Jin Yuan
Full end-to-end diagnostic workflow automation of 3D OCT via foundation model-driven AI for retinal diseases
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has revolutionized retinal disease diagnosis with its high-resolution and three-dimensional imaging nature, yet its full diagnostic automation in clinical practices remains constrained by multi-stage workflows and conventional single-slice single-task AI models. We present Full-process OCT-based Clinical Utility System (FOCUS), a foundation model-driven framework enabling end-to-end automation of 3D OCT retinal disease diagnosis. FOCUS sequentially performs image quality assessment with EfficientNetV2-S, followed by abnormality detection and multi-disease classification using a fine-tuned Vision Foundation Model. Crucially, FOCUS leverages a unified adaptive aggregation method to intelligently integrate 2D slices-level predictions into comprehensive 3D patient-level diagnosis. Trained and tested on 3,300 patients (40,672 slices), and externally validated on 1,345 patients (18,498 slices) across four different-tier centers and diverse OCT devices, FOCUS achieved high F1 scores for quality assessment (99.01%), abnormally detection (97.46%), and patient-level diagnosis (94.39%). Real-world validation across centers also showed stable performance (F1: 90.22%-95.24%). In human-machine comparisons, FOCUS matched expert performance in abnormality detection (F1: 95.47% vs 90.91%) and multi-disease diagnosis (F1: 93.49% vs 91.35%), while demonstrating better efficiency. FOCUS automates the image-to-diagnosis pipeline, representing a critical advance towards unmanned ophthalmology with a validated blueprint for autonomous screening to enhance population scale retinal care accessibility and efficiency.
Cross-modal Context-aware Learning for Visual Prompt Guided Multimodal Image Understanding in Remote Sensing
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in image understanding have enabled methods that leverage large language models for multimodal reasoning in remote sensing. However, existing approaches still struggle to steer models to the user-relevant regions when only simple, generic text prompts are available. Moreover, in large-scale aerial imagery many objects exhibit highly similar visual appearances and carry rich inter-object relationships, which further complicates accurate recognition. To address these challenges, we propose Cross-modal Context-aware Learning for Visual Prompt-Guided Multimodal Image Understanding (CLV-Net). CLV-Net lets users supply a simple visual cue, a bounding box, to indicate a region of interest, and uses that cue to guide the model to generate correlated segmentation masks and captions that faithfully reflect user intent. Central to our design is a Context-Aware Mask Decoder that models and integrates inter-object relationships to strengthen target representations and improve mask quality. In addition, we introduce a Semantic and Relationship Alignment module: a Cross-modal Semantic Consistency Loss enhances fine-grained discrimination among visually similar targets, while a Relationship Consistency Loss enforces alignment between textual relations and visual interactions. Comprehensive experiments on two benchmark datasets show that CLV-Net outperforms existing methods and establishes new state-of-the-art results. The model effectively captures user intent and produces precise, intention-aligned multimodal outputs.
REFINE-CONTROL: A Semi-supervised Distillation Method For Conditional Image Generation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Conditional image generation models have achieved remarkable results by leveraging text-based control to generate customized images. However, the high resource demands of these models and the scarcity of well-annotated data have hindered their deployment on edge devices, leading to enormous costs and privacy concerns, especially when user data is sent to a third party. To overcome these challenges, we propose Refine-Control, a semi-supervised distillation framework. Specifically, we improve the performance of the student model by introducing a tri-level knowledge fusion loss to transfer different levels of knowledge. To enhance generalization and alleviate dataset scarcity, we introduce a semi-supervised distillation method utilizing both labeled and unlabeled data. Our experiments reveal that Refine-Control achieves significant reductions in computational cost and latency, while maintaining high-fidelity generation capabilities and controllability, as quantified by comparative metrics.
AVAM: Universal Training-free Adaptive Visual Anchoring Embedded into Multimodal Large Language Model for Multi-image Question Answering
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:The advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has driven significant progress in Visual Question Answering (VQA), evolving from Single to Multi Image VQA (MVQA). However, the increased number of images in MVQA inevitably introduces substantial visual redundancy that is irrelevant to question answering, negatively impacting both accuracy and efficiency. To address this issue, existing methods lack flexibility in controlling the number of compressed visual tokens and tend to produce discrete visual fragments, which hinder MLLMs' ability to comprehend images holistically. In this paper, we propose a straightforward yet universal Adaptive Visual Anchoring strategy, which can be seamlessly integrated into existing MLLMs, offering significant accuracy improvements through adaptive compression. Meanwhile, to balance the results derived from both global and compressed visual input, we further introduce a novel collaborative decoding mechanism, enabling optimal performance. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating consistent performance improvements across various MLLMs. The code will be publicly available.
From Sparse to Dense: Camera Relocalization with Scene-Specific Detector from Feature Gaussian Splatting
Mar 25, 2025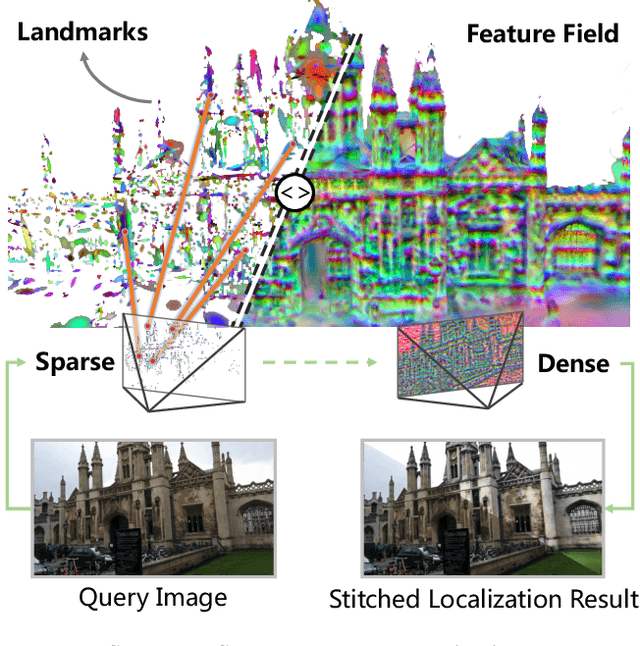
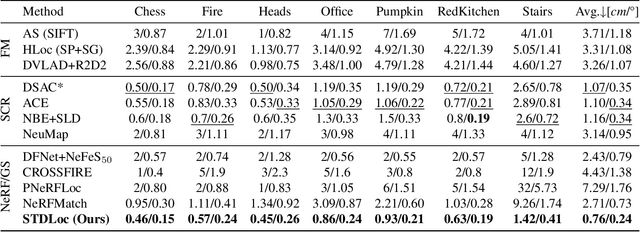
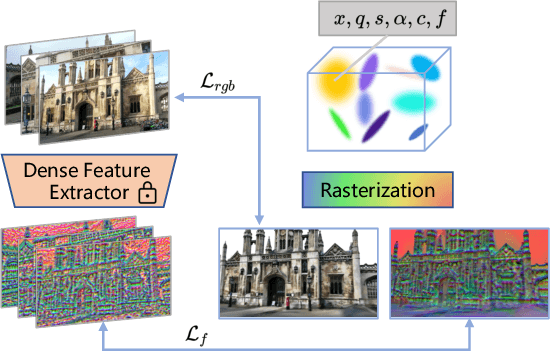

Abstract:This paper presents a novel camera relocalization method, STDLoc, which leverages Feature Gaussian as scene representation. STDLoc is a full relocalization pipeline that can achieve accurate relocalization without relying on any pose prior. Unlike previous coarse-to-fine localization methods that require image retrieval first and then feature matching, we propose a novel sparse-to-dense localization paradigm. Based on this scene representation, we introduce a novel matching-oriented Gaussian sampling strategy and a scene-specific detector to achieve efficient and robust initial pose estimation. Furthermore, based on the initial localization results, we align the query feature map to the Gaussian feature field by dense feature matching to enable accurate localization. The experiments on indoor and outdoor datasets show that STDLoc outperforms current state-of-the-art localization methods in terms of localization accuracy and recall.
DomainVerse: A Benchmark Towards Real-World Distribution Shifts For Tuning-Free Adaptive Domain Generalization
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Traditional cross-domain tasks, including domain adaptation and domain generalization, rely heavily on training model by source domain data. With the recent advance of vision-language models (VLMs), viewed as natural source models, the cross-domain task changes to directly adapt the pre-trained source model to arbitrary target domains equipped with prior domain knowledge, and we name this task Adaptive Domain Generalization (ADG). However, current cross-domain datasets have many limitations, such as unrealistic domains, unclear domain definitions, and the inability to fine-grained domain decomposition, which drives us to establish a novel dataset DomainVerse for ADG. Benefiting from the introduced hierarchical definition of domain shifts, DomainVerse consists of about 0.5 million images from 390 fine-grained realistic domains. With the help of the constructed DomainVerse and VLMs, we propose two methods called Domain CLIP and Domain++ CLIP for tuning-free adaptive domain generalization. Extensive and comprehensive experiments demonstrate the significance of the dataset and the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
S$^3$-MonoDETR: Supervised Shape&Scale-perceptive Deformable Transformer for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Sep 02, 2023



Abstract:Recently, transformer-based methods have shown exceptional performance in monocular 3D object detection, which can predict 3D attributes from a single 2D image. These methods typically use visual and depth representations to generate query points on objects, whose quality plays a decisive role in the detection accuracy. However, current unsupervised attention mechanisms without any geometry appearance awareness in transformers are susceptible to producing noisy features for query points, which severely limits the network performance and also makes the model have a poor ability to detect multi-category objects in a single training process. To tackle this problem, this paper proposes a novel "Supervised Shape&Scale-perceptive Deformable Attention" (S$^3$-DA) module for monocular 3D object detection. Concretely, S$^3$-DA utilizes visual and depth features to generate diverse local features with various shapes and scales and predict the corresponding matching distribution simultaneously to impose valuable shape&scale perception for each query. Benefiting from this, S$^3$-DA effectively estimates receptive fields for query points belonging to any category, enabling them to generate robust query features. Besides, we propose a Multi-classification-based Shape$\&$Scale Matching (MSM) loss to supervise the above process. Extensive experiments on KITTI and Waymo Open datasets demonstrate that S$^3$-DA significantly improves the detection accuracy, yielding state-of-the-art performance of single-category and multi-category 3D object detection in a single training process compared to the existing approaches. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/mikasa3lili/S3-MonoDETR.
AATCT-IDS: A Benchmark Abdominal Adipose Tissue CT Image Dataset for Image Denoising, Semantic Segmentation, and Radiomics Evaluation
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Methods: In this study, a benchmark \emph{Abdominal Adipose Tissue CT Image Dataset} (AATTCT-IDS) containing 300 subjects is prepared and published. AATTCT-IDS publics 13,732 raw CT slices, and the researchers individually annotate the subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue regions of 3,213 of those slices that have the same slice distance to validate denoising methods, train semantic segmentation models, and study radiomics. For different tasks, this paper compares and analyzes the performance of various methods on AATTCT-IDS by combining the visualization results and evaluation data. Thus, verify the research potential of this data set in the above three types of tasks. Results: In the comparative study of image denoising, algorithms using a smoothing strategy suppress mixed noise at the expense of image details and obtain better evaluation data. Methods such as BM3D preserve the original image structure better, although the evaluation data are slightly lower. The results show significant differences among them. In the comparative study of semantic segmentation of abdominal adipose tissue, the segmentation results of adipose tissue by each model show different structural characteristics. Among them, BiSeNet obtains segmentation results only slightly inferior to U-Net with the shortest training time and effectively separates small and isolated adipose tissue. In addition, the radiomics study based on AATTCT-IDS reveals three adipose distributions in the subject population. Conclusion: AATTCT-IDS contains the ground truth of adipose tissue regions in abdominal CT slices. This open-source dataset can attract researchers to explore the multi-dimensional characteristics of abdominal adipose tissue and thus help physicians and patients in clinical practice. AATCT-IDS is freely published for non-commercial purpose at: \url{https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/AATTCT-IDS/23807256}.
Contrast-augmented Diffusion Model with Fine-grained Sequence Alignment for Markup-to-Image Generation
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:The recently rising markup-to-image generation poses greater challenges as compared to natural image generation, due to its low tolerance for errors as well as the complex sequence and context correlations between markup and rendered image. This paper proposes a novel model named "Contrast-augmented Diffusion Model with Fine-grained Sequence Alignment" (FSA-CDM), which introduces contrastive positive/negative samples into the diffusion model to boost performance for markup-to-image generation. Technically, we design a fine-grained cross-modal alignment module to well explore the sequence similarity between the two modalities for learning robust feature representations. To improve the generalization ability, we propose a contrast-augmented diffusion model to explicitly explore positive and negative samples by maximizing a novel contrastive variational objective, which is mathematically inferred to provide a tighter bound for the model's optimization. Moreover, the context-aware cross attention module is developed to capture the contextual information within markup language during the denoising process, yielding better noise prediction results. Extensive experiments are conducted on four benchmark datasets from different domains, and the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed components in FSA-CDM, significantly exceeding state-of-the-art performance by about 2%-12% DTW improvements. The code will be released at https://github.com/zgj77/FSACDM.
VPUFormer: Visual Prompt Unified Transformer for Interactive Image Segmentation
Jun 11, 2023



Abstract:The integration of diverse visual prompts like clicks, scribbles, and boxes in interactive image segmentation could significantly facilitate user interaction as well as improve interaction efficiency. Most existing studies focus on a single type of visual prompt by simply concatenating prompts and images as input for segmentation prediction, which suffers from low-efficiency prompt representation and weak interaction issues. This paper proposes a simple yet effective Visual Prompt Unified Transformer (VPUFormer), which introduces a concise unified prompt representation with deeper interaction to boost the segmentation performance. Specifically, we design a Prompt-unified Encoder (PuE) by using Gaussian mapping to generate a unified one-dimensional vector for click, box, and scribble prompts, which well captures users' intentions as well as provides a denser representation of user prompts. In addition, we present a Prompt-to-Pixel Contrastive Loss (P2CL) that leverages user feedback to gradually refine candidate semantic features, aiming to bring image semantic features closer to the features that are similar to the user prompt, while pushing away those image semantic features that are dissimilar to the user prompt, thereby correcting results that deviate from expectations. On this basis, our approach injects prompt representations as queries into Dual-cross Merging Attention (DMA) blocks to perform a deeper interaction between image and query inputs. A comprehensive variety of experiments on seven challenging datasets demonstrates that the proposed VPUFormer with PuE, DMA, and P2CL achieves consistent improvements, yielding state-of-the-art segmentation performance. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/XuZhang1211/VPUFormer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge