Zhen Zhao
Farewell to Item IDs: Unlocking the Scaling Potential of Large Ranking Models via Semantic Tokens
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent studies on scaling up ranking models have achieved substantial improvement for recommendation systems and search engines. However, most large-scale ranking systems rely on item IDs, where each item is treated as an independent categorical symbol and mapped to a learned embedding. As items rapidly appear and disappear, these embeddings become difficult to train and maintain. This instability impedes effective learning of neural network parameters and limits the scalability of ranking models. In this paper, we show that semantic tokens possess greater scaling potential compared to item IDs. Our proposed framework TRM improves the token generation and application pipeline, leading to 33% reduction in sparse storage while achieving 0.85% AUC increase. Extensive experiments further show that TRM could consistently outperform state-of-the-art models when model capacity scales. Finally, TRM has been successfully deployed on large-scale personalized search engines, yielding 0.26% and 0.75% improvement on user active days and change query ratio respectively through A/B test.
RoboMIND 2.0: A Multimodal, Bimanual Mobile Manipulation Dataset for Generalizable Embodied Intelligence
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:While data-driven imitation learning has revolutionized robotic manipulation, current approaches remain constrained by the scarcity of large-scale, diverse real-world demonstrations. Consequently, the ability of existing models to generalize across long-horizon bimanual tasks and mobile manipulation in unstructured environments remains limited. To bridge this gap, we present RoboMIND 2.0, a comprehensive real-world dataset comprising over 310K dual-arm manipulation trajectories collected across six distinct robot embodiments and 739 complex tasks. Crucially, to support research in contact-rich and spatially extended tasks, the dataset incorporates 12K tactile-enhanced episodes and 20K mobile manipulation trajectories. Complementing this physical data, we construct high-fidelity digital twins of our real-world environments, releasing an additional 20K-trajectory simulated dataset to facilitate robust sim-to-real transfer. To fully exploit the potential of RoboMIND 2.0, we propose MIND-2 system, a hierarchical dual-system frame-work optimized via offline reinforcement learning. MIND-2 integrates a high-level semantic planner (MIND-2-VLM) to decompose abstract natural language instructions into grounded subgoals, coupled with a low-level Vision-Language-Action executor (MIND-2-VLA), which generates precise, proprioception-aware motor actions.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
Self-Supervised Multi-Part Articulated Objects Modeling via Deformable Gaussian Splatting and Progressive Primitive Segmentation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Articulated objects are ubiquitous in everyday life, and accurate 3D representations of their geometry and motion are critical for numerous applications. However, in the absence of human annotation, existing approaches still struggle to build a unified representation for objects that contain multiple movable parts. We introduce DeGSS, a unified framework that encodes articulated objects as deformable 3D Gaussian fields, embedding geometry, appearance, and motion in one compact representation. Each interaction state is modeled as a smooth deformation of a shared field, and the resulting deformation trajectories guide a progressive coarse-to-fine part segmentation that identifies distinct rigid components, all in an unsupervised manner. The refined field provides a spatially continuous, fully decoupled description of every part, supporting part-level reconstruction and precise modeling of their kinematic relationships. To evaluate generalization and realism, we enlarge the synthetic PartNet-Mobility benchmark and release RS-Art, a real-to-sim dataset that pairs RGB captures with accurately reverse-engineered 3D models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods in both accuracy and stability.
FreqPolicy: Efficient Flow-based Visuomotor Policy via Frequency Consistency
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Generative modeling-based visuomotor policies have been widely adopted in robotic manipulation attributed to their ability to model multimodal action distributions. However, the high inference cost of multi-step sampling limits their applicability in real-time robotic systems. To address this issue, existing approaches accelerate the sampling process in generative modeling-based visuomotor policies by adapting acceleration techniques originally developed for image generation. Despite this progress, a major distinction remains: image generation typically involves producing independent samples without temporal dependencies, whereas robotic manipulation involves generating time-series action trajectories that require continuity and temporal coherence. To effectively exploit temporal information in robotic manipulation, we propose FreqPolicy, a novel approach that first imposes frequency consistency constraints on flow-based visuomotor policies. Our work enables the action model to capture temporal structure effectively while supporting efficient, high-quality one-step action generation. We introduce a frequency consistency constraint that enforces alignment of frequency-domain action features across different timesteps along the flow, thereby promoting convergence of one-step action generation toward the target distribution. In addition, we design an adaptive consistency loss to capture structural temporal variations inherent in robotic manipulation tasks. We assess FreqPolicy on 53 tasks across 3 simulation benchmarks, proving its superiority over existing one-step action generators. We further integrate FreqPolicy into the vision-language-action (VLA) model and achieve acceleration without performance degradation on the 40 tasks of Libero. Besides, we show efficiency and effectiveness in real-world robotic scenarios with an inference frequency 93.5Hz. The code will be publicly available.
ArtVIP: Articulated Digital Assets of Visual Realism, Modular Interaction, and Physical Fidelity for Robot Learning
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Robot learning increasingly relies on simulation to advance complex ability such as dexterous manipulations and precise interactions, necessitating high-quality digital assets to bridge the sim-to-real gap. However, existing open-source articulated-object datasets for simulation are limited by insufficient visual realism and low physical fidelity, which hinder their utility for training models mastering robotic tasks in real world. To address these challenges, we introduce ArtVIP, a comprehensive open-source dataset comprising high-quality digital-twin articulated objects, accompanied by indoor-scene assets. Crafted by professional 3D modelers adhering to unified standards, ArtVIP ensures visual realism through precise geometric meshes and high-resolution textures, while physical fidelity is achieved via fine-tuned dynamic parameters. Meanwhile, the dataset pioneers embedded modular interaction behaviors within assets and pixel-level affordance annotations. Feature-map visualization and optical motion capture are employed to quantitatively demonstrate ArtVIP's visual and physical fidelity, with its applicability validated across imitation learning and reinforcement learning experiments. Provided in USD format with detailed production guidelines, ArtVIP is fully open-source, benefiting the research community and advancing robot learning research. Our project is at https://x-humanoid-artvip.github.io/ .
SenseFlow: A Physics-Informed and Self-Ensembling Iterative Framework for Power Flow Estimation
May 18, 2025Abstract:Power flow estimation plays a vital role in ensuring the stability and reliability of electrical power systems, particularly in the context of growing network complexities and renewable energy integration. However, existing studies often fail to adequately address the unique characteristics of power systems, such as the sparsity of network connections and the critical importance of the unique Slack node, which poses significant challenges in achieving high-accuracy estimations. In this paper, we present SenseFlow, a novel physics-informed and self-ensembling iterative framework that integrates two main designs, the Physics-Informed Power Flow Network (FlowNet) and Self-Ensembling Iterative Estimation (SeIter), to carefully address the unique properties of the power system and thereby enhance the power flow estimation. Specifically, SenseFlow enforces the FlowNet to gradually predict high-precision voltage magnitudes and phase angles through the iterative SeIter process. On the one hand, FlowNet employs the Virtual Node Attention and Slack-Gated Feed-Forward modules to facilitate efficient global-local communication in the face of network sparsity and amplify the influence of the Slack node on angle predictions, respectively. On the other hand, SeIter maintains an exponential moving average of FlowNet's parameters to create a robust ensemble model that refines power state predictions throughout the iterative fitting process. Experimental results demonstrate that SenseFlow outperforms existing methods, providing a promising solution for high-accuracy power flow estimation across diverse grid configurations.
DiN: Diffusion Model for Robust Medical VQA with Semantic Noisy Labels
Mar 24, 2025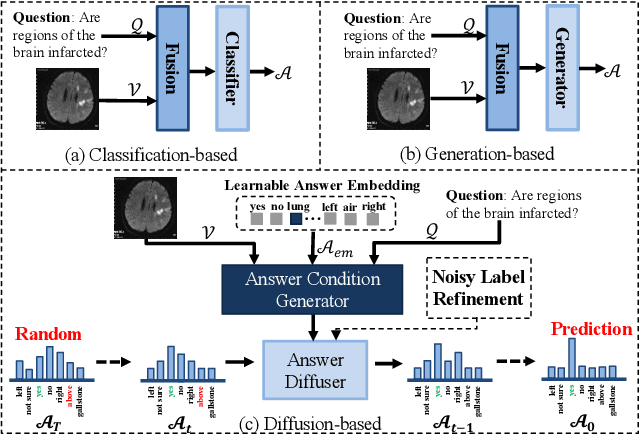
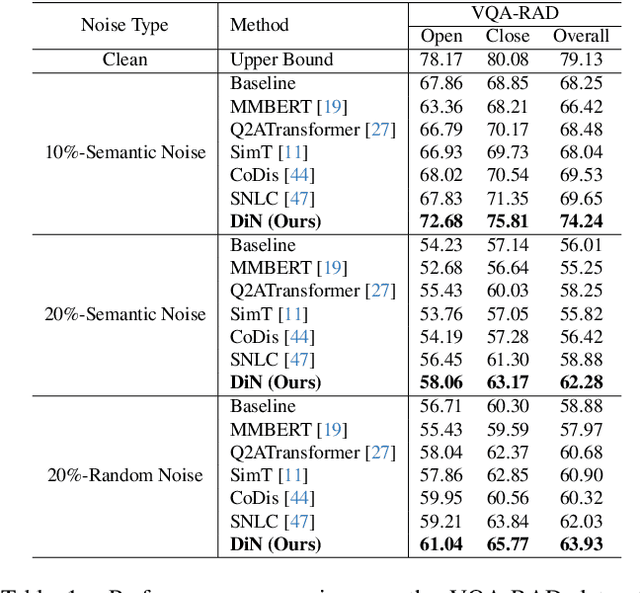
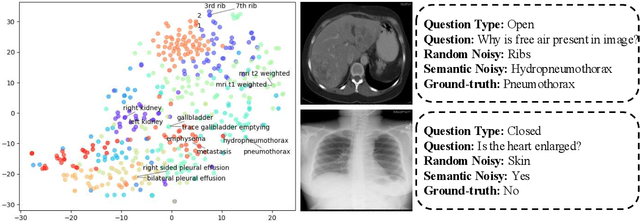
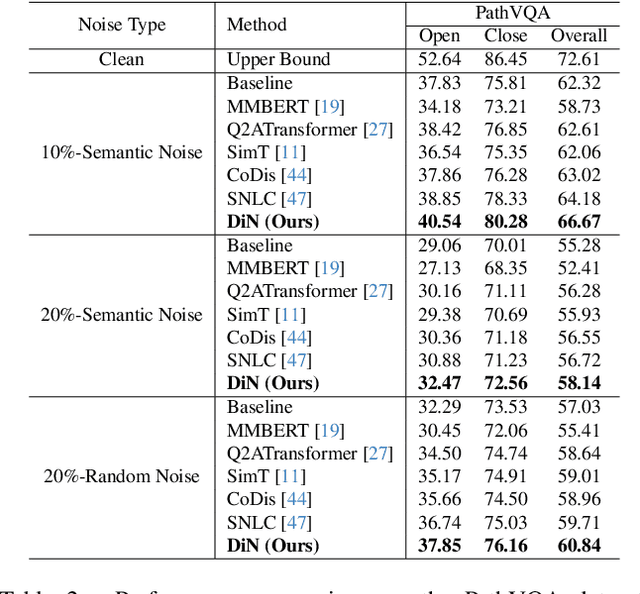
Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) systems benefit the interpretation of medical images containing critical clinical information. However, the challenge of noisy labels and limited high-quality datasets remains underexplored. To address this, we establish the first benchmark for noisy labels in Med-VQA by simulating human mislabeling with semantically designed noise types. More importantly, we introduce the DiN framework, which leverages a diffusion model to handle noisy labels in Med-VQA. Unlike the dominant classification-based VQA approaches that directly predict answers, our Answer Diffuser (AD) module employs a coarse-to-fine process, refining answer candidates with a diffusion model for improved accuracy. The Answer Condition Generator (ACG) further enhances this process by generating task-specific conditional information via integrating answer embeddings with fused image-question features. To address label noise, our Noisy Label Refinement(NLR) module introduces a robust loss function and dynamic answer adjustment to further boost the performance of the AD module.
TimeKAN: KAN-based Frequency Decomposition Learning Architecture for Long-term Time Series Forecasting
Feb 10, 2025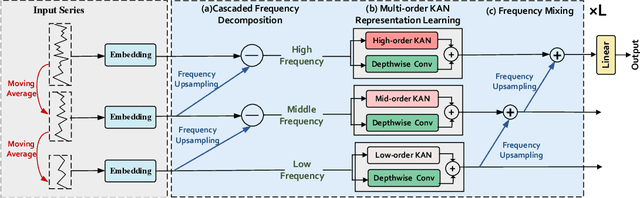



Abstract:Real-world time series often have multiple frequency components that are intertwined with each other, making accurate time series forecasting challenging. Decomposing the mixed frequency components into multiple single frequency components is a natural choice. However, the information density of patterns varies across different frequencies, and employing a uniform modeling approach for different frequency components can lead to inaccurate characterization. To address this challenges, inspired by the flexibility of the recent Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN), we propose a KAN-based Frequency Decomposition Learning architecture (TimeKAN) to address the complex forecasting challenges caused by multiple frequency mixtures. Specifically, TimeKAN mainly consists of three components: Cascaded Frequency Decomposition (CFD) blocks, Multi-order KAN Representation Learning (M-KAN) blocks and Frequency Mixing blocks. CFD blocks adopt a bottom-up cascading approach to obtain series representations for each frequency band. Benefiting from the high flexibility of KAN, we design a novel M-KAN block to learn and represent specific temporal patterns within each frequency band. Finally, Frequency Mixing blocks is used to recombine the frequency bands into the original format. Extensive experimental results across multiple real-world time series datasets demonstrate that TimeKAN achieves state-of-the-art performance as an extremely lightweight architecture. Code is available at https://github.com/huangst21/TimeKAN.
Imbalanced Medical Image Segmentation with Pixel-dependent Noisy Labels
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:Accurate medical image segmentation is often hindered by noisy labels in training data, due to the challenges of annotating medical images. Prior research works addressing noisy labels tend to make class-dependent assumptions, overlooking the pixel-dependent nature of most noisy labels. Furthermore, existing methods typically apply fixed thresholds to filter out noisy labels, risking the removal of minority classes and consequently degrading segmentation performance. To bridge these gaps, our proposed framework, Collaborative Learning with Curriculum Selection (CLCS), addresses pixel-dependent noisy labels with class imbalance. CLCS advances the existing works by i) treating noisy labels as pixel-dependent and addressing them through a collaborative learning framework, and ii) employing a curriculum dynamic thresholding approach adapting to model learning progress to select clean data samples to mitigate the class imbalance issue, and iii) applying a noise balance loss to noisy data samples to improve data utilization instead of discarding them outright. Specifically, our CLCS contains two modules: Curriculum Noisy Label Sample Selection (CNS) and Noise Balance Loss (NBL). In the CNS module, we designed a two-branch network with discrepancy loss for collaborative learning so that different feature representations of the same instance could be extracted from distinct views and used to vote the class probabilities of pixels. Besides, a curriculum dynamic threshold is adopted to select clean-label samples through probability voting. In the NBL module, instead of directly dropping the suspiciously noisy labels, we further adopt a robust loss to leverage such instances to boost the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge