Dongdong Wang
Multimodal Human-AI Synergy for Medical Imaging Quality Control: A Hybrid Intelligence Framework with Adaptive Dataset Curation and Closed-Loop Evaluation
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Medical imaging quality control (QC) is essential for accurate diagnosis, yet traditional QC methods remain labor-intensive and subjective. To address this challenge, in this study, we establish a standardized dataset and evaluation framework for medical imaging QC, systematically assessing large language models (LLMs) in image quality assessment and report standardization. Specifically, we first constructed and anonymized a dataset of 161 chest X-ray (CXR) radiographs and 219 CT reports for evaluation. Then, multiple LLMs, including Gemini 2.0-Flash, GPT-4o, and DeepSeek-R1, were evaluated based on recall, precision, and F1 score to detect technical errors and inconsistencies. Experimental results show that Gemini 2.0-Flash achieved a Macro F1 score of 90 in CXR tasks, demonstrating strong generalization but limited fine-grained performance. DeepSeek-R1 excelled in CT report auditing with a 62.23\% recall rate, outperforming other models. However, its distilled variants performed poorly, while InternLM2.5-7B-chat exhibited the highest additional discovery rate, indicating broader but less precise error detection. These findings highlight the potential of LLMs in medical imaging QC, with DeepSeek-R1 and Gemini 2.0-Flash demonstrating superior performance.
Video-to-Text Pedestrian Monitoring (VTPM): Leveraging Computer Vision and Large Language Models for Privacy-Preserve Pedestrian Activity Monitoring at Intersections
Aug 21, 2024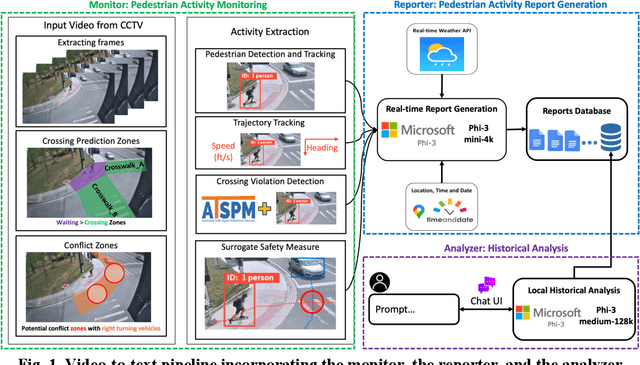
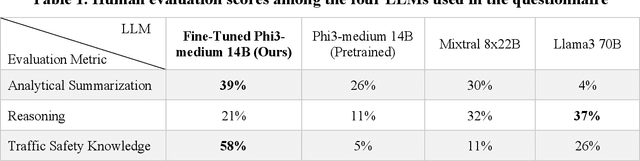
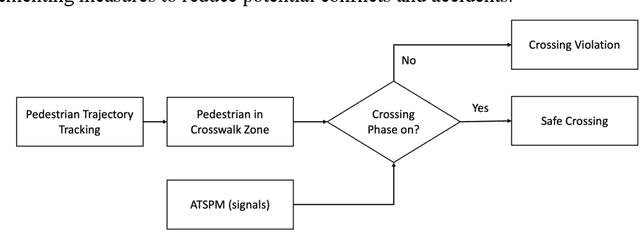
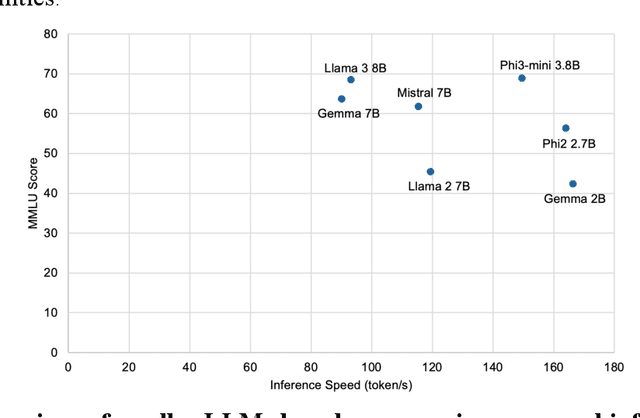
Abstract:Computer vision has advanced research methodologies, enhancing system services across various fields. It is a core component in traffic monitoring systems for improving road safety; however, these monitoring systems don't preserve the privacy of pedestrians who appear in the videos, potentially revealing their identities. Addressing this issue, our paper introduces Video-to-Text Pedestrian Monitoring (VTPM), which monitors pedestrian movements at intersections and generates real-time textual reports, including traffic signal and weather information. VTPM uses computer vision models for pedestrian detection and tracking, achieving a latency of 0.05 seconds per video frame. Additionally, it detects crossing violations with 90.2% accuracy by incorporating traffic signal data. The proposed framework is equipped with Phi-3 mini-4k to generate real-time textual reports of pedestrian activity while stating safety concerns like crossing violations, conflicts, and the impact of weather on their behavior with latency of 0.33 seconds. To enhance comprehensive analysis of the generated textual reports, Phi-3 medium is fine-tuned for historical analysis of these generated textual reports. This fine-tuning enables more reliable analysis about the pedestrian safety at intersections, effectively detecting patterns and safety critical events. The proposed VTPM offers a more efficient alternative to video footage by using textual reports reducing memory usage, saving up to 253 million percent, eliminating privacy issues, and enabling comprehensive interactive historical analysis.
Hunyuan-DiT: A Powerful Multi-Resolution Diffusion Transformer with Fine-Grained Chinese Understanding
May 14, 2024



Abstract:We present Hunyuan-DiT, a text-to-image diffusion transformer with fine-grained understanding of both English and Chinese. To construct Hunyuan-DiT, we carefully design the transformer structure, text encoder, and positional encoding. We also build from scratch a whole data pipeline to update and evaluate data for iterative model optimization. For fine-grained language understanding, we train a Multimodal Large Language Model to refine the captions of the images. Finally, Hunyuan-DiT can perform multi-turn multimodal dialogue with users, generating and refining images according to the context. Through our holistic human evaluation protocol with more than 50 professional human evaluators, Hunyuan-DiT sets a new state-of-the-art in Chinese-to-image generation compared with other open-source models. Code and pretrained models are publicly available at github.com/Tencent/HunyuanDiT
Perturbing Attention Gives You More Bang for the Buck: Subtle Imaging Perturbations That Efficiently Fool Customized Diffusion Models
Apr 23, 2024

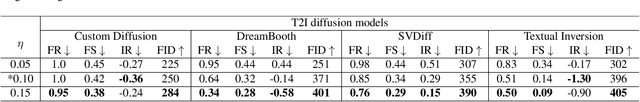
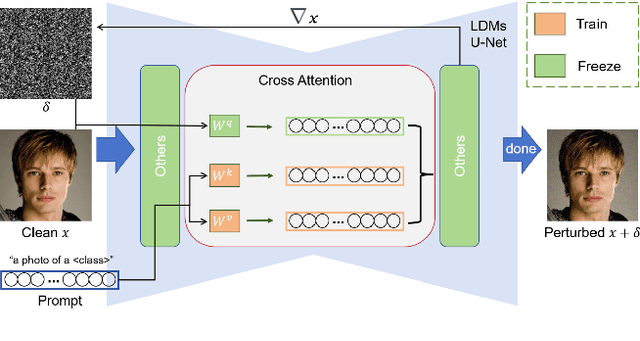
Abstract:Diffusion models (DMs) embark a new era of generative modeling and offer more opportunities for efficient generating high-quality and realistic data samples. However, their widespread use has also brought forth new challenges in model security, which motivates the creation of more effective adversarial attackers on DMs to understand its vulnerability. We propose CAAT, a simple but generic and efficient approach that does not require costly training to effectively fool latent diffusion models (LDMs). The approach is based on the observation that cross-attention layers exhibits higher sensitivity to gradient change, allowing for leveraging subtle perturbations on published images to significantly corrupt the generated images. We show that a subtle perturbation on an image can significantly impact the cross-attention layers, thus changing the mapping between text and image during the fine-tuning of customized diffusion models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CAAT is compatible with diverse diffusion models and outperforms baseline attack methods in a more effective (more noise) and efficient (twice as fast as Anti-DreamBooth and Mist) manner.
Enhancing Traffic Safety with Parallel Dense Video Captioning for End-to-End Event Analysis
Apr 12, 2024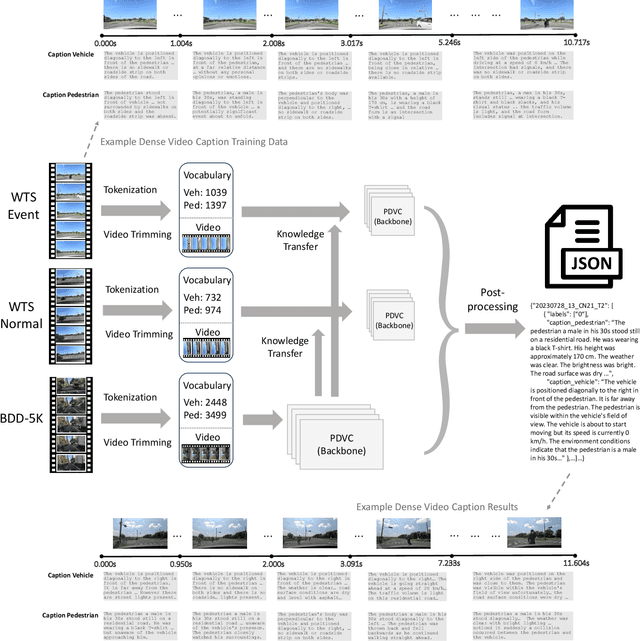
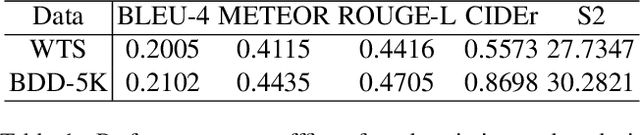

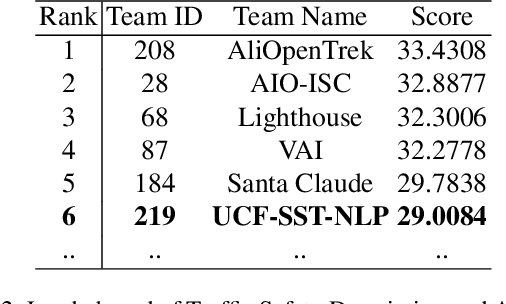
Abstract:This paper introduces our solution for Track 2 in AI City Challenge 2024. The task aims to solve traffic safety description and analysis with the dataset of Woven Traffic Safety (WTS), a real-world Pedestrian-Centric Traffic Video Dataset for Fine-grained Spatial-Temporal Understanding. Our solution mainly focuses on the following points: 1) To solve dense video captioning, we leverage the framework of dense video captioning with parallel decoding (PDVC) to model visual-language sequences and generate dense caption by chapters for video. 2) Our work leverages CLIP to extract visual features to more efficiently perform cross-modality training between visual and textual representations. 3) We conduct domain-specific model adaptation to mitigate domain shift problem that poses recognition challenge in video understanding. 4) Moreover, we leverage BDD-5K captioned videos to conduct knowledge transfer for better understanding WTS videos and more accurate captioning. Our solution has yielded on the test set, achieving 6th place in the competition. The open source code will be available at https://github.com/UCF-SST-Lab/AICity2024CVPRW
The Causal Impact of Credit Lines on Spending Distributions
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Consumer credit services offered by e-commerce platforms provide customers with convenient loan access during shopping and have the potential to stimulate sales. To understand the causal impact of credit lines on spending, previous studies have employed causal estimators, based on direct regression (DR), inverse propensity weighting (IPW), and double machine learning (DML) to estimate the treatment effect. However, these estimators do not consider the notion that an individual's spending can be understood and represented as a distribution, which captures the range and pattern of amounts spent across different orders. By disregarding the outcome as a distribution, valuable insights embedded within the outcome distribution might be overlooked. This paper develops a distribution-valued estimator framework that extends existing real-valued DR-, IPW-, and DML-based estimators to distribution-valued estimators within Rubin's causal framework. We establish their consistency and apply them to a real dataset from a large e-commerce platform. Our findings reveal that credit lines positively influence spending across all quantiles; however, as credit lines increase, consumers allocate more to luxuries (higher quantiles) than necessities (lower quantiles).
DeLELSTM: Decomposition-based Linear Explainable LSTM to Capture Instantaneous and Long-term Effects in Time Series
Aug 26, 2023



Abstract:Time series forecasting is prevalent in various real-world applications. Despite the promising results of deep learning models in time series forecasting, especially the Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), the explanations of time series models, which are critical in high-stakes applications, have received little attention. In this paper, we propose a Decomposition-based Linear Explainable LSTM (DeLELSTM) to improve the interpretability of LSTM. Conventionally, the interpretability of RNNs only concentrates on the variable importance and time importance. We additionally distinguish between the instantaneous influence of new coming data and the long-term effects of historical data. Specifically, DeLELSTM consists of two components, i.e., standard LSTM and tensorized LSTM. The tensorized LSTM assigns each variable with a unique hidden state making up a matrix $\mathbf{h}_t$, and the standard LSTM models all the variables with a shared hidden state $\mathbf{H}_t$. By decomposing the $\mathbf{H}_t$ into the linear combination of past information $\mathbf{h}_{t-1}$ and the fresh information $\mathbf{h}_{t}-\mathbf{h}_{t-1}$, we can get the instantaneous influence and the long-term effect of each variable. In addition, the advantage of linear regression also makes the explanation transparent and clear. We demonstrate the effectiveness and interpretability of DeLELSTM on three empirical datasets. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method achieves competitive performance against the baseline methods and provides a reliable explanation relative to domain knowledge.
TrafficSafetyGPT: Tuning a Pre-trained Large Language Model to a Domain-Specific Expert in Transportation Safety
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable effectiveness in various general-domain natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, their performance in transportation safety domain tasks has been suboptimal, primarily attributed to the requirement for specialized transportation safety expertise in generating accurate responses [1]. To address this challenge, we introduce TrafficSafetyGPT, a novel LLAMA-based model, which has undergone supervised fine-tuning using TrafficSafety-2K dataset which has human labels from government produced guiding books and ChatGPT-generated instruction-output pairs. Our proposed TrafficSafetyGPT model and TrafficSafety-2K train dataset are accessible at https://github.com/ozheng1993/TrafficSafetyGPT.
Deep into The Domain Shift: Transfer Learning through Dependence Regularization
May 31, 2023
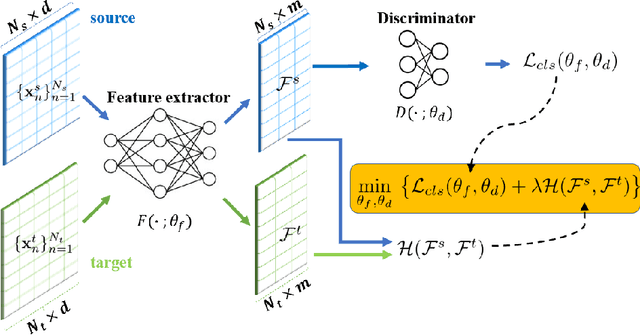
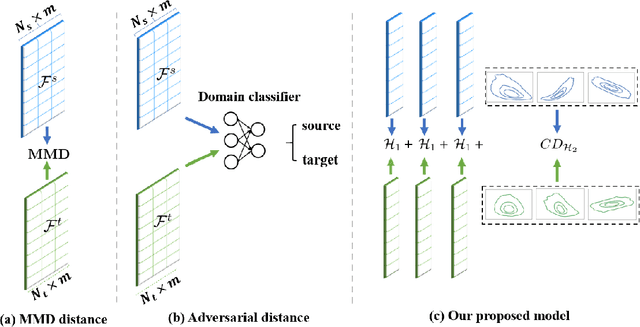
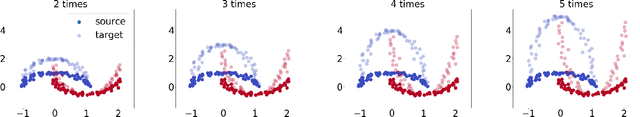
Abstract:Classical Domain Adaptation methods acquire transferability by regularizing the overall distributional discrepancies between features in the source domain (labeled) and features in the target domain (unlabeled). They often do not differentiate whether the domain differences come from the marginals or the dependence structures. In many business and financial applications, the labeling function usually has different sensitivities to the changes in the marginals versus changes in the dependence structures. Measuring the overall distributional differences will not be discriminative enough in acquiring transferability. Without the needed structural resolution, the learned transfer is less optimal. This paper proposes a new domain adaptation approach in which one can measure the differences in the internal dependence structure separately from those in the marginals. By optimizing the relative weights among them, the new regularization strategy greatly relaxes the rigidness of the existing approaches. It allows a learning machine to pay special attention to places where the differences matter the most. Experiments on three real-world datasets show that the improvements are quite notable and robust compared to various benchmark domain adaptation models.
AVOID: Autonomous Vehicle Operation Incident Dataset Across the Globe
Mar 22, 2023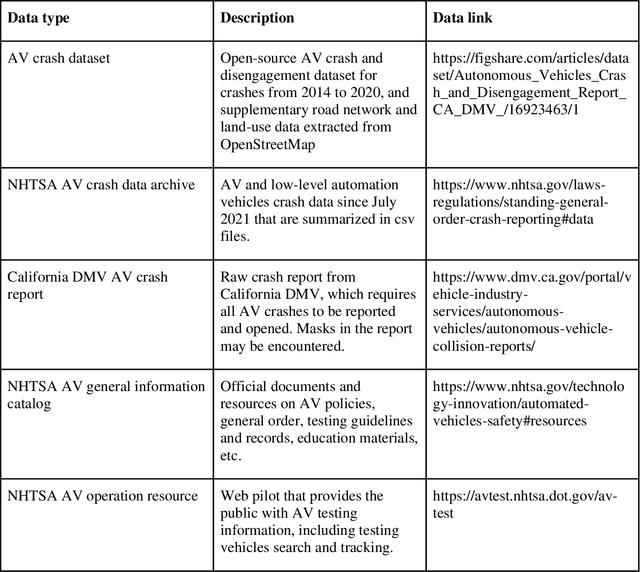
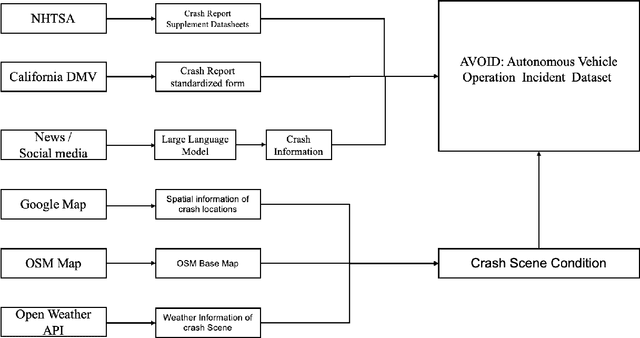
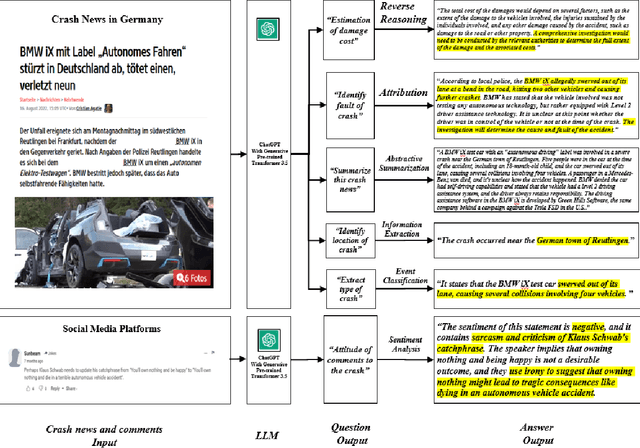
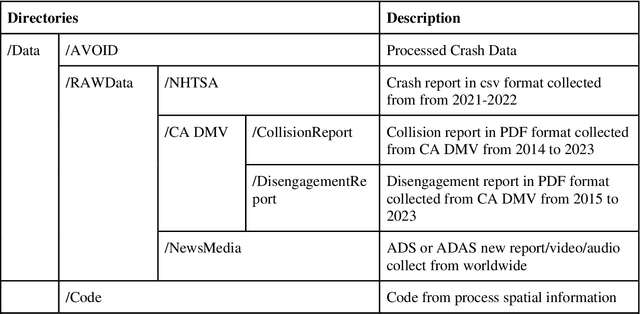
Abstract:Crash data of autonomous vehicles (AV) or vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are the key information to understand the crash nature and to enhance the automation systems. However, most of the existing crash data sources are either limited by the sample size or suffer from missing or unverified data. To contribute to the AV safety research community, we introduce AVOID: an open AV crash dataset. Three types of vehicles are considered: Advanced Driving System (ADS) vehicles, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) vehicles, and low-speed autonomous shuttles. The crash data are collected from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), California Department of Motor Vehicles (CA DMV) and incident news worldwide, and the data are manually verified and summarized in ready-to-use format. In addition, land use, weather, and geometry information are also provided. The dataset is expected to accelerate the research on AV crash analysis and potential risk identification by providing the research community with data of rich samples, diverse data sources, clear data structure, and high data quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge