Iu-thing Kang
SpeechPrompt: Prompting Speech Language Models for Speech Processing Tasks
Aug 23, 2024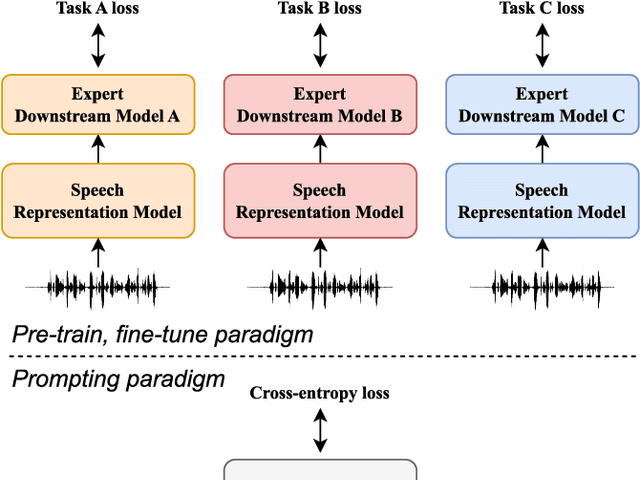
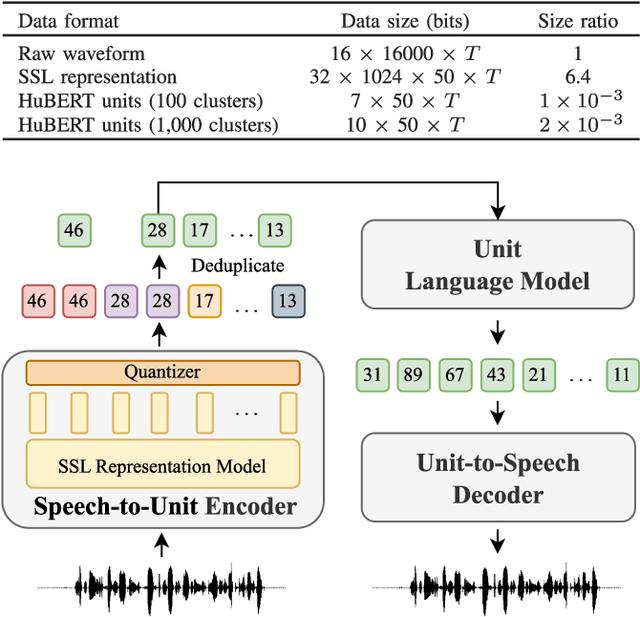
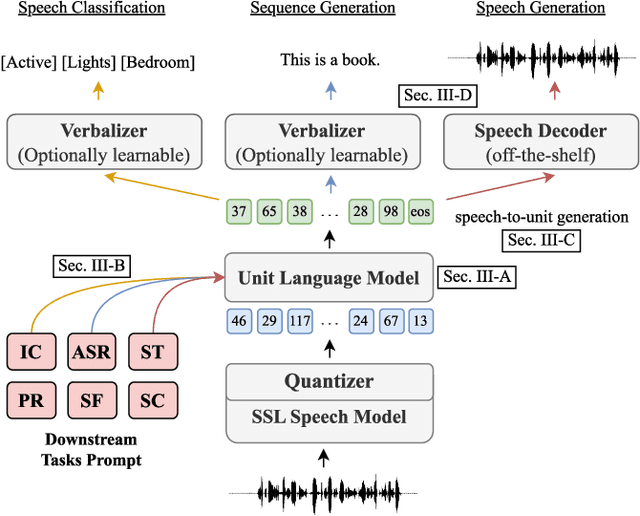
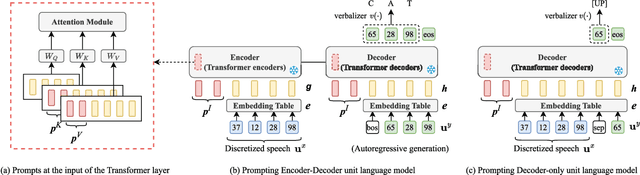
Abstract:Prompting has become a practical method for utilizing pre-trained language models (LMs). This approach offers several advantages. It allows an LM to adapt to new tasks with minimal training and parameter updates, thus achieving efficiency in both storage and computation. Additionally, prompting modifies only the LM's inputs and harnesses the generative capabilities of language models to address various downstream tasks in a unified manner. This significantly reduces the need for human labor in designing task-specific models. These advantages become even more evident as the number of tasks served by the LM scales up. Motivated by the strengths of prompting, we are the first to explore the potential of prompting speech LMs in the domain of speech processing. Recently, there has been a growing interest in converting speech into discrete units for language modeling. Our pioneer research demonstrates that these quantized speech units are highly versatile within our unified prompting framework. Not only can they serve as class labels, but they also contain rich phonetic information that can be re-synthesized back into speech signals for speech generation tasks. Specifically, we reformulate speech processing tasks into speech-to-unit generation tasks. As a result, we can seamlessly integrate tasks such as speech classification, sequence generation, and speech generation within a single, unified prompting framework. The experiment results show that the prompting method can achieve competitive performance compared to the strong fine-tuning method based on self-supervised learning models with a similar number of trainable parameters. The prompting method also shows promising results in the few-shot setting. Moreover, with the advanced speech LMs coming into the stage, the proposed prompting framework attains great potential.
* Published in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing (TASLP)
SpeechPrompt v2: Prompt Tuning for Speech Classification Tasks
Mar 01, 2023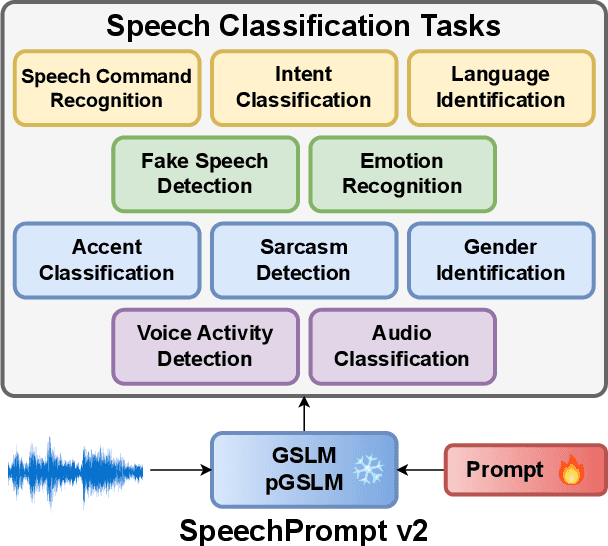
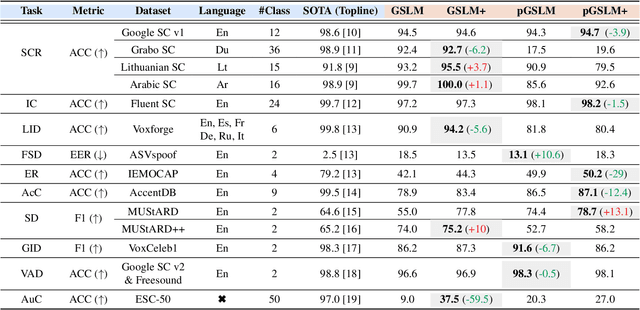
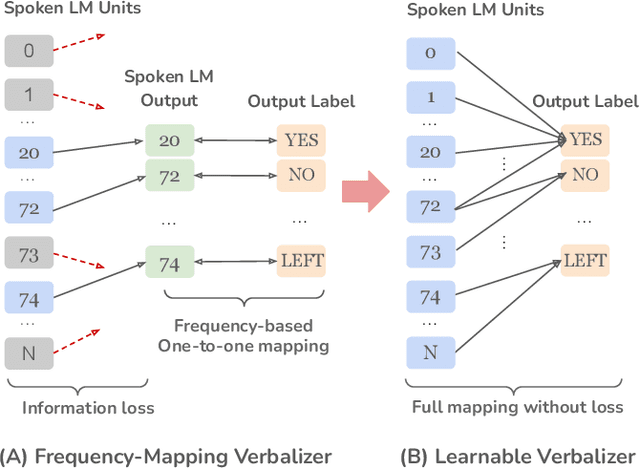
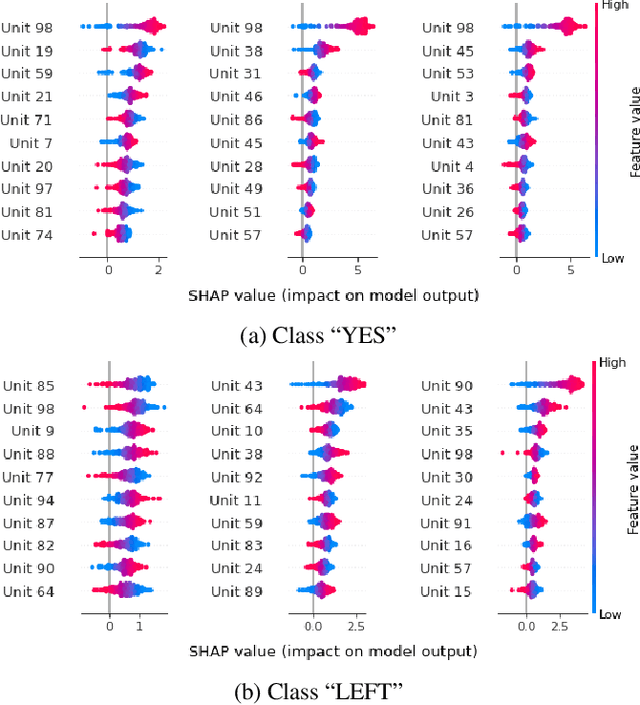
Abstract:Prompt tuning is a technology that tunes a small set of parameters to steer a pre-trained language model (LM) to directly generate the output for downstream tasks. Recently, prompt tuning has demonstrated its storage and computation efficiency in both natural language processing (NLP) and speech processing fields. These advantages have also revealed prompt tuning as a candidate approach to serving pre-trained LM for multiple tasks in a unified manner. For speech processing, SpeechPrompt shows its high parameter efficiency and competitive performance on a few speech classification tasks. However, whether SpeechPrompt is capable of serving a large number of tasks is unanswered. In this work, we propose SpeechPrompt v2, a prompt tuning framework capable of performing a wide variety of speech classification tasks, covering multiple languages and prosody-related tasks. The experiment result shows that SpeechPrompt v2 achieves performance on par with prior works with less than 0.15M trainable parameters in a unified framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge