Yuang Wang
Projection Embedded Diffusion Bridge for CT Reconstruction from Incomplete Data
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing CT images from incomplete projection data remains challenging due to the ill-posed nature of the problem. Diffusion bridge models have recently shown promise in restoring clean images from their corresponding Filtered Back Projection (FBP) reconstructions, but incorporating data consistency into these models remains largely underexplored. Incorporating data consistency can improve reconstruction fidelity by aligning the reconstructed image with the observed projection data, and can enhance detail recovery by integrating structural information contained in the projections. In this work, we propose the Projection Embedded Diffusion Bridge (PEDB). PEDB introduces a novel reverse stochastic differential equation (SDE) to sample from the distribution of clean images conditioned on both the FBP reconstruction and the incomplete projection data. By explicitly conditioning on the projection data in sampling the clean images, PEDB naturally incorporates data consistency. We embed the projection data into the score function of the reverse SDE. Under certain assumptions, we derive a tractable expression for the posterior score. In addition, we introduce a free parameter to control the level of stochasticity in the reverse process. We also design a discretization scheme for the reverse SDE to mitigate discretization error. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PEDB achieves strong performance in CT reconstruction from three types of incomplete data, including sparse-view, limited-angle, and truncated projections. For each of these types, PEDB outperforms evaluated state-of-the-art diffusion bridge models across standard, noisy, and domain-shift evaluations.
An Ordinary Differential Equation Sampler with Stochastic Start for Diffusion Bridge Models
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion bridge models have demonstrated promising performance in conditional image generation tasks, such as image restoration and translation, by initializing the generative process from corrupted images instead of pure Gaussian noise. However, existing diffusion bridge models often rely on Stochastic Differential Equation (SDE) samplers, which result in slower inference speed compared to diffusion models that employ high-order Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) solvers for acceleration. To mitigate this gap, we propose a high-order ODE sampler with a stochastic start for diffusion bridge models. To overcome the singular behavior of the probability flow ODE (PF-ODE) at the beginning of the reverse process, a posterior sampling approach was introduced at the first reverse step. The sampling was designed to ensure a smooth transition from corrupted images to the generative trajectory while reducing discretization errors. Following this stochastic start, Heun's second-order solver is applied to solve the PF-ODE, achieving high perceptual quality with significantly reduced neural function evaluations (NFEs). Our method is fully compatible with pretrained diffusion bridge models and requires no additional training. Extensive experiments on image restoration and translation tasks, including super-resolution, JPEG restoration, Edges-to-Handbags, and DIODE-Outdoor, demonstrated that our sampler outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual quality and Frechet Inception Distance (FID).
Implicit Image-to-Image Schrodinger Bridge for CT Super-Resolution and Denoising
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:Conditional diffusion models have gained recognition for their effectiveness in image restoration tasks, yet their iterative denoising process, starting from Gaussian noise, often leads to slow inference speeds. As a promising alternative, the Image-to-Image Schr\"odinger Bridge (I2SB) initializes the generative process from corrupted images and integrates training techniques from conditional diffusion models. In this study, we extended the I2SB method by introducing the Implicit Image-to-Image Schrodinger Bridge (I3SB), transitioning its generative process to a non-Markovian process by incorporating corrupted images in each generative step. This enhancement empowers I3SB to generate images with better texture restoration using a small number of generative steps. The proposed method was validated on CT super-resolution and denoising tasks and outperformed existing methods, including the conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (cDDPM) and I2SB, in both visual quality and quantitative metrics. These findings underscore the potential of I3SB in improving medical image restoration by providing fast and accurate generative modeling.
SAM-guided Graph Cut for 3D Instance Segmentation
Dec 25, 2023



Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of 3D instance segmentation by simultaneously leveraging 3D geometric and multi-view image information. Many previous works have applied deep learning techniques to 3D point clouds for instance segmentation. However, these methods often failed to generalize to various types of scenes due to the scarcity and low-diversity of labeled 3D point cloud data. Some recent works have attempted to lift 2D instance segmentations to 3D within a bottom-up framework. The inconsistency in 2D instance segmentations among views can substantially degrade the performance of 3D segmentation. In this work, we introduce a novel 3D-to-2D query framework to effectively exploit 2D segmentation models for 3D instance segmentation. Specifically, we pre-segment the scene into several superpoints in 3D, formulating the task into a graph cut problem. The superpoint graph is constructed based on 2D segmentation models, where node features are obtained from multi-view image features and edge weights are computed based on multi-view segmentation results, enabling the better generalization ability. To process the graph, we train a graph neural network using pseudo 3D labels from 2D segmentation models. Experimental results on the ScanNet, ScanNet++ and KITTI-360 datasets demonstrate that our method achieves robust segmentation performance and can generalize across different types of scenes. Our project page is available at https://zju3dv.github.io/sam_graph.
AutoRecon: Automated 3D Object Discovery and Reconstruction
May 15, 2023Abstract:A fully automated object reconstruction pipeline is crucial for digital content creation. While the area of 3D reconstruction has witnessed profound developments, the removal of background to obtain a clean object model still relies on different forms of manual labor, such as bounding box labeling, mask annotations, and mesh manipulations. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named AutoRecon for the automated discovery and reconstruction of an object from multi-view images. We demonstrate that foreground objects can be robustly located and segmented from SfM point clouds by leveraging self-supervised 2D vision transformer features. Then, we reconstruct decomposed neural scene representations with dense supervision provided by the decomposed point clouds, resulting in accurate object reconstruction and segmentation. Experiments on the DTU, BlendedMVS and CO3D-V2 datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of AutoRecon.
OnePose++: Keypoint-Free One-Shot Object Pose Estimation without CAD Models
Jan 18, 2023

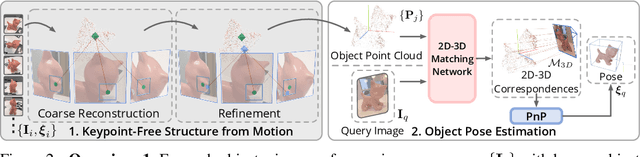

Abstract:We propose a new method for object pose estimation without CAD models. The previous feature-matching-based method OnePose has shown promising results under a one-shot setting which eliminates the need for CAD models or object-specific training. However, OnePose relies on detecting repeatable image keypoints and is thus prone to failure on low-textured objects. We propose a keypoint-free pose estimation pipeline to remove the need for repeatable keypoint detection. Built upon the detector-free feature matching method LoFTR, we devise a new keypoint-free SfM method to reconstruct a semi-dense point-cloud model for the object. Given a query image for object pose estimation, a 2D-3D matching network directly establishes 2D-3D correspondences between the query image and the reconstructed point-cloud model without first detecting keypoints in the image. Experiments show that the proposed pipeline outperforms existing one-shot CAD-model-free methods by a large margin and is comparable to CAD-model-based methods on LINEMOD even for low-textured objects. We also collect a new dataset composed of 80 sequences of 40 low-textured objects to facilitate future research on one-shot object pose estimation. The supplementary material, code and dataset are available on the project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/onepose_plus_plus/.
LoFTR: Detector-Free Local Feature Matching with Transformers
Apr 01, 2021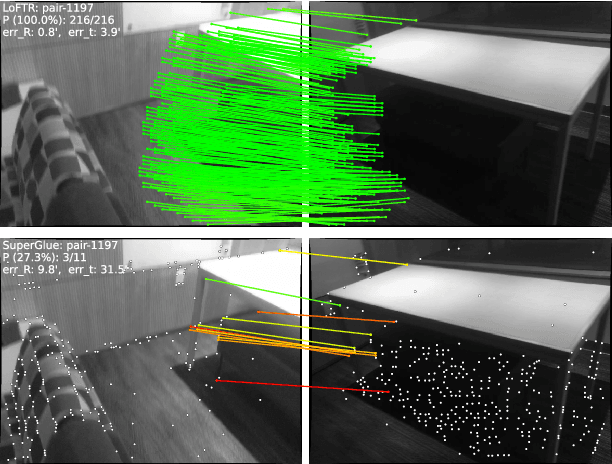
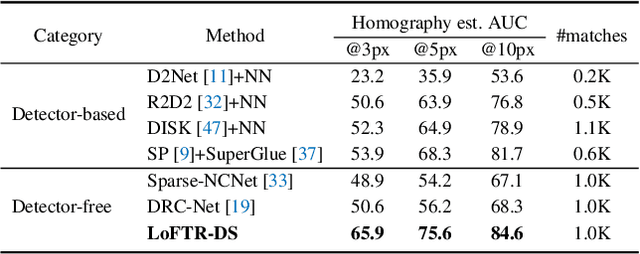
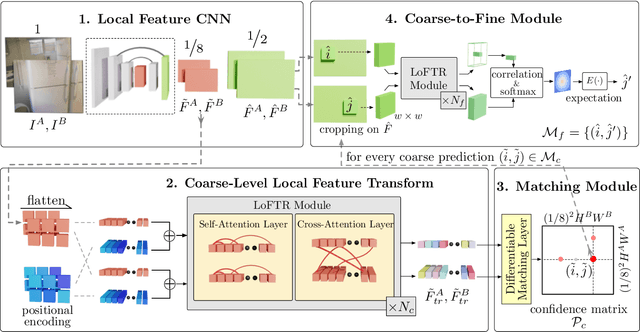
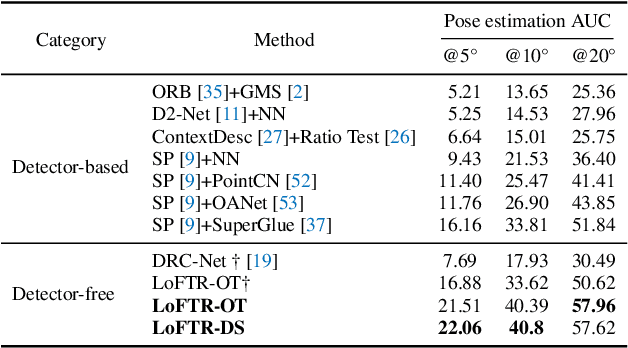
Abstract:We present a novel method for local image feature matching. Instead of performing image feature detection, description, and matching sequentially, we propose to first establish pixel-wise dense matches at a coarse level and later refine the good matches at a fine level. In contrast to dense methods that use a cost volume to search correspondences, we use self and cross attention layers in Transformer to obtain feature descriptors that are conditioned on both images. The global receptive field provided by Transformer enables our method to produce dense matches in low-texture areas, where feature detectors usually struggle to produce repeatable interest points. The experiments on indoor and outdoor datasets show that LoFTR outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. LoFTR also ranks first on two public benchmarks of visual localization among the published methods.
Adaptive and Azimuth-Aware Fusion Network of Multimodal Local Features for 3D Object Detection
Oct 10, 2019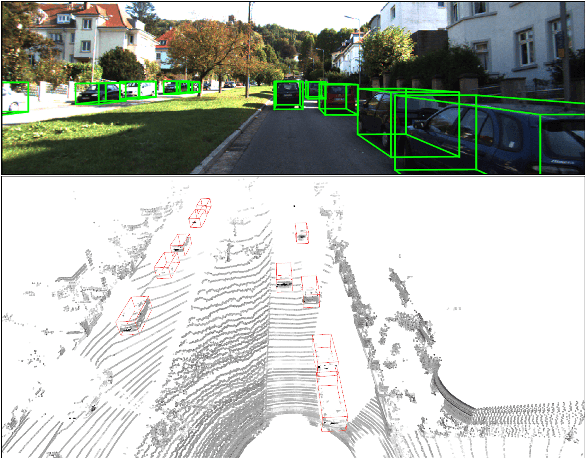

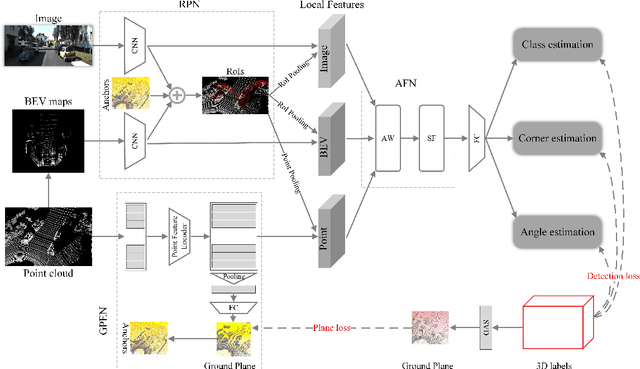

Abstract:This paper focuses on the construction of stronger local features and the effective fusion of image and LiDAR data. We adopt different modalities of LiDAR data to generate richer features and present an adaptive and azimuth-aware network to aggregate local features from image, bird's eye view maps and point cloud. Our network mainly consists of three subnetworks: ground plane estimation network, region proposal network and adaptive fusion network. The ground plane estimation network extracts features of point cloud and predicts the parameters of a plane which are used for generating abundant 3D anchors. The region proposal network generates features of image and bird's eye view maps to output region proposals. To integrate heterogeneous image and point cloud features, the adaptive fusion network explicitly adjusts the intensity of multiple local features and achieves the orientation consistency between image and LiDAR data by introduce an azimuth-aware fusion module. Experiments are conducted on KITTI dataset and the results validate the advantages of our aggregation of multimodal local features and the adaptive fusion network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge