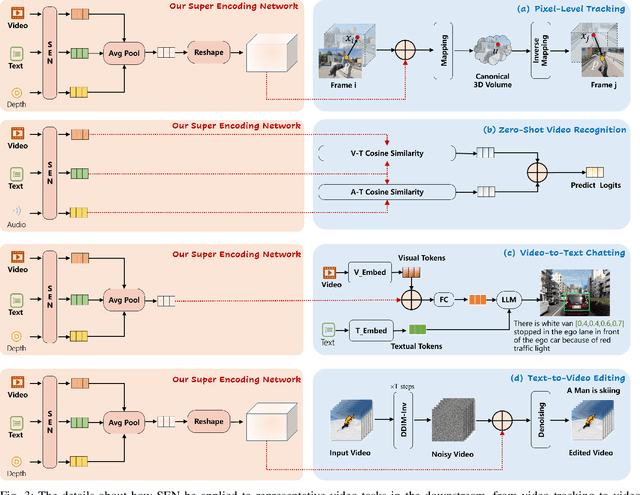

Abstract:Video understanding has been considered as one critical step towards world modeling, which is an important long-term problem in AI research. Recently, multi-modal foundation models have shown such potential via large-scale pretraining. However, these models simply align encoders of different modalities via contrastive learning, while lacking deeper multi-modal interactions, which is critical for understanding complex target movements with diversified video scenes. To fill this gap, we propose a unified Super Encoding Network (SEN) for video understanding, which builds up such distinct interactions through recursive association of multi-modal encoders in the foundation models. Specifically, we creatively treat those well-trained encoders as "super neurons" in our SEN. Via designing a Recursive Association (RA) block, we progressively fuse multi-modalities with the input video, based on knowledge integrating, distributing, and prompting of super neurons in a recursive manner. In this way, our SEN can effectively encode deeper multi-modal interactions, for prompting various video understanding tasks in downstream. Extensive experiments show that, our SEN can remarkably boost the four most representative video tasks, including tracking, recognition, chatting, and editing, e.g., for pixel-level tracking, the average jaccard index improves 2.7%, temporal coherence(TC) drops 8.8% compared to the popular CaDeX++ approach. For one-shot video editing, textual alignment improves 6.4%, and frame consistency increases 4.1% compared to the popular TuneA-Video approach.
Emerging Properties in Unified Multimodal Pretraining
May 20, 2025



Abstract:Unifying multimodal understanding and generation has shown impressive capabilities in cutting-edge proprietary systems. In this work, we introduce BAGEL, an open0source foundational model that natively supports multimodal understanding and generation. BAGEL is a unified, decoder0only model pretrained on trillions of tokens curated from large0scale interleaved text, image, video, and web data. When scaled with such diverse multimodal interleaved data, BAGEL exhibits emerging capabilities in complex multimodal reasoning. As a result, it significantly outperforms open-source unified models in both multimodal generation and understanding across standard benchmarks, while exhibiting advanced multimodal reasoning abilities such as free-form image manipulation, future frame prediction, 3D manipulation, and world navigation. In the hope of facilitating further opportunities for multimodal research, we share the key findings, pretraining details, data creation protocal, and release our code and checkpoints to the community. The project page is at https://bagel-ai.org/
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025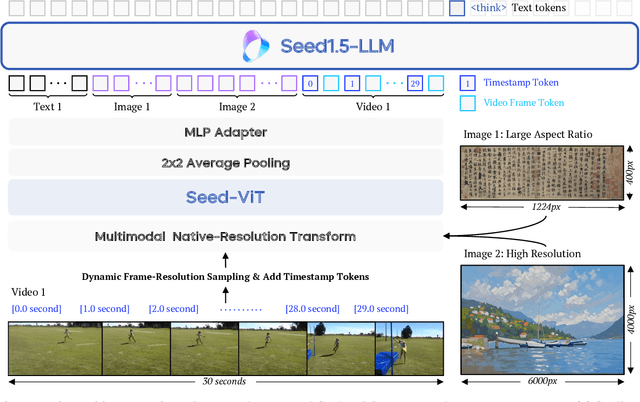

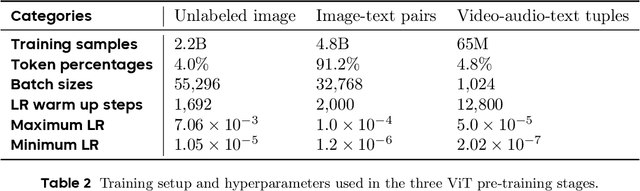
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Make Your Training Flexible: Towards Deployment-Efficient Video Models
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Popular video training methods mainly operate on a fixed number of tokens sampled from a predetermined spatiotemporal grid, resulting in sub-optimal accuracy-computation trade-offs due to inherent video redundancy. They also lack adaptability to varying computational budgets for downstream tasks, hindering applications of the most competitive model in real-world scenes. We thus propose a new test setting, Token Optimization, for maximized input information across budgets, which optimizes the size-limited set of input tokens through token selection from more suitably sampled videos. To this end, we propose a novel augmentation tool termed Flux. By making the sampling grid flexible and leveraging token selection, it is easily adopted in most popular video training frameworks, boosting model robustness with nearly no additional cost. We integrate Flux in large-scale video pre-training, and the resulting FluxViT establishes new state-of-the-art results across extensive tasks at standard costs. Notably, with 1/4 tokens only, it can still match the performance of previous state-of-the-art models with Token Optimization, yielding nearly 90\% savings. All models and data are available at https://github.com/OpenGVLab/FluxViT.
V-Stylist: Video Stylization via Collaboration and Reflection of MLLM Agents
Mar 15, 2025
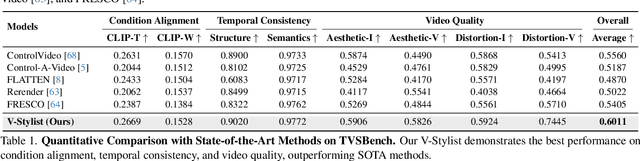

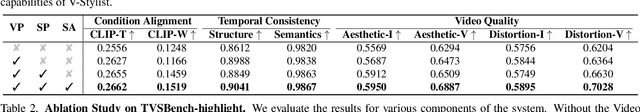
Abstract:Despite the recent advancement in video stylization, most existing methods struggle to render any video with complex transitions, based on an open style description of user query. To fill this gap, we introduce a generic multi-agent system for video stylization, V-Stylist, by a novel collaboration and reflection paradigm of multi-modal large language models. Specifically, our V-Stylist is a systematical workflow with three key roles: (1) Video Parser decomposes the input video into a number of shots and generates their text prompts of key shot content. Via a concise video-to-shot prompting paradigm, it allows our V-Stylist to effectively handle videos with complex transitions. (2) Style Parser identifies the style in the user query and progressively search the matched style model from a style tree. Via a robust tree-of-thought searching paradigm, it allows our V-Stylist to precisely specify vague style preference in the open user query. (3) Style Artist leverages the matched model to render all the video shots into the required style. Via a novel multi-round self-reflection paradigm, it allows our V-Stylist to adaptively adjust detail control, according to the style requirement. With such a distinct design of mimicking human professionals, our V-Stylist achieves a major breakthrough over the primary challenges for effective and automatic video stylization. Moreover,we further construct a new benchmark Text-driven Video Stylization Benchmark (TVSBench), which fills the gap to assess stylization of complex videos on open user queries. Extensive experiments show that, V-Stylist achieves the state-of-the-art, e.g.,V-Stylist surpasses FRESCO and ControlVideo by 6.05% and 4.51% respectively in overall average metrics, marking a significant advance in video stylization.
TimeStep Master: Asymmetrical Mixture of Timestep LoRA Experts for Versatile and Efficient Diffusion Models in Vision
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have driven the advancement of vision generation over the past years. However, it is often difficult to apply these large models in downstream tasks, due to massive fine-tuning cost. Recently, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has been applied for efficient tuning of diffusion models. Unfortunately, the capabilities of LoRA-tuned diffusion models are limited, since the same LoRA is used for different timesteps of the diffusion process. To tackle this problem, we introduce a general and concise TimeStep Master (TSM) paradigm with two key fine-tuning stages. In the fostering stage (1-stage), we apply different LoRAs to fine-tune the diffusion model at different timestep intervals. This results in different TimeStep LoRA experts that can effectively capture different noise levels. In the assembling stage (2-stage), we design a novel asymmetrical mixture of TimeStep LoRA experts, via core-context collaboration of experts at multi-scale intervals. For each timestep, we leverage TimeStep LoRA expert within the smallest interval as the core expert without gating, and use experts within the bigger intervals as the context experts with time-dependent gating. Consequently, our TSM can effectively model the noise level via the expert in the finest interval, and adaptively integrate contexts from the experts of other scales, boosting the versatility of diffusion models. To show the effectiveness of our TSM paradigm, we conduct extensive experiments on three typical and popular LoRA-related tasks of diffusion models, including domain adaptation, post-pretraining, and model distillation. Our TSM achieves the state-of-the-art results on all these tasks, throughout various model structures (UNet, DiT and MM-DiT) and visual data modalities (Image, Video), showing its remarkable generalization capacity.
VideoChat-Flash: Hierarchical Compression for Long-Context Video Modeling
Dec 31, 2024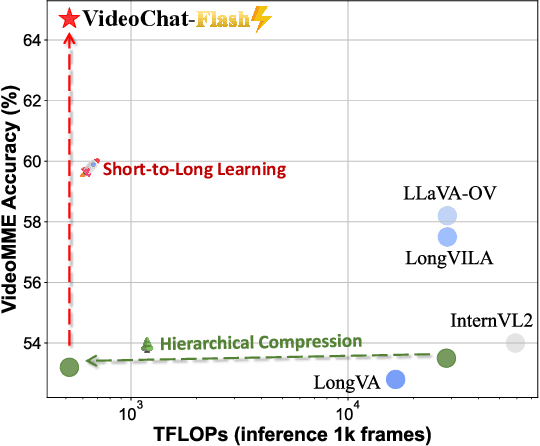
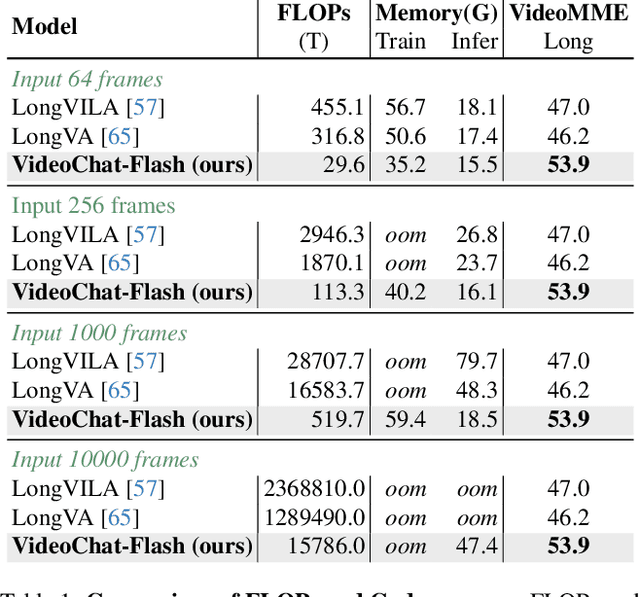
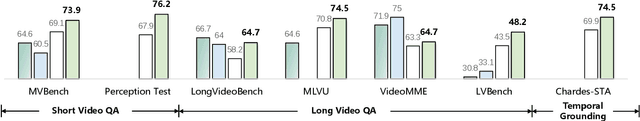
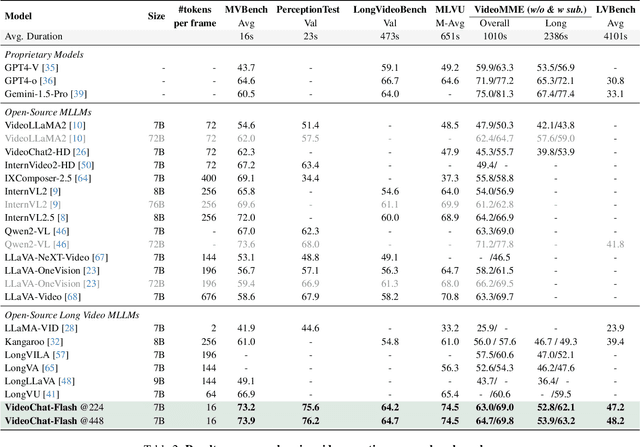
Abstract:Long-context modeling is a critical capability for multimodal large language models (MLLMs), enabling them to process long-form contents with implicit memorization. Despite its advances, handling extremely long videos remains challenging due to the difficulty in maintaining crucial features over extended sequences. This paper introduces a Hierarchical visual token Compression (HiCo) method designed for high-fidelity representation and a practical context modeling system VideoChat-Flash tailored for multimodal long-sequence processing. HiCo capitalizes on the redundancy of visual information in long videos to compress long video context from the clip-level to the video-level, reducing the compute significantly while preserving essential details. VideoChat-Flash features a multi-stage short-to-long learning scheme, a rich dataset of real-world long videos named LongVid, and an upgraded "Needle-In-A-video-Haystack" (NIAH) for evaluating context capacities. In extensive experiments, VideoChat-Flash shows the leading performance on both mainstream long and short video benchmarks at the 7B model scale. It firstly gets 99.1% accuracy over 10,000 frames in NIAH among open-source models.
Task Preference Optimization: Improving Multimodal Large Language Models with Vision Task Alignment
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle with fine-grained or precise understanding of visuals though they give comprehensive perception and reasoning in a spectrum of vision applications. Recent studies either develop tool-using or unify specific visual tasks into the autoregressive framework, often at the expense of overall multimodal performance. To address this issue and enhance MLLMs with visual tasks in a scalable fashion, we propose Task Preference Optimization (TPO), a novel method that utilizes differentiable task preferences derived from typical fine-grained visual tasks. TPO introduces learnable task tokens that establish connections between multiple task-specific heads and the MLLM. By leveraging rich visual labels during training, TPO significantly enhances the MLLM's multimodal capabilities and task-specific performance. Through multi-task co-training within TPO, we observe synergistic benefits that elevate individual task performance beyond what is achievable through single-task training methodologies. Our instantiation of this approach with VideoChat and LLaVA demonstrates an overall 14.6% improvement in multimodal performance compared to baseline models. Additionally, MLLM-TPO demonstrates robust zero-shot capabilities across various tasks, performing comparably to state-of-the-art supervised models. The code will be released at https://github.com/OpenGVLab/TPO
Causal Diffusion Transformers for Generative Modeling
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:We introduce Causal Diffusion as the autoregressive (AR) counterpart of Diffusion models. It is a next-token(s) forecasting framework that is friendly to both discrete and continuous modalities and compatible with existing next-token prediction models like LLaMA and GPT. While recent works attempt to combine diffusion with AR models, we show that introducing sequential factorization to a diffusion model can substantially improve its performance and enables a smooth transition between AR and diffusion generation modes. Hence, we propose CausalFusion - a decoder-only transformer that dual-factorizes data across sequential tokens and diffusion noise levels, leading to state-of-the-art results on the ImageNet generation benchmark while also enjoying the AR advantage of generating an arbitrary number of tokens for in-context reasoning. We further demonstrate CausalFusion's multimodal capabilities through a joint image generation and captioning model, and showcase CausalFusion's ability for zero-shot in-context image manipulations. We hope that this work could provide the community with a fresh perspective on training multimodal models over discrete and continuous data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge