Chen Geng
Choreographing a World of Dynamic Objects
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Dynamic objects in our physical 4D (3D + time) world are constantly evolving, deforming, and interacting with other objects, leading to diverse 4D scene dynamics. In this paper, we present a universal generative pipeline, CHORD, for CHOReographing Dynamic objects and scenes and synthesizing this type of phenomena. Traditional rule-based graphics pipelines to create these dynamics are based on category-specific heuristics, yet are labor-intensive and not scalable. Recent learning-based methods typically demand large-scale datasets, which may not cover all object categories in interest. Our approach instead inherits the universality from the video generative models by proposing a distillation-based pipeline to extract the rich Lagrangian motion information hidden in the Eulerian representations of 2D videos. Our method is universal, versatile, and category-agnostic. We demonstrate its effectiveness by conducting experiments to generate a diverse range of multi-body 4D dynamics, show its advantage compared to existing methods, and demonstrate its applicability in generating robotics manipulation policies. Project page: https://yanzhelyu.github.io/chord
ART: Articulated Reconstruction Transformer
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:We introduce ART, Articulated Reconstruction Transformer -- a category-agnostic, feed-forward model that reconstructs complete 3D articulated objects from only sparse, multi-state RGB images. Previous methods for articulated object reconstruction either rely on slow optimization with fragile cross-state correspondences or use feed-forward models limited to specific object categories. In contrast, ART treats articulated objects as assemblies of rigid parts, formulating reconstruction as part-based prediction. Our newly designed transformer architecture maps sparse image inputs to a set of learnable part slots, from which ART jointly decodes unified representations for individual parts, including their 3D geometry, texture, and explicit articulation parameters. The resulting reconstructions are physically interpretable and readily exportable for simulation. Trained on a large-scale, diverse dataset with per-part supervision, and evaluated across diverse benchmarks, ART achieves significant improvements over existing baselines and establishes a new state of the art for articulated object reconstruction from image inputs.
Coupled Diffusion Sampling for Training-Free Multi-View Image Editing
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:We present an inference-time diffusion sampling method to perform multi-view consistent image editing using pre-trained 2D image editing models. These models can independently produce high-quality edits for each image in a set of multi-view images of a 3D scene or object, but they do not maintain consistency across views. Existing approaches typically address this by optimizing over explicit 3D representations, but they suffer from a lengthy optimization process and instability under sparse view settings. We propose an implicit 3D regularization approach by constraining the generated 2D image sequences to adhere to a pre-trained multi-view image distribution. This is achieved through coupled diffusion sampling, a simple diffusion sampling technique that concurrently samples two trajectories from both a multi-view image distribution and a 2D edited image distribution, using a coupling term to enforce the multi-view consistency among the generated images. We validate the effectiveness and generality of this framework on three distinct multi-view image editing tasks, demonstrating its applicability across various model architectures and highlighting its potential as a general solution for multi-view consistent editing.
Category-Agnostic Neural Object Rigging
May 26, 2025Abstract:The motion of deformable 4D objects lies in a low-dimensional manifold. To better capture the low dimensionality and enable better controllability, traditional methods have devised several heuristic-based methods, i.e., rigging, for manipulating dynamic objects in an intuitive fashion. However, such representations are not scalable due to the need for expert knowledge of specific categories. Instead, we study the automatic exploration of such low-dimensional structures in a purely data-driven manner. Specifically, we design a novel representation that encodes deformable 4D objects into a sparse set of spatially grounded blobs and an instance-aware feature volume to disentangle the pose and instance information of the 3D shape. With such a representation, we can manipulate the pose of 3D objects intuitively by modifying the parameters of the blobs, while preserving rich instance-specific information. We evaluate the proposed method on a variety of object categories and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Project page: https://guangzhaohe.com/canor
Anymate: A Dataset and Baselines for Learning 3D Object Rigging
May 09, 2025Abstract:Rigging and skinning are essential steps to create realistic 3D animations, often requiring significant expertise and manual effort. Traditional attempts at automating these processes rely heavily on geometric heuristics and often struggle with objects of complex geometry. Recent data-driven approaches show potential for better generality, but are often constrained by limited training data. We present the Anymate Dataset, a large-scale dataset of 230K 3D assets paired with expert-crafted rigging and skinning information -- 70 times larger than existing datasets. Using this dataset, we propose a learning-based auto-rigging framework with three sequential modules for joint, connectivity, and skinning weight prediction. We systematically design and experiment with various architectures as baselines for each module and conduct comprehensive evaluations on our dataset to compare their performance. Our models significantly outperform existing methods, providing a foundation for comparing future methods in automated rigging and skinning. Code and dataset can be found at https://anymate3d.github.io/.
Birth and Death of a Rose
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:We study the problem of generating temporal object intrinsics -- temporally evolving sequences of object geometry, reflectance, and texture, such as a blooming rose -- from pre-trained 2D foundation models. Unlike conventional 3D modeling and animation techniques that require extensive manual effort and expertise, we introduce a method that generates such assets with signals distilled from pre-trained 2D diffusion models. To ensure the temporal consistency of object intrinsics, we propose Neural Templates for temporal-state-guided distillation, derived automatically from image features from self-supervised learning. Our method can generate high-quality temporal object intrinsics for several natural phenomena and enable the sampling and controllable rendering of these dynamic objects from any viewpoint, under any environmental lighting conditions, at any time of their lifespan. Project website: https://chen-geng.com/rose4d
Tree-Structured Shading Decomposition
Sep 13, 2023

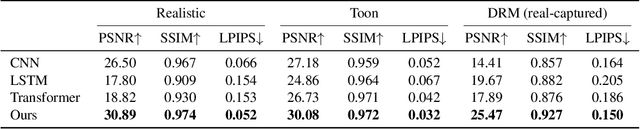
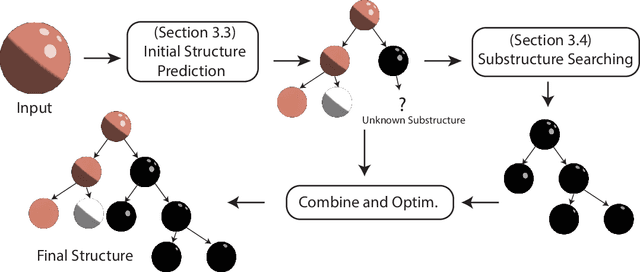
Abstract:We study inferring a tree-structured representation from a single image for object shading. Prior work typically uses the parametric or measured representation to model shading, which is neither interpretable nor easily editable. We propose using the shade tree representation, which combines basic shading nodes and compositing methods to factorize object surface shading. The shade tree representation enables novice users who are unfamiliar with the physical shading process to edit object shading in an efficient and intuitive manner. A main challenge in inferring the shade tree is that the inference problem involves both the discrete tree structure and the continuous parameters of the tree nodes. We propose a hybrid approach to address this issue. We introduce an auto-regressive inference model to generate a rough estimation of the tree structure and node parameters, and then we fine-tune the inferred shade tree through an optimization algorithm. We show experiments on synthetic images, captured reflectance, real images, and non-realistic vector drawings, allowing downstream applications such as material editing, vectorized shading, and relighting. Project website: https://chen-geng.com/inv-shade-trees
Relightable and Animatable Neural Avatar from Sparse-View Video
Aug 17, 2023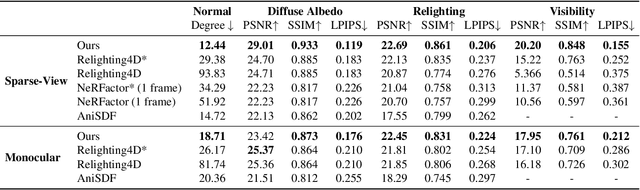
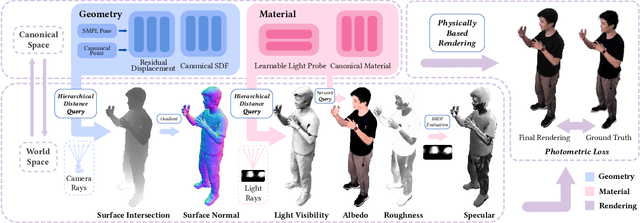
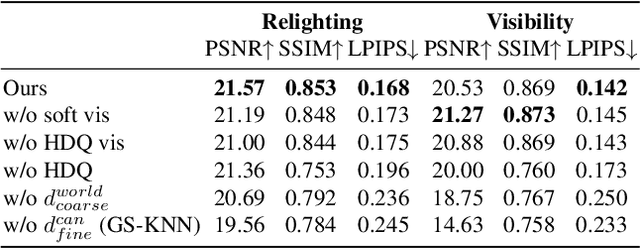
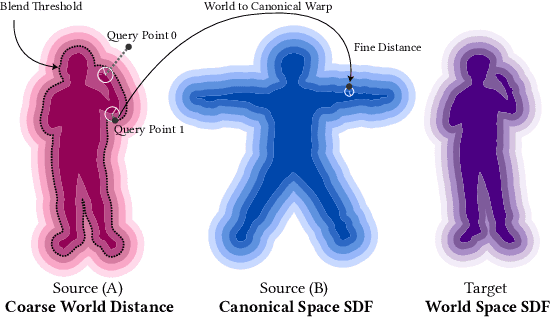
Abstract:This paper tackles the challenge of creating relightable and animatable neural avatars from sparse-view (or even monocular) videos of dynamic humans under unknown illumination. Compared to studio environments, this setting is more practical and accessible but poses an extremely challenging ill-posed problem. Previous neural human reconstruction methods are able to reconstruct animatable avatars from sparse views using deformed Signed Distance Fields (SDF) but cannot recover material parameters for relighting. While differentiable inverse rendering-based methods have succeeded in material recovery of static objects, it is not straightforward to extend them to dynamic humans as it is computationally intensive to compute pixel-surface intersection and light visibility on deformed SDFs for inverse rendering. To solve this challenge, we propose a Hierarchical Distance Query (HDQ) algorithm to approximate the world space distances under arbitrary human poses. Specifically, we estimate coarse distances based on a parametric human model and compute fine distances by exploiting the local deformation invariance of SDF. Based on the HDQ algorithm, we leverage sphere tracing to efficiently estimate the surface intersection and light visibility. This allows us to develop the first system to recover animatable and relightable neural avatars from sparse view (or monocular) inputs. Experiments demonstrate that our approach is able to produce superior results compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be released for reproducibility.
Learning Neural Volumetric Representations of Dynamic Humans in Minutes
Feb 24, 2023Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of quickly reconstructing free-viewpoint videos of dynamic humans from sparse multi-view videos. Some recent works represent the dynamic human as a canonical neural radiance field (NeRF) and a motion field, which are learned from videos through differentiable rendering. But the per-scene optimization generally requires hours. Other generalizable NeRF models leverage learned prior from datasets and reduce the optimization time by only finetuning on new scenes at the cost of visual fidelity. In this paper, we propose a novel method for learning neural volumetric videos of dynamic humans from sparse view videos in minutes with competitive visual quality. Specifically, we define a novel part-based voxelized human representation to better distribute the representational power of the network to different human parts. Furthermore, we propose a novel 2D motion parameterization scheme to increase the convergence rate of deformation field learning. Experiments demonstrate that our model can be learned 100 times faster than prior per-scene optimization methods while being competitive in the rendering quality. Training our model on a $512 \times 512$ video with 100 frames typically takes about 5 minutes on a single RTX 3090 GPU. The code will be released on our project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/instant_nvr
Animatable Neural Implicit Surfaces for Creating Avatars from Videos
Mar 15, 2022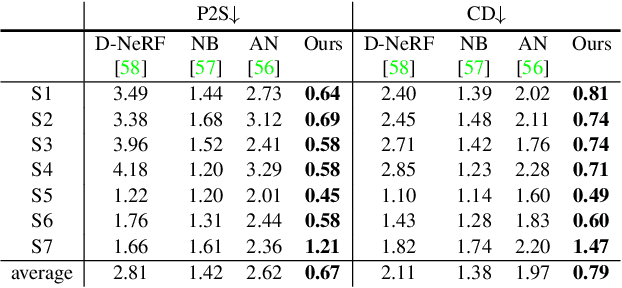
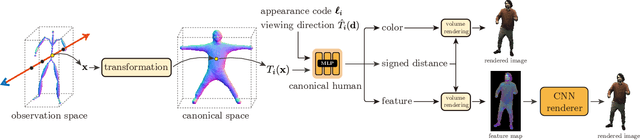
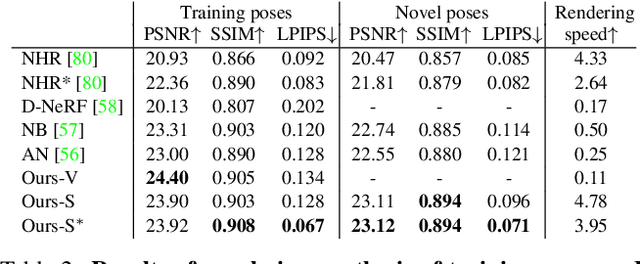
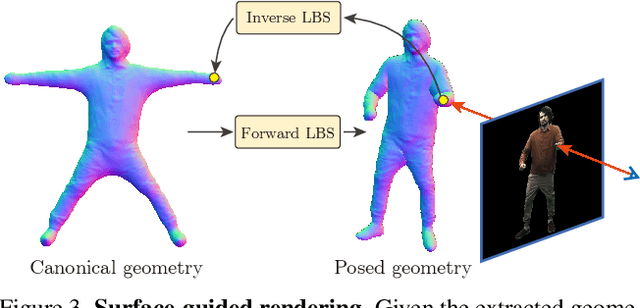
Abstract:This paper aims to reconstruct an animatable human model from a video of very sparse camera views. Some recent works represent human geometry and appearance with neural radiance fields and utilize parametric human models to produce deformation fields for animation, which enables them to recover detailed 3D human models from videos. However, their reconstruction results tend to be noisy due to the lack of surface constraints on radiance fields. Moreover, as they generate the human appearance in 3D space, their rendering quality heavily depends on the accuracy of deformation fields. To solve these problems, we propose Animatable Neural Implicit Surface (AniSDF), which models the human geometry with a signed distance field and defers the appearance generation to the 2D image space with a 2D neural renderer. The signed distance field naturally regularizes the learned geometry, enabling the high-quality reconstruction of human bodies, which can be further used to improve the rendering speed. Moreover, the 2D neural renderer can be learned to compensate for geometric errors, making the rendering more robust to inaccurate deformations. Experiments on several datasets show that the proposed approach outperforms recent human reconstruction and synthesis methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge