Gordon Wetzstein
Image2Garment: Simulation-ready Garment Generation from a Single Image
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Estimating physically accurate, simulation-ready garments from a single image is challenging due to the absence of image-to-physics datasets and the ill-posed nature of this problem. Prior methods either require multi-view capture and expensive differentiable simulation or predict only garment geometry without the material properties required for realistic simulation. We propose a feed-forward framework that sidesteps these limitations by first fine-tuning a vision-language model to infer material composition and fabric attributes from real images, and then training a lightweight predictor that maps these attributes to the corresponding physical fabric parameters using a small dataset of material-physics measurements. Our approach introduces two new datasets (FTAG and T2P) and delivers simulation-ready garments from a single image without iterative optimization. Experiments show that our estimator achieves superior accuracy in material composition estimation and fabric attribute prediction, and by passing them through our physics parameter estimator, we further achieve higher-fidelity simulations compared to state-of-the-art image-to-garment methods.
Pretraining Frame Preservation in Autoregressive Video Memory Compression
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We present PFP, a neural network structure to compress long videos into short contexts, with an explicit pretraining objective to preserve the high-frequency details of single frames at arbitrary temporal positions. The baseline model can compress a 20-second video into a context at about 5k length, where random frames can be retrieved with perceptually preserved appearances. Such pretrained models can be directly fine-tuned as memory encoders for autoregressive video models, enabling long history memory with low context cost and relatively low fidelity loss. We evaluate the framework with ablative settings and discuss the trade-offs of possible neural architecture designs.
Envision: Embodied Visual Planning via Goal-Imagery Video Diffusion
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Embodied visual planning aims to enable manipulation tasks by imagining how a scene evolves toward a desired goal and using the imagined trajectories to guide actions. Video diffusion models, through their image-to-video generation capability, provide a promising foundation for such visual imagination. However, existing approaches are largely forward predictive, generating trajectories conditioned on the initial observation without explicit goal modeling, thus often leading to spatial drift and goal misalignment. To address these challenges, we propose Envision, a diffusion-based framework that performs visual planning for embodied agents. By explicitly constraining the generation with a goal image, our method enforces physical plausibility and goal consistency throughout the generated trajectory. Specifically, Envision operates in two stages. First, a Goal Imagery Model identifies task-relevant regions, performs region-aware cross attention between the scene and the instruction, and synthesizes a coherent goal image that captures the desired outcome. Then, an Env-Goal Video Model, built upon a first-and-last-frame-conditioned video diffusion model (FL2V), interpolates between the initial observation and the goal image, producing smooth and physically plausible video trajectories that connect the start and goal states. Experiments on object manipulation and image editing benchmarks demonstrate that Envision achieves superior goal alignment, spatial consistency, and object preservation compared to baselines. The resulting visual plans can directly support downstream robotic planning and control, providing reliable guidance for embodied agents.
VULCAN: Tool-Augmented Multi Agents for Iterative 3D Object Arrangement
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Despite the remarkable progress of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in 2D vision-language tasks, their application to complex 3D scene manipulation remains underexplored. In this paper, we bridge this critical gap by tackling three key challenges in 3D object arrangement task using MLLMs. First, to address the weak visual grounding of MLLMs, which struggle to link programmatic edits with precise 3D outcomes, we introduce an MCP-based API. This shifts the interaction from brittle raw code manipulation to more robust, function-level updates. Second, we augment the MLLM's 3D scene understanding with a suite of specialized visual tools to analyze scene state, gather spatial information, and validate action outcomes. This perceptual feedback loop is critical for closing the gap between language-based updates and precise 3D-aware manipulation. Third, to manage the iterative, error-prone updates, we propose a collaborative multi-agent framework with designated roles for planning, execution, and verification. This decomposition allows the system to robustly handle multi-step instructions and recover from intermediate errors. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on a diverse set of 25 complex object arrangement tasks, where it significantly outperforms existing baselines. Website: vulcan-3d.github.io
BAgger: Backwards Aggregation for Mitigating Drift in Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Autoregressive video models are promising for world modeling via next-frame prediction, but they suffer from exposure bias: a mismatch between training on clean contexts and inference on self-generated frames, causing errors to compound and quality to drift over time. We introduce Backwards Aggregation (BAgger), a self-supervised scheme that constructs corrective trajectories from the model's own rollouts, teaching it to recover from its mistakes. Unlike prior approaches that rely on few-step distillation and distribution-matching losses, which can hurt quality and diversity, BAgger trains with standard score or flow matching objectives, avoiding large teachers and long-chain backpropagation through time. We instantiate BAgger on causal diffusion transformers and evaluate on text-to-video, video extension, and multi-prompt generation, observing more stable long-horizon motion and better visual consistency with reduced drift.
pi-Flow: Policy-Based Few-Step Generation via Imitation Distillation
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Few-step diffusion or flow-based generative models typically distill a velocity-predicting teacher into a student that predicts a shortcut towards denoised data. This format mismatch has led to complex distillation procedures that often suffer from a quality-diversity trade-off. To address this, we propose policy-based flow models ($\pi$-Flow). $\pi$-Flow modifies the output layer of a student flow model to predict a network-free policy at one timestep. The policy then produces dynamic flow velocities at future substeps with negligible overhead, enabling fast and accurate ODE integration on these substeps without extra network evaluations. To match the policy's ODE trajectory to the teacher's, we introduce a novel imitation distillation approach, which matches the policy's velocity to the teacher's along the policy's trajectory using a standard $\ell_2$ flow matching loss. By simply mimicking the teacher's behavior, $\pi$-Flow enables stable and scalable training and avoids the quality-diversity trade-off. On ImageNet 256$^2$, it attains a 1-NFE FID of 2.85, outperforming MeanFlow of the same DiT architecture. On FLUX.1-12B and Qwen-Image-20B at 4 NFEs, $\pi$-Flow achieves substantially better diversity than state-of-the-art few-step methods, while maintaining teacher-level quality.
Taming Flow-based I2V Models for Creative Video Editing
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Although image editing techniques have advanced significantly, video editing, which aims to manipulate videos according to user intent, remains an emerging challenge. Most existing image-conditioned video editing methods either require inversion with model-specific design or need extensive optimization, limiting their capability of leveraging up-to-date image-to-video (I2V) models to transfer the editing capability of image editing models to the video domain. To this end, we propose IF-V2V, an Inversion-Free method that can adapt off-the-shelf flow-matching-based I2V models for video editing without significant computational overhead. To circumvent inversion, we devise Vector Field Rectification with Sample Deviation to incorporate information from the source video into the denoising process by introducing a deviation term into the denoising vector field. To further ensure consistency with the source video in a model-agnostic way, we introduce Structure-and-Motion-Preserving Initialization to generate motion-aware temporally correlated noise with structural information embedded. We also present a Deviation Caching mechanism to minimize the additional computational cost for denoising vector rectification without significantly impacting editing quality. Evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves superior editing quality and consistency over existing approaches, offering a lightweight plug-and-play solution to realize visual creativity.
Mixture of Contexts for Long Video Generation
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Long video generation is fundamentally a long context memory problem: models must retain and retrieve salient events across a long range without collapsing or drifting. However, scaling diffusion transformers to generate long-context videos is fundamentally limited by the quadratic cost of self-attention, which makes memory and computation intractable and difficult to optimize for long sequences. We recast long-context video generation as an internal information retrieval task and propose a simple, learnable sparse attention routing module, Mixture of Contexts (MoC), as an effective long-term memory retrieval engine. In MoC, each query dynamically selects a few informative chunks plus mandatory anchors (caption, local windows) to attend to, with causal routing that prevents loop closures. As we scale the data and gradually sparsify the routing, the model allocates compute to salient history, preserving identities, actions, and scenes over minutes of content. Efficiency follows as a byproduct of retrieval (near-linear scaling), which enables practical training and synthesis, and the emergence of memory and consistency at the scale of minutes.
Random-phase Gaussian Wave Splatting for Computer-generated Holography
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Holographic near-eye displays offer ultra-compact form factors for virtual and augmented reality systems, but rely on advanced computer-generated holography (CGH) algorithms to convert 3D scenes into interference patterns that can be displayed on spatial light modulators (SLMs). Gaussian Wave Splatting (GWS) has recently emerged as a powerful CGH paradigm that allows for the conversion of Gaussians, a state-of-the-art neural 3D representation, into holograms. However, GWS assumes smooth-phase distributions over the Gaussian primitives, limiting their ability to model view-dependent effects and reconstruct accurate defocus blur, and severely under-utilizing the space-bandwidth product of the SLM. In this work, we propose random-phase GWS (GWS-RP) to improve bandwidth utilization, which has the effect of increasing eyebox size, reconstructing accurate defocus blur and parallax, and supporting time-multiplexed rendering to suppress speckle artifacts. At the core of GWS-RP are (1) a fundamentally new wavefront compositing procedure and (2) an alpha-blending scheme specifically designed for random-phase Gaussian primitives, ensuring physically correct color reconstruction and robust occlusion handling. Additionally, we present the first formally derived algorithm for applying random phase to Gaussian primitives, grounded in rigorous statistical optics analysis and validated through practical near-eye display applications. Through extensive simulations and experimental validations, we demonstrate that these advancements, collectively with time-multiplexing, uniquely enables full-bandwith light field CGH that supports accurate accurate parallax and defocus, yielding state-of-the-art image quality and perceptually faithful 3D holograms for next-generation near-eye displays.
Captain Cinema: Towards Short Movie Generation
Jul 24, 2025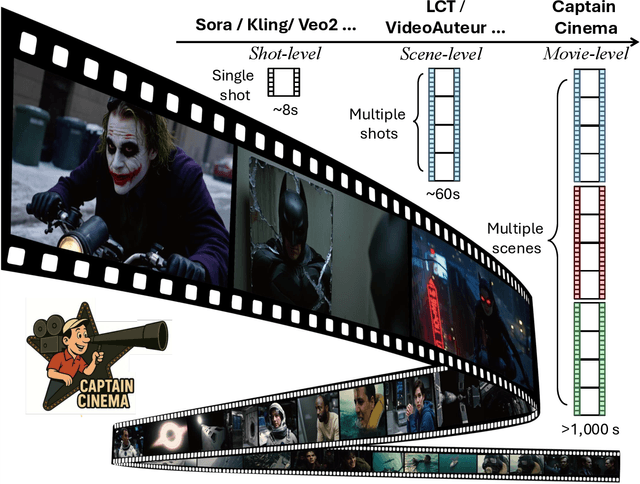
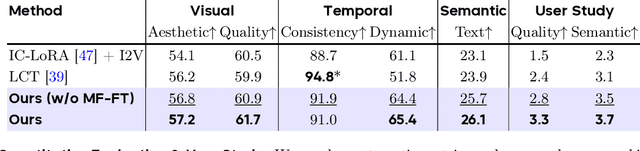

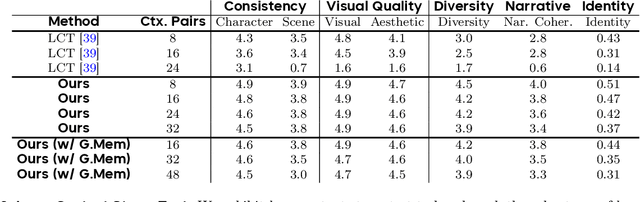
Abstract:We present Captain Cinema, a generation framework for short movie generation. Given a detailed textual description of a movie storyline, our approach firstly generates a sequence of keyframes that outline the entire narrative, which ensures long-range coherence in both the storyline and visual appearance (e.g., scenes and characters). We refer to this step as top-down keyframe planning. These keyframes then serve as conditioning signals for a video synthesis model, which supports long context learning, to produce the spatio-temporal dynamics between them. This step is referred to as bottom-up video synthesis. To support stable and efficient generation of multi-scene long narrative cinematic works, we introduce an interleaved training strategy for Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiT), specifically adapted for long-context video data. Our model is trained on a specially curated cinematic dataset consisting of interleaved data pairs. Our experiments demonstrate that Captain Cinema performs favorably in the automated creation of visually coherent and narrative consistent short movies in high quality and efficiency. Project page: https://thecinema.ai
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge