Jian Tang
Baidu
PerturbDiff: Functional Diffusion for Single-Cell Perturbation Modeling
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Building Virtual Cells that can accurately simulate cellular responses to perturbations is a long-standing goal in systems biology. A fundamental challenge is that high-throughput single-cell sequencing is destructive: the same cell cannot be observed both before and after a perturbation. Thus, perturbation prediction requires mapping unpaired control and perturbed populations. Existing models address this by learning maps between distributions, but typically assume a single fixed response distribution when conditioned on observed cellular context (e.g., cell type) and the perturbation type. In reality, responses vary systematically due to unobservable latent factors such as microenvironmental fluctuations and complex batch effects, forming a manifold of possible distributions for the same observed conditions. To account for this variability, we introduce PerturbDiff, which shifts modeling from individual cells to entire distributions. By embedding distributions as points in a Hilbert space, we define a diffusion-based generative process operating directly over probability distributions. This allows PerturbDiff to capture population-level response shifts across hidden factors. Benchmarks on established datasets show that PerturbDiff achieves state-of-the-art performance in single-cell response prediction and generalizes substantially better to unseen perturbations. See our project page (https://katarinayuan.github.io/PerturbDiff-ProjectPage/), where code and data will be made publicly available (https://github.com/DeepGraphLearning/PerturbDiff).
RoboGene: Boosting VLA Pre-training via Diversity-Driven Agentic Framework for Real-World Task Generation
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:The pursuit of general-purpose robotic manipulation is hindered by the scarcity of diverse, real-world interaction data. Unlike data collection from web in vision or language, robotic data collection is an active process incurring prohibitive physical costs. Consequently, automated task curation to maximize data value remains a critical yet under-explored challenge. Existing manual methods are unscalable and biased toward common tasks, while off-the-shelf foundation models often hallucinate physically infeasible instructions. To address this, we introduce RoboGene, an agentic framework designed to automate the generation of diverse, physically plausible manipulation tasks across single-arm, dual-arm, and mobile robots. RoboGene integrates three core components: diversity-driven sampling for broad task coverage, self-reflection mechanisms to enforce physical constraints, and human-in-the-loop refinement for continuous improvement. We conduct extensive quantitative analysis and large-scale real-world experiments, collecting datasets of 18k trajectories and introducing novel metrics to assess task quality, feasibility, and diversity. Results demonstrate that RoboGene significantly outperforms state-of-the-art foundation models (e.g., GPT-4o, Gemini 2.5 Pro). Furthermore, real-world experiments show that VLA models pre-trained with RoboGene achieve higher success rates and superior generalization, underscoring the importance of high-quality task generation. Our project is available at https://robogene-boost-vla.github.io.
MeshMimic: Geometry-Aware Humanoid Motion Learning through 3D Scene Reconstruction
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:Humanoid motion control has witnessed significant breakthroughs in recent years, with deep reinforcement learning (RL) emerging as a primary catalyst for achieving complex, human-like behaviors. However, the high dimensionality and intricate dynamics of humanoid robots make manual motion design impractical, leading to a heavy reliance on expensive motion capture (MoCap) data. These datasets are not only costly to acquire but also frequently lack the necessary geometric context of the surrounding physical environment. Consequently, existing motion synthesis frameworks often suffer from a decoupling of motion and scene, resulting in physical inconsistencies such as contact slippage or mesh penetration during terrain-aware tasks. In this work, we present MeshMimic, an innovative framework that bridges 3D scene reconstruction and embodied intelligence to enable humanoid robots to learn coupled "motion-terrain" interactions directly from video. By leveraging state-of-the-art 3D vision models, our framework precisely segments and reconstructs both human trajectories and the underlying 3D geometry of terrains and objects. We introduce an optimization algorithm based on kinematic consistency to extract high-quality motion data from noisy visual reconstructions, alongside a contact-invariant retargeting method that transfers human-environment interaction features to the humanoid agent. Experimental results demonstrate that MeshMimic achieves robust, highly dynamic performance across diverse and challenging terrains. Our approach proves that a low-cost pipeline utilizing only consumer-grade monocular sensors can facilitate the training of complex physical interactions, offering a scalable path toward the autonomous evolution of humanoid robots in unstructured environments.
RoboAug: One Annotation to Hundreds of Scenes via Region-Contrastive Data Augmentation for Robotic Manipulation
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Enhancing the generalization capability of robotic learning to enable robots to operate effectively in diverse, unseen scenes is a fundamental and challenging problem. Existing approaches often depend on pretraining with large-scale data collection, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming, or on semantic data augmentation techniques that necessitate an impractical assumption of flawless upstream object detection in real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose RoboAug, a novel generative data augmentation framework that significantly minimizes the reliance on large-scale pretraining and the perfect visual recognition assumption by requiring only the bounding box annotation of a single image during training. Leveraging this minimal information, RoboAug employs pre-trained generative models for precise semantic data augmentation and integrates a plug-and-play region-contrastive loss to help models focus on task-relevant regions, thereby improving generalization and boosting task success rates. We conduct extensive real-world experiments on three robots, namely UR-5e, AgileX, and Tien Kung 2.0, spanning over 35k rollouts. Empirical results demonstrate that RoboAug significantly outperforms state-of-the-art data augmentation baselines. Specifically, when evaluating generalization capabilities in unseen scenes featuring diverse combinations of backgrounds, distractors, and lighting conditions, our method achieves substantial gains over the baseline without augmentation. The success rates increase from 0.09 to 0.47 on UR-5e, from 0.16 to 0.60 on AgileX, and from 0.19 to 0.67 on Tien Kung 2.0. These results highlight the superior generalization and effectiveness of RoboAug in real-world manipulation tasks. Our project is available at https://x-roboaug.github.io/.
CRAFT: Adapting VLA Models to Contact-rich Manipulation via Force-aware Curriculum Fine-tuning
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown a strong capability in enabling robots to execute general instructions, yet they struggle with contact-rich manipulation tasks, where success requires precise alignment, stable contact maintenance, and effective handling of deformable objects. A fundamental challenge arises from the imbalance between high-entropy vision and language inputs and low-entropy but critical force signals, which often leads to over-reliance on perception and unstable control. To address this, we introduce CRAFT, a force-aware curriculum fine-tuning framework that integrates a variational information bottleneck module to regulate vision and language embeddings during early training. This curriculum strategy encourages the model to prioritize force signals initially, before progressively restoring access to the full multimodal information. To enable force-aware learning, we further design a homologous leader-follower teleoperation system that collects synchronized vision, language, and force data across diverse contact-rich tasks. Real-world experiments demonstrate that CRAFT consistently improves task success, generalizes to unseen objects and novel task variations, and adapts effectively across diverse VLA architectures, enabling robust and generalizable contact-rich manipulation.
TC-IDM: Grounding Video Generation for Executable Zero-shot Robot Motion
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The vision-language-action (VLA) paradigm has enabled powerful robotic control by leveraging vision-language models, but its reliance on large-scale, high-quality robot data limits its generalization. Generative world models offer a promising alternative for general-purpose embodied AI, yet a critical gap remains between their pixel-level plans and physically executable actions. To this end, we propose the Tool-Centric Inverse Dynamics Model (TC-IDM). By focusing on the tool's imagined trajectory as synthesized by the world model, TC-IDM establishes a robust intermediate representation that bridges the gap between visual planning and physical control. TC-IDM extracts the tool's point cloud trajectories via segmentation and 3D motion estimation from generated videos. Considering diverse tool attributes, our architecture employs decoupled action heads to project these planned trajectories into 6-DoF end-effector motions and corresponding control signals. This plan-and-translate paradigm not only supports a wide range of end-effectors but also significantly improves viewpoint invariance. Furthermore, it exhibits strong generalization capabilities across long-horizon and out-of-distribution tasks, including interacting with deformable objects. In real-world evaluations, the world model with TC-IDM achieves an average success rate of 61.11 percent, with 77.7 percent on simple tasks and 38.46 percent on zero-shot deformable object tasks. It substantially outperforms end-to-end VLA-style baselines and other inverse dynamics models.
Wow, wo, val! A Comprehensive Embodied World Model Evaluation Turing Test
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As world models gain momentum in Embodied AI, an increasing number of works explore using video foundation models as predictive world models for downstream embodied tasks like 3D prediction or interactive generation. However, before exploring these downstream tasks, video foundation models still have two critical questions unanswered: (1) whether their generative generalization is sufficient to maintain perceptual fidelity in the eyes of human observers, and (2) whether they are robust enough to serve as a universal prior for real-world embodied agents. To provide a standardized framework for answering these questions, we introduce the Embodied Turing Test benchmark: WoW-World-Eval (Wow,wo,val). Building upon 609 robot manipulation data, Wow-wo-val examines five core abilities, including perception, planning, prediction, generalization, and execution. We propose a comprehensive evaluation protocol with 22 metrics to assess the models' generation ability, which achieves a high Pearson Correlation between the overall score and human preference (>0.93) and establishes a reliable foundation for the Human Turing Test. On Wow-wo-val, models achieve only 17.27 on long-horizon planning and at best 68.02 on physical consistency, indicating limited spatiotemporal consistency and physical reasoning. For the Inverse Dynamic Model Turing Test, we first use an IDM to evaluate the video foundation models' execution accuracy in the real world. However, most models collapse to $\approx$ 0% success, while WoW maintains a 40.74% success rate. These findings point to a noticeable gap between the generated videos and the real world, highlighting the urgency and necessity of benchmarking World Model in Embodied AI.
RoboMIND 2.0: A Multimodal, Bimanual Mobile Manipulation Dataset for Generalizable Embodied Intelligence
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:While data-driven imitation learning has revolutionized robotic manipulation, current approaches remain constrained by the scarcity of large-scale, diverse real-world demonstrations. Consequently, the ability of existing models to generalize across long-horizon bimanual tasks and mobile manipulation in unstructured environments remains limited. To bridge this gap, we present RoboMIND 2.0, a comprehensive real-world dataset comprising over 310K dual-arm manipulation trajectories collected across six distinct robot embodiments and 739 complex tasks. Crucially, to support research in contact-rich and spatially extended tasks, the dataset incorporates 12K tactile-enhanced episodes and 20K mobile manipulation trajectories. Complementing this physical data, we construct high-fidelity digital twins of our real-world environments, releasing an additional 20K-trajectory simulated dataset to facilitate robust sim-to-real transfer. To fully exploit the potential of RoboMIND 2.0, we propose MIND-2 system, a hierarchical dual-system frame-work optimized via offline reinforcement learning. MIND-2 integrates a high-level semantic planner (MIND-2-VLM) to decompose abstract natural language instructions into grounded subgoals, coupled with a low-level Vision-Language-Action executor (MIND-2-VLA), which generates precise, proprioception-aware motor actions.
Real-world Reinforcement Learning from Suboptimal Interventions
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Real-world reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising approach to training precise and dexterous robotic manipulation policies in an online manner, enabling robots to learn from their own experience while gradually reducing human labor. However, prior real-world RL methods often assume that human interventions are optimal across the entire state space, overlooking the fact that even expert operators cannot consistently provide optimal actions in all states or completely avoid mistakes. Indiscriminately mixing intervention data with robot-collected data inherits the sample inefficiency of RL, while purely imitating intervention data can ultimately degrade the final performance achievable by RL. The question of how to leverage potentially suboptimal and noisy human interventions to accelerate learning without being constrained by them thus remains open. To address this challenge, we propose SiLRI, a state-wise Lagrangian reinforcement learning algorithm for real-world robot manipulation tasks. Specifically, we formulate the online manipulation problem as a constrained RL optimization, where the constraint bound at each state is determined by the uncertainty of human interventions. We then introduce a state-wise Lagrange multiplier and solve the problem via a min-max optimization, jointly optimizing the policy and the Lagrange multiplier to reach a saddle point. Built upon a human-as-copilot teleoperation system, our algorithm is evaluated through real-world experiments on diverse manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that SiLRI effectively exploits human suboptimal interventions, reducing the time required to reach a 90% success rate by at least 50% compared with the state-of-the-art RL method HIL-SERL, and achieving a 100% success rate on long-horizon manipulation tasks where other RL methods struggle to succeed. Project website: https://silri-rl.github.io/.
Contextual Biasing for LLM-Based ASR with Hotword Retrieval and Reinforcement Learning
Dec 26, 2025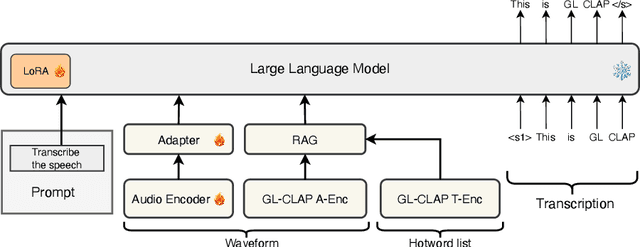
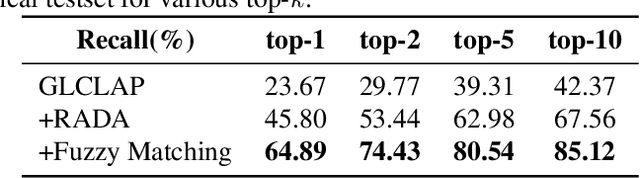
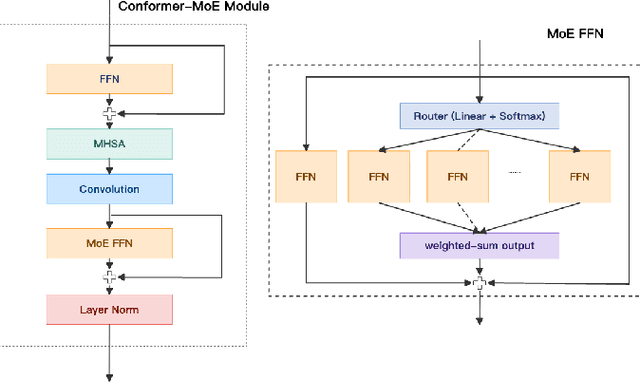
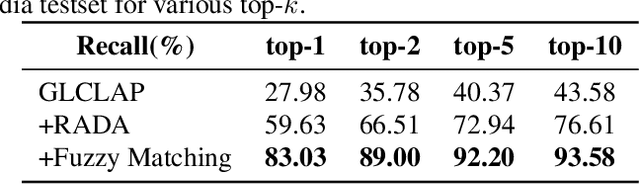
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) has recently achieved strong performance across diverse tasks, yet contextual biasing for named entities and hotwords under large vocabularies remains challenging. In this work, we propose a scalable two-stage framework that integrates hotword retrieval with LLM-ASR adaptation. First, we extend the Global-Local Contrastive Language-Audio pre-trained model (GLCLAP) to retrieve a compact top-k set of hotword candidates from a large vocabulary via robustness-aware data augmentation and fuzzy matching. Second, we inject the retrieved candidates as textual prompts into an LLM-ASR model and fine-tune it with Generative Rejection-Based Policy Optimization (GRPO), using a task-driven reward that jointly optimizes hotword recognition and overall transcription accuracy. Experiments on hotword-focused test sets show substantial keyword error rate (KER) reductions while maintaining sentence accuracy on general ASR benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed framework for large-vocabulary contextual biasing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge