Hao He
Unraveling the Hidden Dynamical Structure in Recurrent Neural Policies
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recurrent neural policies are widely used in partially observable control and meta-RL tasks. Their abilities to maintain internal memory and adapt quickly to unseen scenarios have offered them unparalleled performance when compared to non-recurrent counterparts. However, until today, the underlying mechanisms for their superior generalization and robustness performance remain poorly understood. In this study, by analyzing the hidden state domain of recurrent policies learned over a diverse set of training methods, model architectures, and tasks, we find that stable cyclic structures consistently emerge during interaction with the environment. Such cyclic structures share a remarkable similarity with \textit{limit cycles} in dynamical system analysis, if we consider the policy and the environment as a joint hybrid dynamical system. Moreover, we uncover that the geometry of such limit cycles also has a structured correspondence with the policies' behaviors. These findings offer new perspectives to explain many nice properties of recurrent policies: the emergence of limit cycles stabilizes both the policies' internal memory and the task-relevant environmental states, while suppressing nuisance variability arising from environmental uncertainty; the geometry of limit cycles also encodes relational structures of behaviors, facilitating easier skill adaptation when facing non-stationary environments.
Physiology as Language: Translating Respiration to Sleep EEG
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces a novel cross-physiology translation task: synthesizing sleep electroencephalography (EEG) from respiration signals. To address the significant complexity gap between the two modalities, we propose a waveform-conditional generative framework that preserves fine-grained respiratory dynamics while constraining the EEG target space through discrete tokenization. Trained on over 28,000 individuals, our model achieves a 7% Mean Absolute Error in EEG spectrogram reconstruction. Beyond reconstruction, the synthesized EEG supports downstream tasks with performance comparable to ground truth EEG on age estimation (MAE 5.0 vs. 5.1 years), sex detection (AUROC 0.81 vs. 0.82), and sleep staging (Accuracy 0.84 vs. 0.88), significantly outperforming baselines trained directly on breathing. Finally, we demonstrate that the framework generalizes to contactless sensing by synthesizing EEG from wireless radio-frequency reflections, highlighting the feasibility of remote, non-contact neurological assessment during sleep.
Signal-Adaptive Trust Regions for Gradient-Free Optimization of Recurrent Spiking Neural Networks
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recurrent spiking neural networks (RSNNs) are a promising substrate for energy-efficient control policies, but training them for high-dimensional, long-horizon reinforcement learning remains challenging. Population-based, gradient-free optimization circumvents backpropagation through non-differentiable spike dynamics by estimating gradients. However, with finite populations, high variance of these estimates can induce harmful and overly aggressive update steps. Inspired by trust-region methods in reinforcement learning that constrain policy updates in distribution space, we propose \textbf{Signal-Adaptive Trust Regions (SATR)}, a distributional update rule that constrains relative change by bounding KL divergence normalized by an estimated signal energy. SATR automatically expands the trust region under strong signals and contracts it when updates are noise-dominated. We instantiate SATR for Bernoulli connectivity distributions, which have shown strong empirical performance for RSNN optimization. Across a suite of high-dimensional continuous-control benchmarks, SATR improves stability under limited populations and reaches competitive returns against strong baselines including PPO-LSTM. In addition, to make SATR practical at scale, we introduce a bitset implementation for binary spiking and binary weights, substantially reducing wall-clock training time and enabling fast RSNN policy search.
When Personalization Legitimizes Risks: Uncovering Safety Vulnerabilities in Personalized Dialogue Agents
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Long-term memory enables large language model (LLM) agents to support personalized and sustained interactions. However, most work on personalized agents prioritizes utility and user experience, treating memory as a neutral component and largely overlooking its safety implications. In this paper, we reveal intent legitimation, a previously underexplored safety failure in personalized agents, where benign personal memories bias intent inference and cause models to legitimize inherently harmful queries. To study this phenomenon, we introduce PS-Bench, a benchmark designed to identify and quantify intent legitimation in personalized interactions. Across multiple memory-augmented agent frameworks and base LLMs, personalization increases attack success rates by 15.8%-243.7% relative to stateless baselines. We further provide mechanistic evidence for intent legitimation from internal representations space, and propose a lightweight detection-reflection method that effectively reduces safety degradation. Overall, our work provides the first systematic exploration and evaluation of intent legitimation as a safety failure mode that naturally arises from benign, real-world personalization, highlighting the importance of assessing safety under long-term personal context. WARNING: This paper may contain harmful content.
End-to-End Training for Autoregressive Video Diffusion via Self-Resampling
Dec 17, 2025
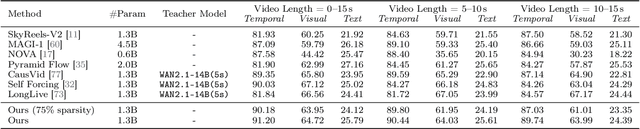
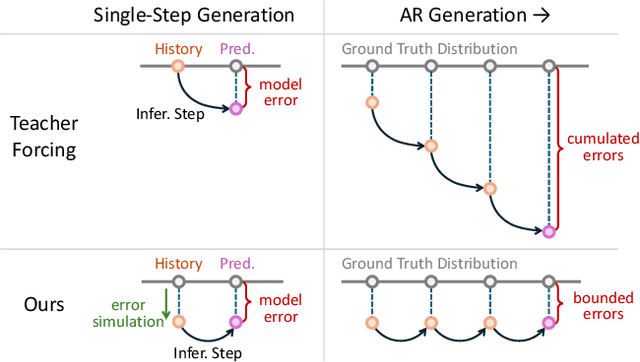

Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models hold promise for world simulation but are vulnerable to exposure bias arising from the train-test mismatch. While recent works address this via post-training, they typically rely on a bidirectional teacher model or online discriminator. To achieve an end-to-end solution, we introduce Resampling Forcing, a teacher-free framework that enables training autoregressive video models from scratch and at scale. Central to our approach is a self-resampling scheme that simulates inference-time model errors on history frames during training. Conditioned on these degraded histories, a sparse causal mask enforces temporal causality while enabling parallel training with frame-level diffusion loss. To facilitate efficient long-horizon generation, we further introduce history routing, a parameter-free mechanism that dynamically retrieves the top-k most relevant history frames for each query. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves performance comparable to distillation-based baselines while exhibiting superior temporal consistency on longer videos owing to native-length training.
Does AI-Assisted Coding Deliver? A Difference-in-Differences Study of Cursor's Impact on Software Projects
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the promise to revolutionize the field of software engineering. Among other things, LLM agents are rapidly gaining momentum in their application to software development, with practitioners claiming a multifold productivity increase after adoption. Yet, empirical evidence is lacking around these claims. In this paper, we estimate the causal effect of adopting a widely popular LLM agent assistant, namely Cursor, on development velocity and software quality. The estimation is enabled by a state-of-the-art difference-in-differences design comparing Cursor-adopting GitHub projects with a matched control group of similar GitHub projects that do not use Cursor. We find that the adoption of Cursor leads to a significant, large, but transient increase in project-level development velocity, along with a significant and persistent increase in static analysis warnings and code complexity. Further panel generalized method of moments estimation reveals that the increase in static analysis warnings and code complexity acts as a major factor causing long-term velocity slowdown. Our study carries implications for software engineering practitioners, LLM agent assistant designers, and researchers.
Speed at the Cost of Quality? The Impact of LLM Agent Assistance on Software Development
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the promise to revolutionize the field of software engineering. Among other things, LLM agents are rapidly gaining momentum in their application to software development, with practitioners claiming a multifold productivity increase after adoption. Yet, empirical evidence is lacking around these claims. In this paper, we estimate the causal effect of adopting a widely popular LLM agent assistant, namely Cursor, on development velocity and software quality. The estimation is enabled by a state-of-the-art difference-in-differences design comparing Cursor-adopting GitHub projects with a matched control group of similar GitHub projects that do not use Cursor. We find that the adoption of Cursor leads to a significant, large, but transient increase in project-level development velocity, along with a significant and persistent increase in static analysis warnings and code complexity. Further panel generalized method of moments estimation reveals that the increase in static analysis warnings and code complexity acts as a major factor causing long-term velocity slowdown. Our study carries implications for software engineering practitioners, LLM agent assistant designers, and researchers.
Vision as a Dialect: Unifying Visual Understanding and Generation via Text-Aligned Representations
Jun 23, 2025
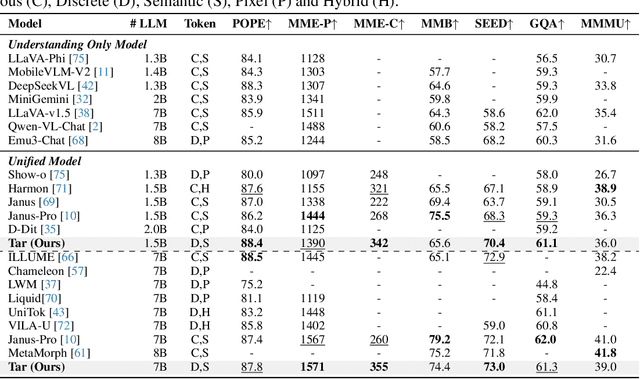
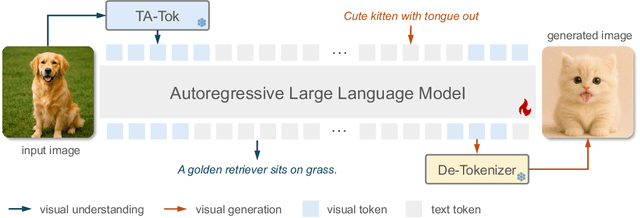
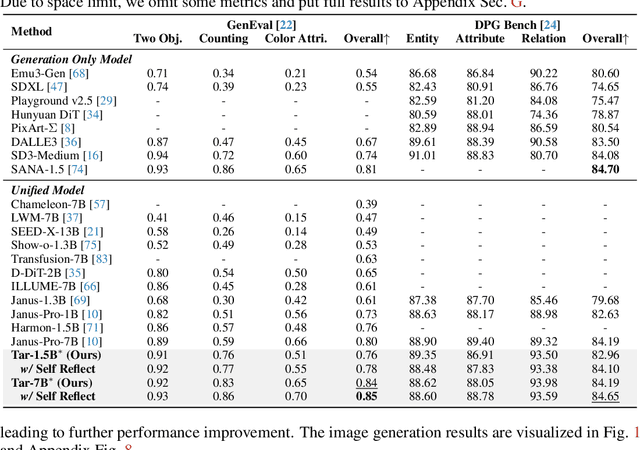
Abstract:This paper presents a multimodal framework that attempts to unify visual understanding and generation within a shared discrete semantic representation. At its core is the Text-Aligned Tokenizer (TA-Tok), which converts images into discrete tokens using a text-aligned codebook projected from a large language model's (LLM) vocabulary. By integrating vision and text into a unified space with an expanded vocabulary, our multimodal LLM, Tar, enables cross-modal input and output through a shared interface, without the need for modality-specific designs. Additionally, we propose scale-adaptive encoding and decoding to balance efficiency and visual detail, along with a generative de-tokenizer to produce high-fidelity visual outputs. To address diverse decoding needs, we utilize two complementary de-tokenizers: a fast autoregressive model and a diffusion-based model. To enhance modality fusion, we investigate advanced pre-training tasks, demonstrating improvements in both visual understanding and generation. Experiments across benchmarks show that Tar matches or surpasses existing multimodal LLM methods, achieving faster convergence and greater training efficiency. Code, models, and data are available at https://tar.csuhan.com
Autoregressive Adversarial Post-Training for Real-Time Interactive Video Generation
Jun 11, 2025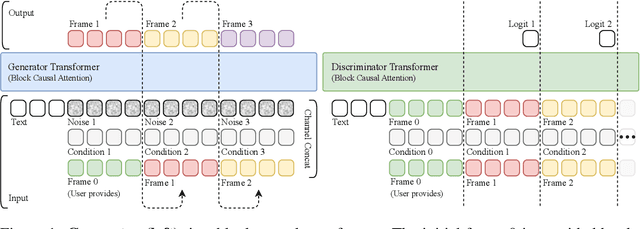
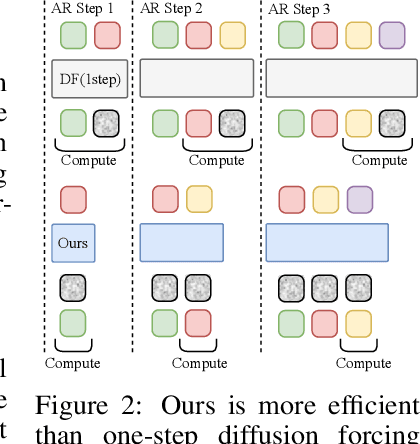
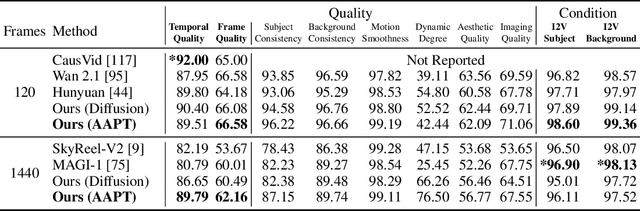

Abstract:Existing large-scale video generation models are computationally intensive, preventing adoption in real-time and interactive applications. In this work, we propose autoregressive adversarial post-training (AAPT) to transform a pre-trained latent video diffusion model into a real-time, interactive video generator. Our model autoregressively generates a latent frame at a time using a single neural function evaluation (1NFE). The model can stream the result to the user in real time and receive interactive responses as controls to generate the next latent frame. Unlike existing approaches, our method explores adversarial training as an effective paradigm for autoregressive generation. This not only allows us to design an architecture that is more efficient for one-step generation while fully utilizing the KV cache, but also enables training the model in a student-forcing manner that proves to be effective in reducing error accumulation during long video generation. Our experiments demonstrate that our 8B model achieves real-time, 24fps, streaming video generation at 736x416 resolution on a single H100, or 1280x720 on 8xH100 up to a minute long (1440 frames). Visit our research website at https://seaweed-apt.com/2
UI-Genie: A Self-Improving Approach for Iteratively Boosting MLLM-based Mobile GUI Agents
May 27, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce UI-Genie, a self-improving framework addressing two key challenges in GUI agents: verification of trajectory outcome is challenging and high-quality training data are not scalable. These challenges are addressed by a reward model and a self-improving pipeline, respectively. The reward model, UI-Genie-RM, features an image-text interleaved architecture that efficiently pro- cesses historical context and unifies action-level and task-level rewards. To sup- port the training of UI-Genie-RM, we develop deliberately-designed data genera- tion strategies including rule-based verification, controlled trajectory corruption, and hard negative mining. To address the second challenge, a self-improvement pipeline progressively expands solvable complex GUI tasks by enhancing both the agent and reward models through reward-guided exploration and outcome verification in dynamic environments. For training the model, we generate UI- Genie-RM-517k and UI-Genie-Agent-16k, establishing the first reward-specific dataset for GUI agents while demonstrating high-quality synthetic trajectory gen- eration without manual annotation. Experimental results show that UI-Genie achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple GUI agent benchmarks with three generations of data-model self-improvement. We open-source our complete framework implementation and generated datasets to facilitate further research in https://github.com/Euphoria16/UI-Genie.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge