FlexMoE: Scaling Large-scale Sparse Pre-trained Model Training via Dynamic Device Placement
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2023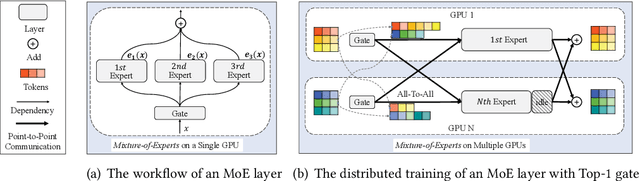

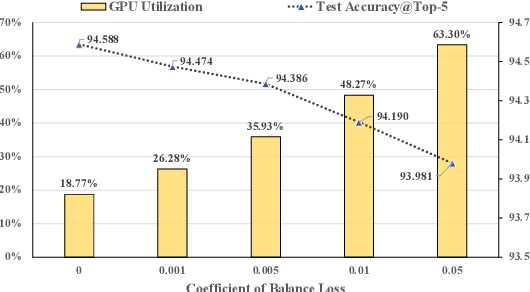
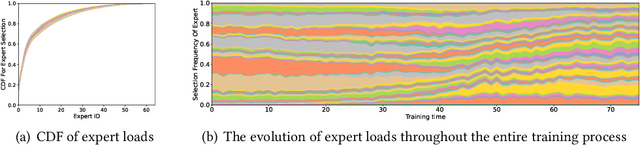
With the increasing data volume, there is a trend of using large-scale pre-trained models to store the knowledge into an enormous number of model parameters. The training of these models is composed of lots of dense algebras, requiring a huge amount of hardware resources. Recently, sparsely-gated Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs) are becoming more popular and have demonstrated impressive pretraining scalability in various downstream tasks. However, such a sparse conditional computation may not be effective as expected in practical systems due to the routing imbalance and fluctuation problems. Generally, MoEs are becoming a new data analytics paradigm in the data life cycle and suffering from unique challenges at scales, complexities, and granularities never before possible. In this paper, we propose a novel DNN training framework, FlexMoE, which systematically and transparently address the inefficiency caused by dynamic dataflow. We first present an empirical analysis on the problems and opportunities of training MoE models, which motivates us to overcome the routing imbalance and fluctuation problems by a dynamic expert management and device placement mechanism. Then we introduce a novel scheduling module over the existing DNN runtime to monitor the data flow, make the scheduling plans, and dynamically adjust the model-to-hardware mapping guided by the real-time data traffic. A simple but efficient heuristic algorithm is exploited to dynamically optimize the device placement during training. We have conducted experiments on both NLP models (e.g., BERT and GPT) and vision models (e.g., Swin). And results show FlexMoE can achieve superior performance compared with existing systems on real-world workloads -- FlexMoE outperforms DeepSpeed by 1.70x on average and up to 2.10x, and outperforms FasterMoE by 1.30x on average and up to 1.45x.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge