Yu-Kai Wang
BrainStack: Neuro-MoE with Functionally Guided Expert Routing for EEG-Based Language Decoding
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Decoding linguistic information from electroencephalography (EEG) remains challenging due to the brain's distributed and nonlinear organization. We present BrainStack, a functionally guided neuro-mixture-of-experts (Neuro-MoE) framework that models the brain's modular functional architecture through anatomically partitioned expert networks. Each functional region is represented by a specialized expert that learns localized neural dynamics, while a transformer-based global expert captures cross-regional dependencies. A learnable routing gate adaptively aggregates these heterogeneous experts, enabling context-dependent expert coordination and selective fusion. To promote coherent representation across the hierarchy, we introduce cross-regional distillation, where the global expert provides top-down regularization to the regional experts. We further release SilentSpeech-EEG (SS-EEG), a large-scale benchmark comprising over 120 hours of EEG recordings from 12 subjects performing 24 silent words, the largest dataset of its kind. Experiments demonstrate that BrainStack consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models, achieving superior accuracy and generalization across subjects. Our results establish BrainStack as a functionally modular, neuro-inspired MoE paradigm that unifies neuroscientific priors with adaptive expert routing, paving the way for scalable and interpretable brain-language decoding.
Wow, wo, val! A Comprehensive Embodied World Model Evaluation Turing Test
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As world models gain momentum in Embodied AI, an increasing number of works explore using video foundation models as predictive world models for downstream embodied tasks like 3D prediction or interactive generation. However, before exploring these downstream tasks, video foundation models still have two critical questions unanswered: (1) whether their generative generalization is sufficient to maintain perceptual fidelity in the eyes of human observers, and (2) whether they are robust enough to serve as a universal prior for real-world embodied agents. To provide a standardized framework for answering these questions, we introduce the Embodied Turing Test benchmark: WoW-World-Eval (Wow,wo,val). Building upon 609 robot manipulation data, Wow-wo-val examines five core abilities, including perception, planning, prediction, generalization, and execution. We propose a comprehensive evaluation protocol with 22 metrics to assess the models' generation ability, which achieves a high Pearson Correlation between the overall score and human preference (>0.93) and establishes a reliable foundation for the Human Turing Test. On Wow-wo-val, models achieve only 17.27 on long-horizon planning and at best 68.02 on physical consistency, indicating limited spatiotemporal consistency and physical reasoning. For the Inverse Dynamic Model Turing Test, we first use an IDM to evaluate the video foundation models' execution accuracy in the real world. However, most models collapse to $\approx$ 0% success, while WoW maintains a 40.74% success rate. These findings point to a noticeable gap between the generated videos and the real world, highlighting the urgency and necessity of benchmarking World Model in Embodied AI.
WoW: Towards a World omniscient World model Through Embodied Interaction
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Humans develop an understanding of intuitive physics through active interaction with the world. This approach is in stark contrast to current video models, such as Sora, which rely on passive observation and therefore struggle with grasping physical causality. This observation leads to our central hypothesis: authentic physical intuition of the world model must be grounded in extensive, causally rich interactions with the real world. To test this hypothesis, we present WoW, a 14-billion-parameter generative world model trained on 2 million robot interaction trajectories. Our findings reveal that the model's understanding of physics is a probabilistic distribution of plausible outcomes, leading to stochastic instabilities and physical hallucinations. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this emergent capability can be actively constrained toward physical realism by SOPHIA, where vision-language model agents evaluate the DiT-generated output and guide its refinement by iteratively evolving the language instructions. In addition, a co-trained Inverse Dynamics Model translates these refined plans into executable robotic actions, thus closing the imagination-to-action loop. We establish WoWBench, a new benchmark focused on physical consistency and causal reasoning in video, where WoW achieves state-of-the-art performance in both human and autonomous evaluation, demonstrating strong ability in physical causality, collision dynamics, and object permanence. Our work provides systematic evidence that large-scale, real-world interaction is a cornerstone for developing physical intuition in AI. Models, data, and benchmarks will be open-sourced.
AEGIS: Human Attention-based Explainable Guidance for Intelligent Vehicle Systems
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Improving decision-making capabilities in Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles (AIVs) has been a heated topic in recent years. Despite advancements, training machines to capture regions of interest for comprehensive scene understanding, like human perception and reasoning, remains a significant challenge. This study introduces a novel framework, Human Attention-based Explainable Guidance for Intelligent Vehicle Systems (AEGIS). AEGIS utilizes human attention, converted from eye-tracking, to guide reinforcement learning (RL) models to identify critical regions of interest for decision-making. AEGIS uses a pre-trained human attention model to guide RL models to identify critical regions of interest for decision-making. By collecting 1.2 million frames from 20 participants across six scenarios, AEGIS pre-trains a model to predict human attention patterns.
3D UAV Trajectory Planning for IoT Data Collection via Matrix-Based Evolutionary Computation
Oct 08, 2024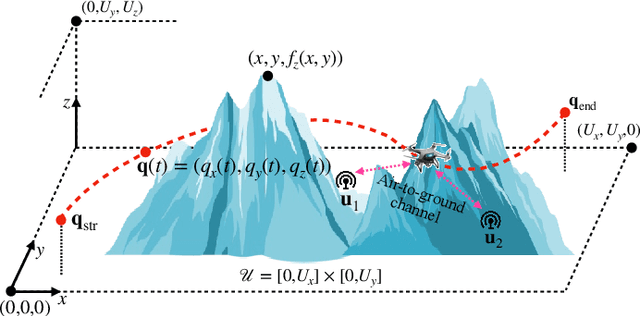
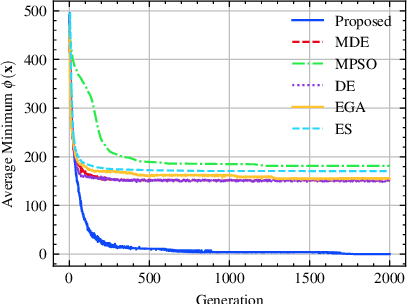
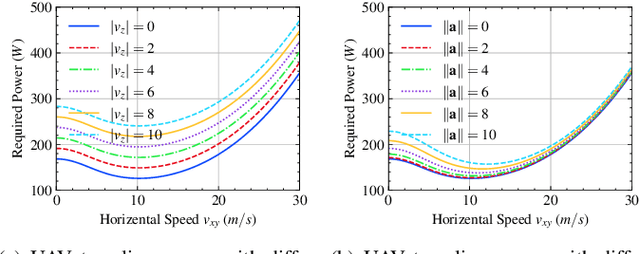
Abstract:UAVs are increasingly becoming vital tools in various wireless communication applications including internet of things (IoT) and sensor networks, thanks to their rapid and agile non-terrestrial mobility. Despite recent research, planning three-dimensional (3D) UAV trajectories over a continuous temporal-spatial domain remains challenging due to the need to solve computationally intensive optimization problems. In this paper, we study UAV-assisted IoT data collection aimed at minimizing total energy consumption while accounting for the UAV's physical capabilities, the heterogeneous data demands of IoT nodes, and 3D terrain. We propose a matrix-based differential evolution with constraint handling (MDE-CH), a computation-efficient evolutionary algorithm designed to address non-convex constrained optimization problems with several different types of constraints. Numerical evaluations demonstrate that the proposed MDE-CH algorithm provides a continuous 3D temporal-spatial UAV trajectory capable of efficiently minimizing energy consumption under various practical constraints and outperforms the conventional fly-hover-fly model for both two-dimensional (2D) and 3D trajectory planning.
BELT-2: Bootstrapping EEG-to-Language representation alignment for multi-task brain decoding
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:The remarkable success of large language models (LLMs) across various multi-modality applications is well established. However, integrating large language models with humans, or brain dynamics, remains relatively unexplored. In this paper, we introduce BELT-2, a pioneering multi-task model designed to enhance both encoding and decoding performance from EEG signals. To bolster the quality of the EEG encoder, BELT-2 is the first work to innovatively 1) adopt byte-pair encoding (BPE)-level EEG-language alignment and 2) integrate multi-task training and decoding in the EEG domain. Inspired by the idea of \textbf{\textit{Bridging the Brain with GPT}}, we further connect the multi-task EEG encoder with LLMs by utilizing prefix-tuning on intermediary output from the EEG encoder. These innovative efforts make BELT-2 a pioneering breakthrough, making it the first work in the field capable of decoding coherent and readable sentences from non-invasive brain signals. Our experiments highlight significant advancements over prior techniques in both quantitative and qualitative measures, achieving a decoding performance with a BLEU-1 score of 52.2\% on the ZuCo dataset. Furthermore, BELT-2 shows a remarkable improvement ranging from 31\% to 162\% on other translation benchmarks. Codes can be accessed via the provided anonymous link~\footnote{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/BELT-2-0048}.
SpeechPrompt: Prompting Speech Language Models for Speech Processing Tasks
Aug 23, 2024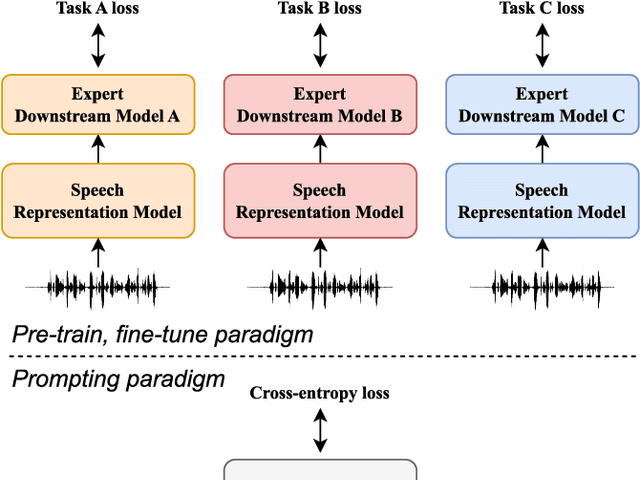
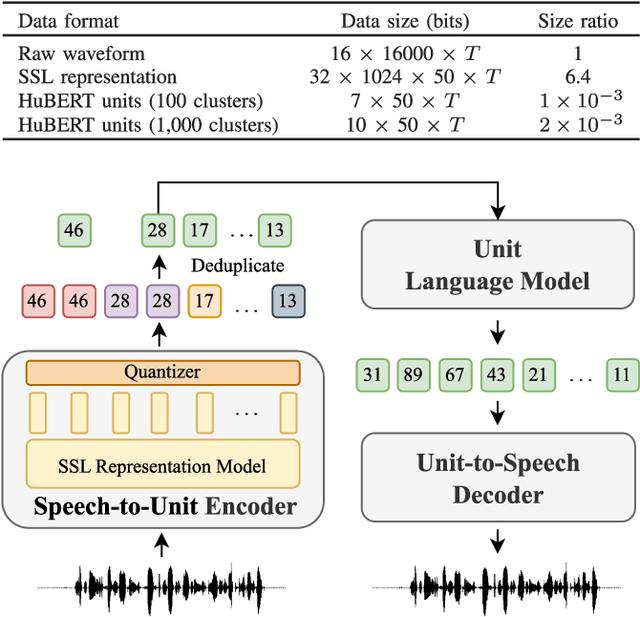
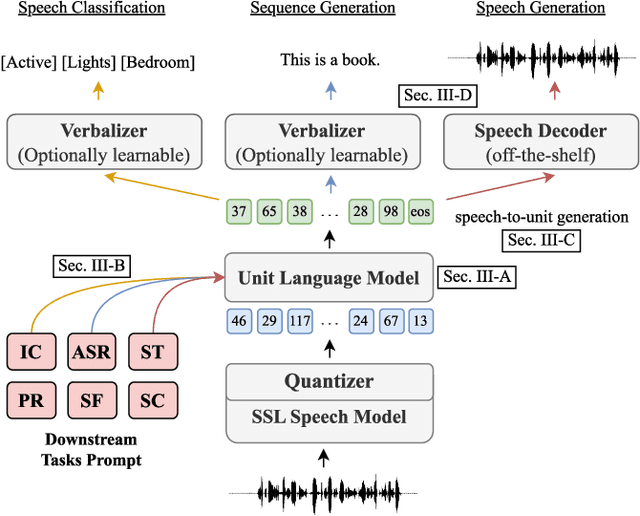
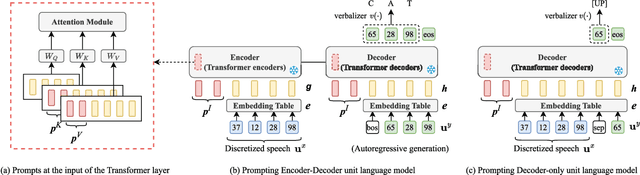
Abstract:Prompting has become a practical method for utilizing pre-trained language models (LMs). This approach offers several advantages. It allows an LM to adapt to new tasks with minimal training and parameter updates, thus achieving efficiency in both storage and computation. Additionally, prompting modifies only the LM's inputs and harnesses the generative capabilities of language models to address various downstream tasks in a unified manner. This significantly reduces the need for human labor in designing task-specific models. These advantages become even more evident as the number of tasks served by the LM scales up. Motivated by the strengths of prompting, we are the first to explore the potential of prompting speech LMs in the domain of speech processing. Recently, there has been a growing interest in converting speech into discrete units for language modeling. Our pioneer research demonstrates that these quantized speech units are highly versatile within our unified prompting framework. Not only can they serve as class labels, but they also contain rich phonetic information that can be re-synthesized back into speech signals for speech generation tasks. Specifically, we reformulate speech processing tasks into speech-to-unit generation tasks. As a result, we can seamlessly integrate tasks such as speech classification, sequence generation, and speech generation within a single, unified prompting framework. The experiment results show that the prompting method can achieve competitive performance compared to the strong fine-tuning method based on self-supervised learning models with a similar number of trainable parameters. The prompting method also shows promising results in the few-shot setting. Moreover, with the advanced speech LMs coming into the stage, the proposed prompting framework attains great potential.
* Published in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing (TASLP)
Enhancing End-to-End Autonomous Driving Systems Through Synchronized Human Behavior Data
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a pioneering exploration into the integration of fine-grained human supervision within the autonomous driving domain to enhance system performance. The current advances in End-to-End autonomous driving normally are data-driven and rely on given expert trials. However, this reliance limits the systems' generalizability and their ability to earn human trust. Addressing this gap, our research introduces a novel approach by synchronously collecting data from human and machine drivers under identical driving scenarios, focusing on eye-tracking and brainwave data to guide machine perception and decision-making processes. This paper utilizes the Carla simulation to evaluate the impact brought by human behavior guidance. Experimental results show that using human attention to guide machine attention could bring a significant improvement in driving performance. However, guidance by human intention still remains a challenge. This paper pioneers a promising direction and potential for utilizing human behavior guidance to enhance autonomous systems.
Towards Linguistic Neural Representation Learning and Sentence Retrieval from Electroencephalogram Recordings
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Decoding linguistic information from non-invasive brain signals using EEG has gained increasing research attention due to its vast applicational potential. Recently, a number of works have adopted a generative-based framework to decode electroencephalogram (EEG) signals into sentences by utilizing the power generative capacity of pretrained large language models (LLMs). However, this approach has several drawbacks that hinder the further development of linguistic applications for brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). Specifically, the ability of the EEG encoder to learn semantic information from EEG data remains questionable, and the LLM decoder's tendency to generate sentences based on its training memory can be hard to avoid. These issues necessitate a novel approach for converting EEG signals into sentences. In this paper, we propose a novel two-step pipeline that addresses these limitations and enhances the validity of linguistic EEG decoding research. We first confirm that word-level semantic information can be learned from EEG data recorded during natural reading by training a Conformer encoder via a masked contrastive objective for word-level classification. To achieve sentence decoding results, we employ a training-free retrieval method to retrieve sentences based on the predictions from the EEG encoder. Extensive experiments and ablation studies were conducted in this paper for a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed approach. Visualization of the top prediction candidates reveals that our model effectively groups EEG segments into semantic categories with similar meanings, thereby validating its ability to learn patterns from unspoken EEG recordings. Despite the exploratory nature of this work, these results suggest that our method holds promise for providing more reliable solutions for converting EEG signals into text.
Masked EEG Modeling for Driving Intention Prediction
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Driving under drowsy conditions significantly escalates the risk of vehicular accidents. Although recent efforts have focused on using electroencephalography to detect drowsiness, helping prevent accidents caused by driving in such states, seamless human-machine interaction in driving scenarios requires a more versatile EEG-based system. This system should be capable of understanding a driver's intention while demonstrating resilience to artifacts induced by sudden movements. This paper pioneers a novel research direction in BCI-assisted driving, studying the neural patterns related to driving intentions and presenting a novel method for driving intention prediction. In particular, our preliminary analysis of the EEG signal using independent component analysis suggests a close relation between the intention of driving maneuvers and the neural activities in central-frontal and parietal areas. Power spectral density analysis at a group level also reveals a notable distinction among various driving intentions in the frequency domain. To exploit these brain dynamics, we propose a novel Masked EEG Modeling framework for predicting human driving intentions, including the intention for left turning, right turning, and straight proceeding. Extensive experiments, encompassing comprehensive quantitative and qualitative assessments on public dataset, demonstrate the proposed method is proficient in predicting driving intentions across various vigilance states. Specifically, our model attains an accuracy of 85.19% when predicting driving intentions for drowsy subjects, which shows its promising potential for mitigating traffic accidents related to drowsy driving. Notably, our method maintains over 75% accuracy when more than half of the channels are missing or corrupted, underscoring its adaptability in real-life driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge