Shihan Cai
EmbodiedVSR: Dynamic Scene Graph-Guided Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Visual Spatial Tasks
Mar 14, 2025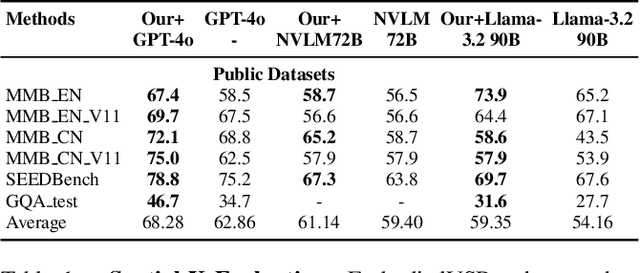
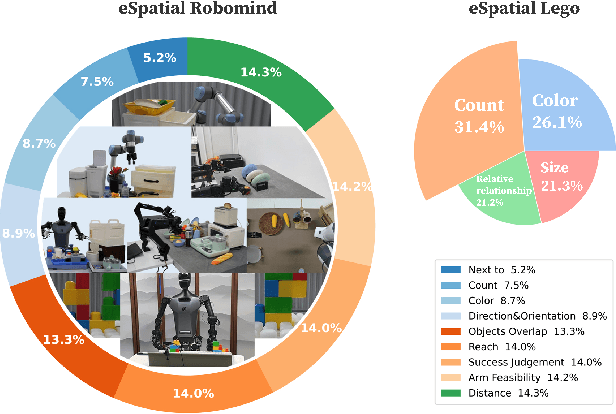
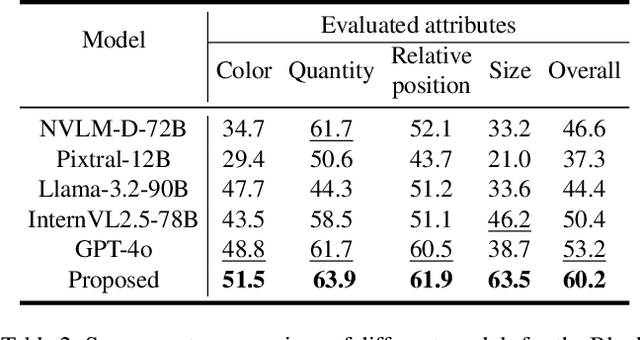
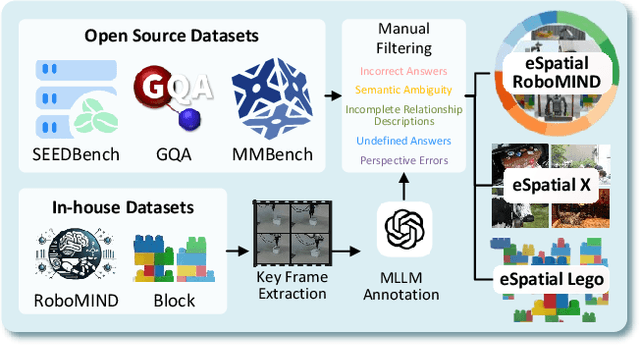
Abstract:While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made groundbreaking progress in embodied intelligence, they still face significant challenges in spatial reasoning for complex long-horizon tasks. To address this gap, we propose EmbodiedVSR (Embodied Visual Spatial Reasoning), a novel framework that integrates dynamic scene graph-guided Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to enhance spatial understanding for embodied agents. By explicitly constructing structured knowledge representations through dynamic scene graphs, our method enables zero-shot spatial reasoning without task-specific fine-tuning. This approach not only disentangles intricate spatial relationships but also aligns reasoning steps with actionable environmental dynamics. To rigorously evaluate performance, we introduce the eSpatial-Benchmark, a comprehensive dataset including real-world embodied scenarios with fine-grained spatial annotations and adaptive task difficulty levels. Experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms existing MLLM-based methods in accuracy and reasoning coherence, particularly in long-horizon tasks requiring iterative environment interaction. The results reveal the untapped potential of MLLMs for embodied intelligence when equipped with structured, explainable reasoning mechanisms, paving the way for more reliable deployment in real-world spatial applications. The codes and datasets will be released soon.
Object Tracking in Satellite Videos Based on a Multi-Frame Optical Flow Tracker
Apr 25, 2018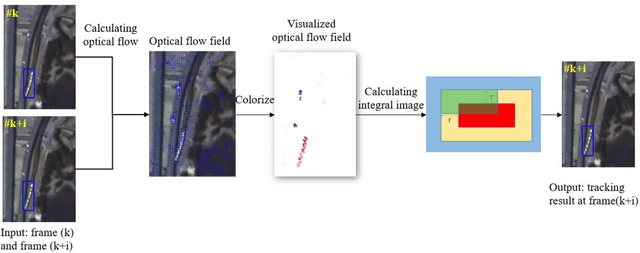
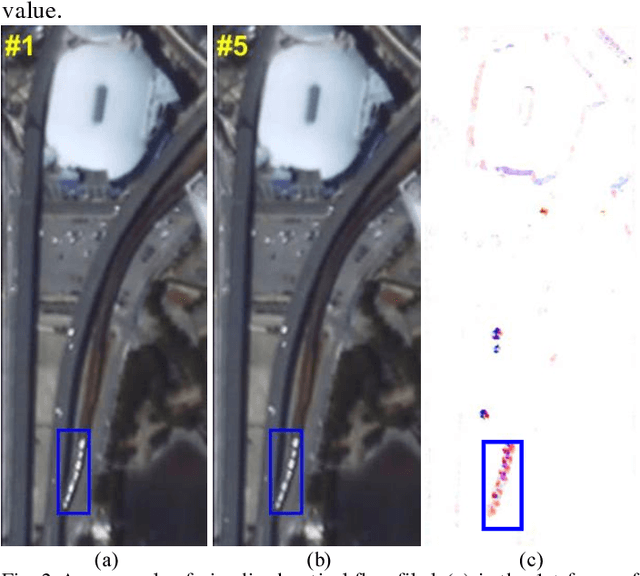
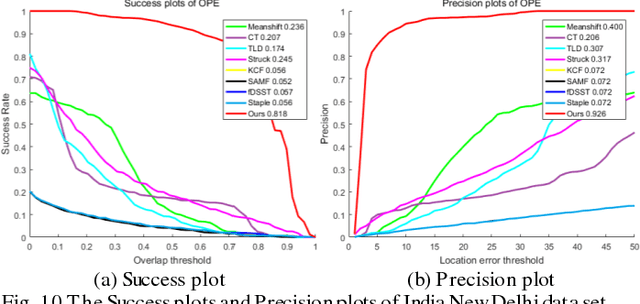
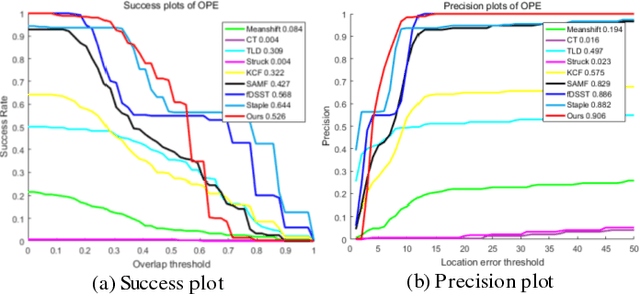

Abstract:Object tracking is a hot topic in computer vision. Thanks to the booming of the very high resolution (VHR) remote sensing techniques, it is now possible to track targets of interests in satellite videos. However, since the targets in the satellite videos are usually too small compared with the entire image, and too similar with the background, most state-of-the-art algorithms failed to track the target in satellite videos with a satisfactory accuracy. Due to the fact that optical flow shows the great potential to detect even the slight movement of the targets, we proposed a multi-frame optical flow tracker (MOFT) for object tracking in satellite videos. The Lucas-Kanade optical flow method was fused with the HSV color system and integral image to track the targets in the satellite videos, while multi-frame difference method was utilized in the optical flow tracker for a better interpretation. The experiments with three VHR remote sensing satellite video datasets indicate that compared with state-of-the-art object tracking algorithms, the proposed method can track the target more accurately.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge